|
Yorùbá Mythology
The Yorùbá religion ( Yoruba: Ìṣẹ̀ṣe), West African Orisa (Òrìṣà), or Isese (Ìṣẹ̀ṣe), comprises the traditional religious and spiritual concepts and practice of the Yoruba people. Its homeland is in present-day Southwestern Nigeria and Southern Benin, which comprises the majority of the states of; Oyo, Ogun, Osun, Ondo, Ekiti, Kwara, Lagos and parts of Kogi in Nigeria, the Departments of; Collines, Oueme, Plateau in Benin, and the adjoining parts of central Togo, commonly known as Yorubaland (). It has become the largest indigenous African tradition / belief system in the world with several million adherents worldwide. It shares some parallels with the Vodun practised by the neighbouring Fon and Ewe peoples to its west and with the religion of the Edo people to its east. Yorùbá religion is the basis for several religions in the New World, notably Santería, Umbanda, Trinidad Orisha, and Candomblé. Yorùbá religious beliefs are part of Ìtàn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
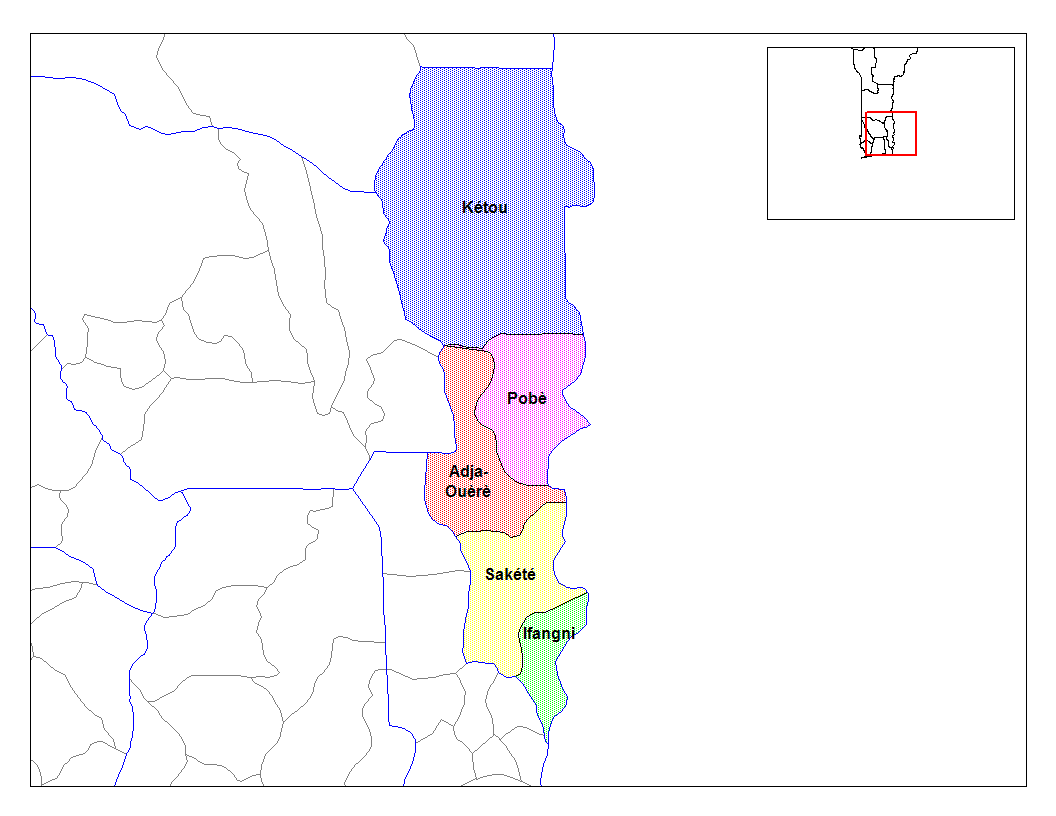
Plateau Department
Plateau is one of the twelve departments of Benin. The department of Plateau was created in 1999 with an area of when it was split off from Ouémé Department. Plateau is subdivided into five communes, each centred at one of the principal towns: Adja-Ouèrè, Ifangni, Kétou, Pobè and Sakété. , the total population of the department was 622,372, with 300,065 males and 322,307 females. The proportion of women was 51.80%. The total rural population was 54.80%, while the urban population was 45.20%. The total labour force in the department was 185,815, of which 43.10% were women. The proportion of households with no level of education was 65.50%. Geography Plateau Department border Collines Department to the north, Nigeria to the east, Ouémé Department to the southwest, and Zou Department to the west. It is characterised by plateaus ranging from above the mean sea level. The plateaus are split by valleys running from north to south, created by the Iguidi river. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoruba Divination Board
Yoruba may refer to: * Yoruba people, an ethnic group of West Africa * Yoruba language, a West African language of the Volta–Niger language family * Yoruba alphabet, a Latin alphabet used to write in the Yoruba language * Yoruba religion, West African religion * Yorubaland Yorubaland () is the homeland and cultural region of the Yoruba people in West Africa. It spans the modern-day countries of Nigeria, Togo and Benin, and covers a total land area of . Of this land area, 106,016 km2 (74.6%) lies within Niger ..., the region occupied by the Yoruba people * ''Yoruba'' (spider), a genus of ground spiders See also * {{Disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isese (Yoruba Religion) Global Symbol With Labels
The Yorùbá religion (Yoruba language, Yoruba: Ìṣẹ̀ṣe), West African Orisa (Òrìṣà), or Isese (Ìṣẹ̀ṣe), comprises the traditional religious and spiritual concepts and practice of the Yoruba people. Its homeland is in present-day Southwestern Nigeria and Southern Benin, which comprises the majority of the States of Nigeria, states of; Oyo State, Oyo, Ogun State, Ogun, Osun State, Osun, Ondo State, Ondo, Ekiti State, Ekiti, Kwara State, Kwara, Lagos State, Lagos and parts of Kogi State, Kogi in Nigeria, the Departments of Benin, Departments of; Collines Department, Collines, Ouémé Department, Oueme, Plateau Department, Plateau in Benin, and the adjoining parts of central Togo, commonly known as Yorubaland (). It has become the largest indigenous African tradition / belief system in the world with several million adherents worldwide. It shares some parallels with the Vodun practised by the neighbouring Fon people, Fon and Ewe people, Ewe peoples to its west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candomblé
Candomblé () is an African diaspora religions, African diasporic religion that developed in Brazil during the 19th century. It arose through a process of syncretism between several of the traditional religions of West and Central Africa, especially those of Yoruba religion, the Yoruba, Bantu mythology, Bantu, and Gbe languages, Gbe, coupled with influences from Roman Catholicism. There is no central authority in control of Candomblé, which is organized around autonomous ''terreiros'' (houses). Candomblé venerates spirits, known varyingly as ''Orisha, orixás'', ''inkice'', or ''vodun'', which are deemed subservient to a transcendent creator god, Olorun, Oludumaré. Deriving their names and attributes from traditional West African deities, the ''orixás'' are linked with Roman Catholic saints. Each individual is believed to have a tutelary ''orixá'' who has been connected to them since before birth and who informs their personality. An initiatory tradition, Candomblé's member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad Orisha
Trinidad Orisha, also known as Orisha religion and Shango, is a syncretic religion in Trinidad and Tobago and the Caribbean, originally from West Africa (Yoruba religion). Trinidad Orisha incorporates elements of Spiritual Baptism, and the closeness between Orisha and Spiritual Baptism has led to use of the term "Shango Baptist" to refer to members of either or both religions. Anthropologist James Houk described Trinidad Orisha as an " Afro-American religious complex", incorporating elements mainly from traditional African religion and Yoruba and including some elements from Christianity (Catholicism and Protestantism), Hinduism, Islam (especially Sufism), Buddhism, Judaism (especially Kabbalah), Baháʼí, and Amerindian mythologies. "The religious practice involves a music-centered worship service, in which collective singing and drumming accompany spirit possession and animal sacrifice (typically goats, sheep, and fowl)." History Trinidad Orisha's beginnings and develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbanda
Umbanda () is a religion that emerged in Brazil during the 1920s. Deriving largely from Kardecist spiritism, Spiritism, it also combines elements from African diasporic religions, Afro-Brazilian traditions like Candomblé as well as Roman Catholicism. There is no central authority in control of Umbanda, which is organized around autonomous places of worship termed ''centros'' or ''terreiros'', the followers of which are called ''Umbandistas''. Adherents of this monotheism, monotheistic religion believe in a single God who is distant from humanity. Beneath this entity are powerful non-human spirits called ''Orisha, orixás''. In the more Spiritist-oriented wing of the religion, White Umbanda, these are viewed as divine energies or forces of nature; in more Africanised forms they are seen as West African deities and are offered animal sacrifices. The emissaries of the ''orixás'' are the ''pretos velhos'' and ''caboclos'', spirits of enslaved Africans and of Indigenous peoples in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santería
Santería (), also known as Regla de Ocha, Regla Lucumí, or Lucumí, is an African diaspora religions, Afro-Caribbean religion that developed in Cuba during the late 19th century. It arose amid a process of syncretism between the traditional Yoruba religion of West Africa, Catholicism, and Kardecist spiritism, Spiritism. There is no central authority in control of Santería and much diversity exists among practitioners, who are known as ''creyentes'' ("believers"). Santería teaches the existence of a transcendent creator divinity, Olodumare, under whom are spirits known as ''Orisha, oricha''. Typically deriving their names and attributes from traditional Yoruba deities, these ''oricha'' are equated with Roman Catholic saints and associated with various myths. Each human is deemed to have a personal link to a particular ''oricha'' who influences their personality. Olodumare is believed to be the ultimate source of ''Aṣẹ, aché'', a supernatural force permeating the univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
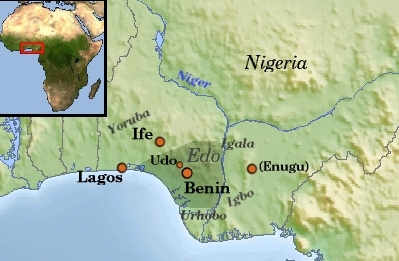
Edo People
The Edo people, also referred to as the Benin City, Benin people, are an Edoid languages, Edoid-speaking Ethnicity, ethnic group. They are prominently native to seven Edo South Senatorial District, southern Local government areas of Nigeria, local government areas of Edo State, Nigeria. They are speakers of the Edo language and are the descendants of the founders of the Benin Empire, Benin Kingdom, Ogiso Igodo. They are closely related to other Edoid languages, Edoid ethnic groups, such as the Esan people, Esan, the Etsakọ people, Etsakọ, the Isoko language, Isoko and Owan, Urhobo as well as other southern ethnic groups. The names ''Benin City, Benin'' and ''Bini'' are Portuguese people, Portuguese corruptions, ultimately from the word ''Ubini'', which came into use during the reign of Oba of Benin, Oba (ruler) Ewuare, c. 1440. ''Ubini'' is an Edo State, Edo word meaning 'livable', used by Pa Idu, the progenitor of the Edo state people, to describe the area found as a livable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ewe People
The Ewe people (; , lit. "Ewe people"; or ''Mono Kple Amu (Volta) Tɔ́sisiwo Dome'', lit. "Between the Rivers Mono and Volta"; ''Eʋenyígbá'' Eweland) are a Gbe languages, Gbe-speaking ethnic group. The largest population of Ewe people is in Ghana (6.0 million), and the second largest population is in Togo (3.1 million). They speak the Ewe language () which belongs to the Gbe languages, Gbe family of languages. They are related to other speakers of Gbe languages such as the Fon people, Fon, Gen language, Gen, Phla–Pherá languages, Phla/Phera, Ogu people, Ogu/Gun, Fon language, Maxi (Mahi), and the Aja people of Togo and Benin. Demographics Ewe people are located primarily in the coastal regions of West Africa: in the region south and east of the Volta River to around the Mono River at the border of Togo and Benin; and in the southwestern part of Nigeria (close to the Atlantic Ocean, stretching from the Nigeria and Benin border to Epe). They are primarily found in the Volta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fon People
The Fon people, also called Dahomeans, Fon nu, Agadja and historically called Jeji (Djedji) by the Yoruba in the South American diaspora and in colonial French literature are a Gbe ethnic group.Fon people Encyclopædia Britannica, undated, 1.7 million population, Retrieved June 29, 2019 They are the largest ethnic group in Benin, found particularly in its south region; they are also found in southwest and Togo. Their total population is estimated to be about 3,500,000 people, and they speak the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |