|
Yorktown, Indiana
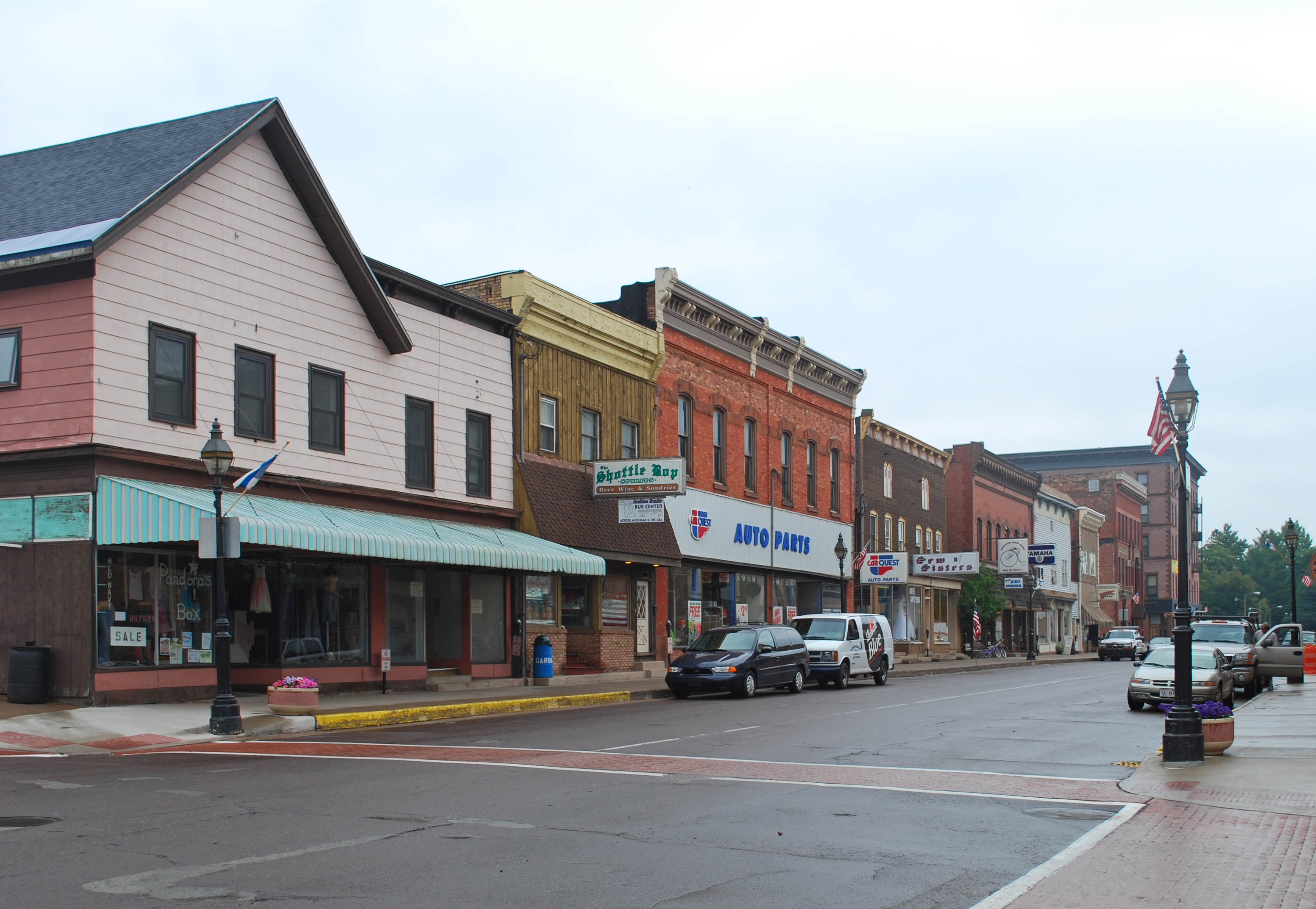
Yorktown is a town in Mount Pleasant Township, Delaware County, Indiana, Mount Pleasant Township, Delaware County, Indiana, Delaware County, Indiana, United States. The population was 11,548 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Muncie, Indiana Metropolitan Statistical Area. History During the Woodland period Native Americans built an earthen enclosure just to the east of Yorktown, still visible on Google Earth at . Yorktown lies at the junction of the White River (Indiana), White River and Buck Creek. According to local legend, the Miami Indians believed that the peculiar configuration of the junction made Yorktown immune from tornadoes. Yorktown was platted in 1837 by Oliver H. Smith who represented Indiana in the U.S. Senate from 1837 to 1843 and was a member of the Committee on Public Lands. Smith eventually became involved in the railroad business, and Yorktown was joined to Indianapolis by railroad in the early 1850s. Yorktown's main street bears Smith's name. Yorktown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town
A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city. The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative status, or historical significance. In some regions, towns are formally defined by legal charters or government designations, while in others, the term is used informally. Towns typically feature centralized services, infrastructure, and governance, such as municipal authorities, and serve as hubs for commerce, education, and cultural activities within their regions. The concept of a town varies culturally and legally. For example, in the United Kingdom, a town may historically derive its status from a market town designation or City status in the United Kingdom, royal charter, while in the United States, the term is often loosely applied to incorporated municipality, municipalities. In some countries, such as Australia and Canada, distinction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland Period
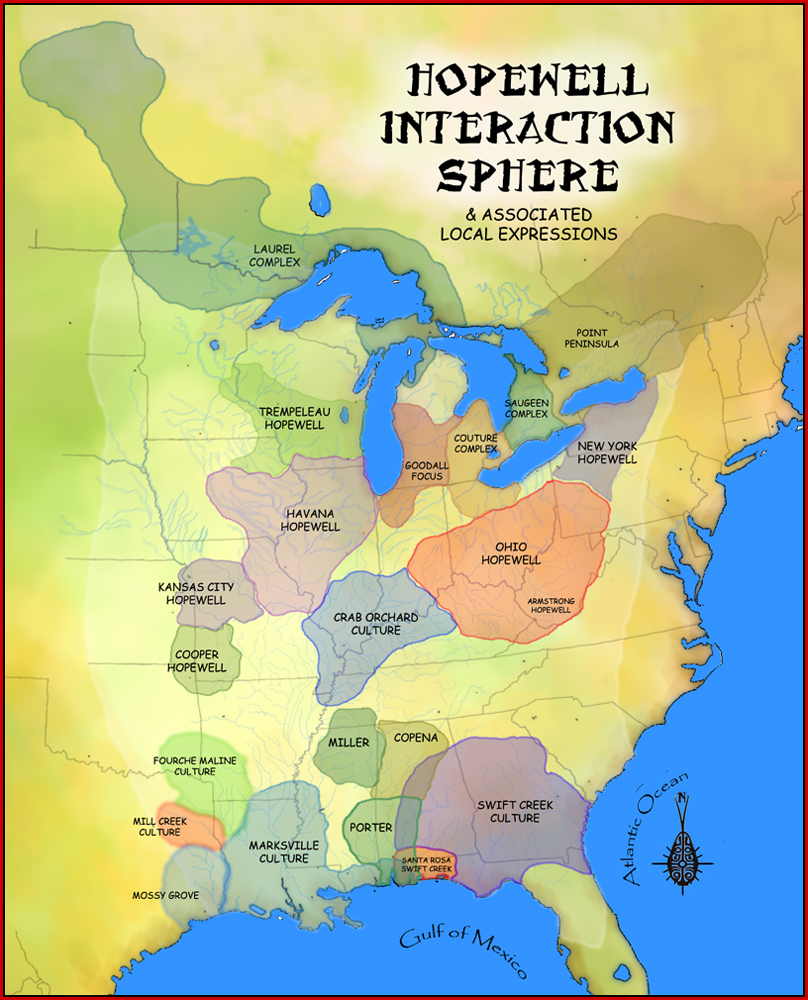
In the classification of :category:Archaeological cultures of North America, archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BC to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 AD to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric, prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic period in the Americas, Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anderson, Indiana
Anderson is a city in and the county seat of Madison County, Indiana, United States. The population was 54,788 at the 2020 census. It is named after Chief William Anderson. The city is the headquarters of the Church of God and its Anderson University. Highlights of the city include the historic Paramount Theatre and the Gruenewald House. History Prior to the organization of Madison County, William Conner entered the land upon which Anderson is located. Conner later sold the ground to John and Sarah Berry, who donated of their land to Madison County on the condition that the county seat be moved from Pendleton to Anderson. John Berry laid out the first plat of Anderson on November 7, 1827. In 1828 the seat of justice was moved from Pendleton to Anderson. The city is named for Chief William "Adam" Anderson, whose mother was Lenape and whose father was of Swedish descent. Chief Anderson's name in Lenape was ''Kikthawenund'', meaning "creaking boughs". The Lenape village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indiana Railroad
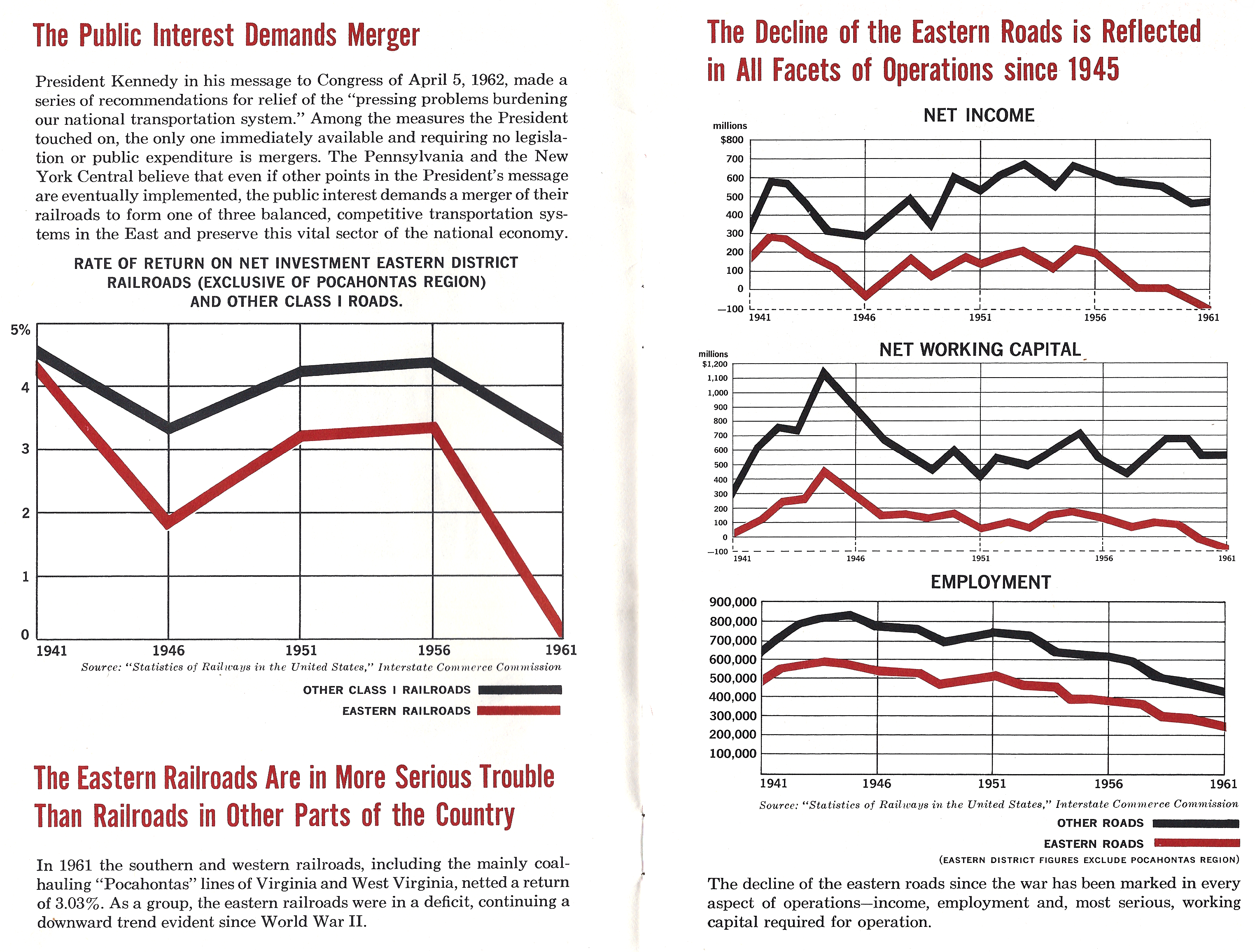
The Indiana Railroad (IR) was the last of the typical Midwestern United States interurban lines. It was formed in 1930–31 by combining the operations of the five major interurban systems in central Indiana into one entity. The predecessor companies came under the control of Midland Utilities, owned by Samuel Insull. His plan was to modernize the profitable routes and abandon the unprofitable ones. With the onset of the Great Depression, the Insull empire collapsed and the Indiana Railroad was left with a decaying infrastructure and little hope of overcoming the growing competition of the automobile for passenger business and the truck for freight business. The IR faced bankruptcy in 1933, and Bowman Elder was designated as the receiver to run the company. Payments on bonded debt were suspended. Elder was able to keep the system virtually intact for four years, and IR operated about of interurban lines throughout Indiana during this period. During the late 1930s, the routes were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conrail
Conrail , formally the Consolidated Rail Corporation, was the primary Class I railroad in the Northeastern United States between 1976 and 1999. The trade name Conrail is a portmanteau based on the company's legal name. It continues to do business as an asset management and network services provider in three Shared Assets Areas that were excluded from the division of its operations during its acquisition by CSX Corporation and the Norfolk Southern Railway. The federal government created Conrail to take over the potentially profitable lines of multiple bankrupt carriers, including the Penn Central Transportation Company and Erie Lackawanna Railway. After railroad regulations were lifted by the 4R Act and the Staggers Act, Conrail began to turn a profit in the 1980s and was privatized in 1987. The two remaining Class I railroads in the East, CSX Transportation and the Norfolk Southern Railway (NS), agreed in 1997 to acquire the system and split it into two roughly-equal parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penn Central
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals, the Pennsylvania, New York Central and the New York, New Haven and Hartford railroad, each of which were united by large-scale service into the New York metropolitan area and to a lesser extent New England and Chicago. The new company failed barely two years after formation, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history at the time. Penn Central's railroad assets were nationalized into Conrail along with those of other bankrupt northeastern railroads; its real estate and insurance holdings successfully reorganized into American Premier Underwriters. History Pre-merger The Penn Central railroad system developed in response to challenges facing northeastern American railroads during the late 1960s. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew revenues from long-distance shipment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Central
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest, along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, Rochester and Syracuse. The New York Central was headquartered in the New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal. The railroad was established in 1853, consolidating several existing railroad companies. In 1968, the NYC merged with its former rival, the Pennsylvania Railroad, to form Penn Central. Penn Central went into bankruptcy in 1970 and, with extensive Federal government support, emerged as Conrail in 1976. In 1999, Conrail was broken up, and portions of its system were transferred to CSX and Norfolk Southern Railway (NS), with CSX acquiring most of the NYC's eastern trackage and NS acquiring most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Four Railroad
The Cleveland, Cincinnati, Chicago and St. Louis Railway, also known as the Big Four Railroad and commonly abbreviated CCC&StL, was a railroad company in the Midwestern United States. It operated in affiliation with the New York Central system. Its primary routes were in Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, and Ohio. At the end of 1925 it reported 2,391 route-miles and 4,608 track-miles; that year it carried 8180 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 488 million passenger-miles. History The railroad was formed on June 30, 1889, by the merger of the Cleveland, Columbus, Cincinnati and Indianapolis Railway, the Cincinnati, Indianapolis, St. Louis and Chicago Railway and the Indianapolis and St. Louis Railway. The following year, the company gained control of the former Indiana, Bloomington and Western Railway (through the foreclosed Ohio, Indiana and Western Railway and through an operating agreement with the Peoria and Eastern Railway). In 1906, the Big Four was acquired by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ball Brothers
The Ball brothers (Lucius, William, Edmund, Frank, and George) were five American industrialists and philanthropists who established a manufacturing business in New York and Indiana in the 1880s that was renamed the Ball Corporation in 1969. The Ball brothers' firm became a global manufacturer of plastic and metal food and beverage containers as well as a manufacturer of equipment and supplier of services to the aerospace industry. In addition to the brothers' manufacturing business, they were also noted for their philanthropy and community service. Earnings from their business ventures provided the financial resources to support a number of other projects in the community of Muncie, Indiana, and elsewhere. Most notably, the brothers became benefactors of several Muncie institutions including Ball State University, Ball Memorial Hospital, Keuka College, the YMCA, Ball stores department store, and Minnetrista. The Ball Brothers Foundation, established in 1926, continues the fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas City, Indiana
Gas City is a city in Grant County, Indiana, United States, along the Mississinewa River. The population was 6,157 at the 2020 census. History Gas City was first known as Harrisburg when settled on May 25, 1867, by Noah Harris. It became a boom town when natural gas was found in the area in 1887 as part of the Indiana gas boom. The Gas City Land Company was founded on March 21, 1892, and the town of about 150 people changed its name to Gas City a few days later. However, much of the natural gas was depleted by the late 1800s and early 1900s, often due to inefficient extraction. The Gas City High School, Thompson-Ray House, and West Ward School are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Gas City annually hosts the Ducktail Run Rod and Custom Car Show in the Fall. The "Ducktail Run," as it is known to locals, is a large car show featuring vehicles from 1972 and older. In the year 2020, the Festival had 2,020 vehicles register to appear. Geography According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaston, Indiana
Gaston is a town in Washington Township, Delaware County, Indiana, United States. The population was 796 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Muncie Metropolitan Statistical Area. History Gaston was originally called Snag Town and then New Corner, and under the former name was platted on February 27, 1855 by David L. Jones. The name Gaston was adopted when the railroad was built through the town in 1901 during a local gas boom. In late 1904, Gaston was officially incorporated as a town. Gaston currently has a preschool, elementary, and high school in the Wes-Del community school district. It also has a few churches, an ice cream parlor/restaurant called The Barking Cow, a funeral home and a few cemeteries located outside of the town center, a volunteer fire department and police department, a Dollar General and several small businesses. The town has also had a newspaper, ''The Voice'', which was released every other week until it was discontinued in May 2016 after producing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliver H
Oliver may refer to: Arts, entertainment and literature Books * ''Oliver the Western Engine'', volume 24 in ''The Railway Series'' by Rev. W. Awdry * ''Oliver Twist'', a novel by Charles Dickens Fictional characters * Ariadne Oliver, in the novels of Agatha Christie * Oliver (Disney character) * Oliver Fish, a gay police officer on the American soap opera ''One Life to Live'' * Oliver Hampton, in the American television series ''How to Get Away with Murder'' * Oliver Jones (''The Bold and the Beautiful''), on the American soap opera ''The Bold and the Beautiful'' * Oliver Lightload, in the movie ''Cars'' * Oliver Oken, from ''Hannah Montana'' * Oliver (paladin), a paladin featured in the Matter of France * Oliver Queen, DC Comic book hero also known as the Green Arrow * Oliver (Thomas and Friends character), a locomotive in the Thomas and Friends franchise * Oliver Trask, a controversial minor character from the first season of ''The O.C.'' * Oliver Twist (charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |