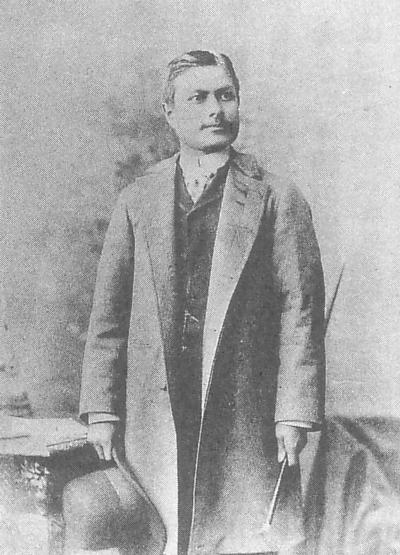|
Yatarō Mishima
Viscount was a Japanese businessman, central banker and the 8th Governor of the Bank of Japan (BOJ). Viscount Mishima was a member of Japan's House of Peers.Masaoka, Naoichi. (1914) ''Japan to America,'' p. 127./ref> Early life Mishima was born in Kagoshima Prefecture. In 1893, Mishima briefly married a daughter of Ōyama Iwao, whom he was forced to divorce when she caught tuberculosis. Their relationship was the basis for Kenjirō Tokutomi's popular 1899 novel ''The Cuckoo''. In 1894–1900 he studied at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York where he earned a M.A. degree. Career During 1911–1913, Mishima was head of the Yokohama Specie Bank The was a Japanese bank founded in Yokohama in 1880, which dominated the Japanese market for trade finance in subsequent decades. It has been described as a "quasi-governmental exchange bank that was the overseas financial agent of the Japanese .... Mishima was Governor of the Bank of Japan from February 28, 1913 to March 7, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michiharu Mishima
was a novelist, playwright and drama critic. His pen name was Shōdō Mishima (三島 章道 ''Mishima Shōdō''). Early life Mishima was born in Azabu, Tōkyō, to an aristocratic family. His grandfather Michitsune Mishima had been ennobled as a viscount in the new Japanese nobility in 1884, while his father was Yatarō Mishima, the 8th Governor of the Bank of Japan. His mother was Marquis Takauta Shijō (四条 隆謌 ''Shijō Takauta'')'s third daughter, Kaneko (加根子), through whom he was related to the old court aristocracy and the greater Fujiwara clan. His younger sister was married to Yoshi Hijikata. He was a Peers School graduate, and succeeded his father as the third Viscount Mishima in 1919. Career Mishima was a member of the House of Peers and the House of Councillors and was parliamentary vice-minister to the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. Scouting Mishima formed the nationwide ''Boy Scouts of Japan'' with Count Futa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Bankers
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japanese studies , sometimes known as Japanology in Europe, is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese language, history, culture, litera ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governors Of The Bank Of Japan
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the type of political region or polity, a ''governor'' may be either appointed or elected, and the governor's powers can vary significantly, depending on the public laws in place locally. The adjective pertaining to a governor is gubernatorial, from the Latin root ''gubernare''. In a federated state, the governor may serve as head of state and head of government for their regional polity, while still operating under the laws of the federation, which has its own head of state for the entire federation. Ancient empires Pre-Roman empires Though the legal and administrative framework of provinces, each administered by a governor, was created by the Romans, the term ''governor'' has been a convenient term for historians to describe similar systems in antiquity. Indeed, many regions of the pre-Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornell University Alumni
Cornell University is a private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson White in 1865. Since its founding, Cornell University has been a co-educational and nonsectarian institution. As of fall 2024, the student body included 16,128 undergraduate and 10,665 graduate students from all 50 U.S. states and 130 countries. The university is organized into eight undergraduate colleges and seven graduate divisions on its main Ithaca campus. Each college and academic division has near autonomy in defining its respective admission standards and academic curriculum. In addition to its primary campus in Ithaca, Cornell University administers three satellite campuses, including two in New York City, the medical school and Cornell Tech, and a branch of the medical school in Al Rayyan, Qatar's Education City. Cornell is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1919 Deaths
Events January * January 1 ** The Czechoslovak Legions occupy much of the self-proclaimed "free city" of Bratislava, Pressburg (later Bratislava), enforcing its incorporation into the new republic of Czechoslovakia. ** HMY Iolaire, HMY ''Iolaire'' sinks off the coast of the Hebrides; 201 people, mostly servicemen returning home to Lewis and Harris, are killed. * January 2–January 22, 22 – Russian Civil War: The Red Army's Caspian-Caucasian Front begins the Northern Caucasus Operation (1918–1919), Northern Caucasus Operation against the White Army, but fails to make progress. * January 3 – The Faisal–Weizmann Agreement is signed by Faisal I of Iraq, Emir Faisal (representing the Arab Kingdom of Hejaz) and Zionism, Zionist leader Chaim Weizmann, for Arab–Jewish cooperation in the development of a Jewish homeland in Palestine (region), Palestine, and an Arab nation in a large part of the Middle East. * January 5 – In Germany: ** Spartacist uprising in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1867 Births
There were only 354 days this year in the newly purchased territory of Alaska. When the territory transferred from the Russian Empire to the United States, the calendric transition from the Julian to the Gregorian Calendar was made with only 11 days instead of 12 during the 19th century. This change was made due to the territorial and Geopolitics, geopolitical shift from the Asian to the American side of the International Date Line. Friday, 6 October 1867 ''(Julian Calendar)'' was followed by Friday again on 18 October 1867 (instead of Saturday, 19 October 1867 in the Gregorian Calendar). Events January * January 1 – The John A. Roebling Suspension Bridge, Covington–Cincinnati Suspension Bridge opens between Cincinnati, Ohio, and Covington, Kentucky, in the United States, becoming the longest single-span bridge in the world. It was renamed after its designer, John A. Roebling, in 1983. * January 8 – African-American men are granted the right to vote in the District ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junnosuke Inoue
was a Japanese financier and statesman of the Taisho and Showa eras. He was the 9th and 11th Governor of the Bank of Japan (BOJ), and Minister of Finance in 1923-1924 and 1929-1931. He was assassinated during the League of Blood Incident in 1932. Biography Inoue was born in Ōita Prefecture. He graduated from the Imperial University of Tokyo. In 1896, Inoue entered the Bank of Japan and in 1897 he was a BOJ trainee along with Hisaakira Hijikata. Both young men were sent by the bank to learn about British banking practices in London. From 1913-1919, Inoue was head of the Yokohama Specie Bank. Inoue was Governor of the Bank of Japan from March 13, 1919 – September 2, 1923 and again from May 10, 1927 – June 1, 1928.BOJList of Governors He was Minister of Finance in 1923-1924 and 1929-1931. He briefly presided the Institute of Pacific Relations between Ray Lyman Wilbur nomination as United States Secretary of the Interior The United States secretary of the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korekiyo Takahashi
Viscount was a Japanese politician who served as prime minister of Japan from 1921 to 1922 and Minister of Finance when he was assassinated. He was also a member of the House of Peers and head of the Bank of Japan. Takahashi made many contributions to Japan's development during the early 20th century, including introducing its first patent system and securing foreign financing for the Russo-Japanese War. Following the onset of the Great Depression, he introduced controversial financial policies which included abandoning the gold standard, lowering interest rates, and using the Bank of Japan to finance deficit spending by the central government. His decision to cut government spending in 1935 led to unrest within the Japanese military, who assassinated him in February 1936. Takahashi's policies are credited for pulling Japan out of the Depression, but led to soaring inflation following his assassination, as Takahashi's successors became highly reluctant to cut off funding to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Society (Manhattan)
Japan Society is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, formed in 1907 to promote relations between the United States and Japan. Its headquarters was designed by Junzo Yoshimura and opened in 1971 at 333 East 47th Street near the United Nations. With a focus on "arts and culture, public policy, business, language, and education", the organization has regularly held events in its many facilities, including a library, art gallery, and theater, since its opening. After suspending all activities during World War II, Japan Society expanded under the leadership of John D. Rockefeller III. History Incorporation In 1907, Tamemoto Kuroki and Goro Ijuin were chosen to represent Japan at the Jamestown Exposition. They attended a welcome dinner in New York City with Japanese ambassador to the United States, Shuzo Aoki, where there was talk of forming an organization to promote US-Japan relations in the city. Two days later at a luncheon held by Kuroki, Japan Society was born. The orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yokohama Specie Bank
The was a Japanese bank founded in Yokohama in 1880, which dominated the Japanese market for trade finance in subsequent decades. It has been described as a "quasi-governmental exchange bank that was the overseas financial agent of the Japanese government". During the 1920s, the YSB accounted for nearly 50 per cent of foreign exchange transactions for Japanese exports and imports, and in 1929 was Japan's largest and most profitable bank aside from the Bank of Japan. It also played a significant role in Japanese colonial ventures, not least in Manchuria and elsewhere in China. In 1946, following the loss of Japan's overseas possessions, the Yokohama Specie Bank was reorganized and rebranded as the Bank of Tokyo, one of the predecessor entities of MUFG Bank. Background Following the signing of the Japan-U.S. Treaty of Amity and Commerce in 1859, Yokohama was opened as a port for foreign trade and quickly grew in importance. Through the New Currency Act of 1871, Japan implement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Of Japan
The is the central bank of Japan.Louis Frédéric, Nussbaum, Louis Frédéric. (2005). "Nihon Ginkō" in The bank is often called for short. It is headquartered in Nihonbashi, Chūō, Tokyo, Chūō, Tokyo. The said bank is a corporate entity independent of the Government of Japan, Japanese government, and while it is not an Administrative organisation, administrative organisation of the state, its monetary policy falls within the scope of administration. From a Macroeconomics, macroeconomic perspective, long-term stability of prices is deemed crucial. However, the political sector tends to favour short-term measures. Thus, the bank's autonomy and independence are granted from the standpoint of ensuring long-term public welfare and political neutrality. History Background Like most modern Japanese institutions, the Bank of Japan was founded after the Meiji Restoration. Prior to the Restoration, Japan's feudal fiefs all issued their own money, ''Scrip of Edo period Japan, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |