|
Yamato Period
The is the period of Japanese history when the Imperial court ruled from modern-day Nara Prefecture, then known as Yamato Province. While conventionally assigned to the period 250–710, including both the Kofun period (–538) and the Asuka period (538–710), the actual start of Yamato rule is disputed. The Yamato court's supremacy was challenged during the Kofun period by other polities centered in various parts of Japan. What is certain is that Yamato clans had major advantages over their neighbouring clans in the 6th century. This period is divided by the relocation of the capital to Asuka, in modern Nara Prefecture. However, the Kofun period is an archaeological period while the Asuka period is a historical period. Therefore, many think of this as an old division and this concept of period division is no longer applicable. At the era of Prince Shōtoku in the early 7th century, a new constitution was prescribed for Japan based on the Chinese model. After the fall of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Japan
The first human inhabitants of the Japanese archipelago have been traced to the Japanese Paleolithic, Paleolithic, around 38–39,000 years ago. The Jōmon period, named after its cord-marked pottery, was followed by the Yayoi period in the first millennium BC when new inventions were introduced from Asia. During this period, the first known written reference to Japan was recorded in the Chinese ''Book of Han'' in the first century AD. Around the 3rd century BC, the Yayoi people from the continent immigrated to the Japanese archipelago and introduced iron technology and agricultural civilization. Because they had an agricultural civilization, the population of the Yayoi began to grow rapidly and ultimately overwhelmed the Jōmon period, Jōmon people, natives of the Japanese archipelago who were hunter-gatherers. Between the fourth and ninth centuries, Japan's many kingdoms and tribes gradually came to be unified under a centralized government, nominally controlled by the Empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 Province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions: 22 provinces of China, provinces, 5 autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, 4 direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is List of cities in China by population, its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryukyuan Languages
The , also Lewchewan or Luchuan (), are the indigenous languages of the Ryukyu Islands, the southernmost part of the Japanese archipelago. Along with the Japanese language and the Hachijō language, they make up the Japonic language family. Just as among Japanese dialects it is hard to understand each other, the Ryukyu and mainland Japanese languages are not mutually intelligible. It is not known how many speakers of these languages remain, but language shift toward the use of Standard Japanese and dialects like Okinawan Japanese has resulted in these languages becoming endangered language, endangered; Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger, UNESCO labels four of the languages "definitely endangered" and two others "severely endangered". Overview Phonologically, the Ryukyuan languages have some cross-linguistically unusual features. Southern Ryukyuan languages have a number of syllabic consonants, including unvoiced syllabic fricatives (e.g. Ōgami Miyako language, Miyako ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okinawa Island
, officially , is the largest of the Okinawa Islands and the Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Islands of Japan in the Kyushu region. It is the smallest and least populated of the five Japanese archipelago, main islands of Japan. The island is approximately long, an average wide, and has an area of . It is roughly south of the main island of Kyushu and the rest of Japan. It is northeast of Taiwan. The total population of Okinawa Island was 1,384,762 in 2009. The greater Naha area has roughly 800,000 residents, while the city itself has about 320,000 people. Naha is the seat of Okinawa Prefecture on the southwestern part of Okinawa Island. Okinawa has a humid subtropical climate. Okinawa has been a strategic location for the United States Armed Forces since the Battle of Okinawa and the end of World War II. The island was formally controlled by the United States Civil Administration of the Ryukyu Islands until 1972, with around 26,000 U.S. military personnel stationed on Oki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Geography of Taiwan, Taiwan: the Ryukyu Islands are divided into the Satsunan Islands (Ōsumi Islands, Ōsumi, Tokara Islands, Tokara and Amami Islands, Amami) and Okinawa Prefecture (Daitō Islands, Daitō, Miyako Islands, Miyako, Yaeyama Islands, Yaeyama, Senkaku Islands, Senkaku, Okinawa Islands, Okinawa, Sakishima Islands (further divided into the Miyako Islands, Miyako and Yaeyama Islands), and Yonaguni as the westernmost). The larger ones are mostly volcanic islands and the smaller mostly coral island, coral. The largest is Okinawa Island. The climate of the islands ranges from humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') in the north to tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification ''Af'') in the south. Precipitation is very high and is affected by the rainy season and typhoons. Except the outlying Daitō Islands, the island chain ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japonic Languages
Japonic or Japanese–Ryukyuan () is a language family comprising Japanese language, Japanese, spoken in the main islands of Japan, and the Ryukyuan languages, spoken in the Ryukyu Islands. The family is universally accepted by linguists, and significant progress has been made in reconstructing the proto-language, Proto-Japonic. The reconstruction implies a split between all dialects of Japanese and all Ryukyuan varieties, probably before the 7th century. The Hachijō language, spoken on the Izu Islands, is also included, but its position within the family is unclear. Most scholars believe that Japonic was brought to the Japanese archipelago from the Korean peninsula with the Yayoi culture during the 1st millennium BC. There is some fragmentary evidence suggesting that Japonic languages may still have been spoken in central and southern parts of the Korean peninsula (see Peninsular Japonic) in the early centuries AD. Possible genetic relationships with many other language familie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yayoi
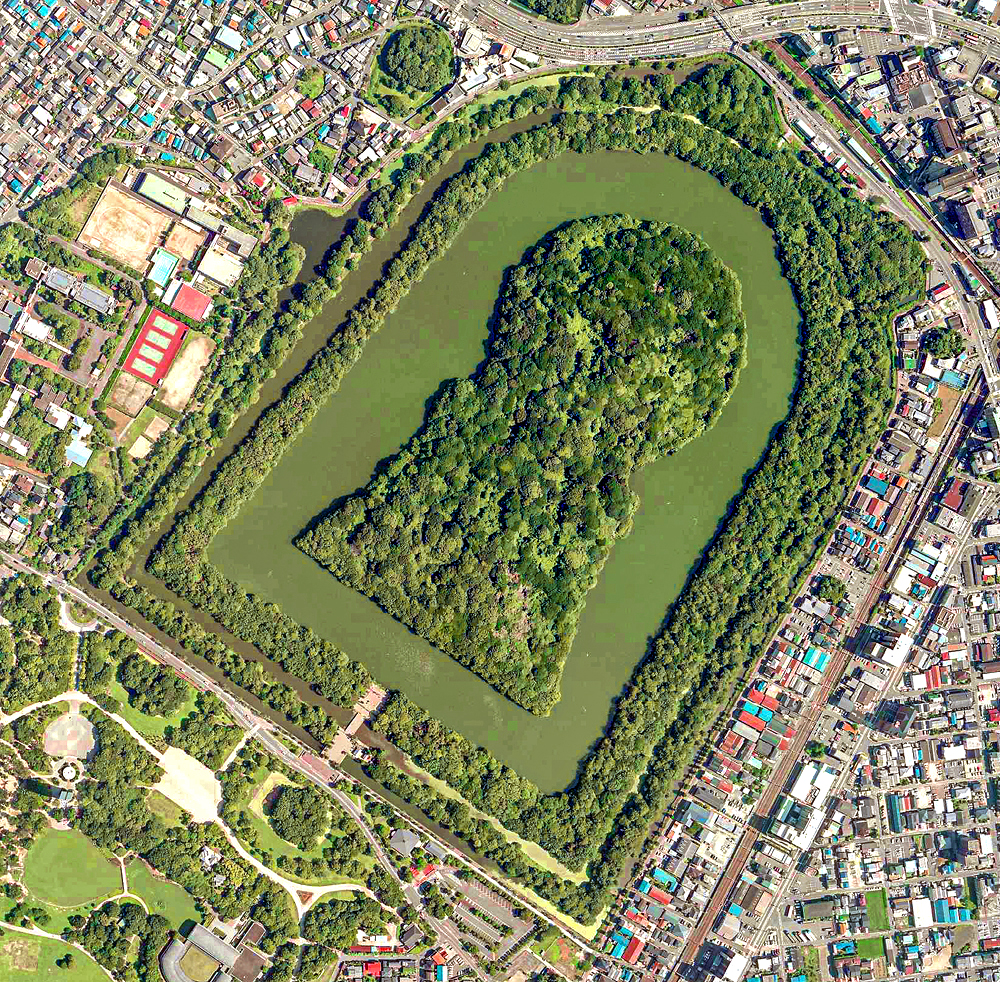
The Yayoi period (弥生時代, ''Yayoi jidai'') (c. 300 BC – 300 AD) is one of the major historical periods of the Japanese archipelago. It is generally defined as the era between the beginning of food production in Japan and the emergence of keyhole-shaped burial mounds (前方後円墳, ''zenpō-kōen-fun''). Chronologically, it spans from around the 10th century BCE or 9th–8th century BCE to the mid-3rd century CE. Following the Jōmon period, which was characterized by a hunter-gatherer economy, the Yayoi period marked the transition to a productive economy based on wet-rice agriculture. In the latter half of the late Yayoi period (around the 1st century CE), large regional powers emerged throughout western Japan, including the Tokai and Hokuriku regions. By the end of the 2nd century, the political entity known as Wa-koku (倭国) had formed. It is generally considered that the Yayoi period transitioned into the Kofun period around the mid-3rd century, although the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the History of agriculture, introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of sedentism, settlement. The term 'Neolithic' was coined by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, Sir John Lubbock in 1865 as a refinement of the three-age system. The Neolithic began about 12,000 years ago, when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East and Mesopotamia, and later in other parts of the world. It lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BCE), marked by the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tajimamori
is a Japanese legendary figure of the Kofun period, also worshipped as the god of sweets. His name is written in kanji as 多遅麻毛理 in the ''Kojiki'', and as 田道間守 in the ''Nihon Shoki''. Legendary narrative Tajimamori's ancestry is described differently in the ''Kojiki'' and ''Nihon Shoki''. The ''Kojiki'' lists him as the son of and elder brother of , while the ''Nihon Shoki'' records him as the son of 's son . Emperor Suinin commanded Tajimamori to go and get him a magical fruit called . To this end Tajimamori crossed to the magical land of , and after ten years he returned with some branches with leaves and some with fruit. However, by this time Emperor Suinin was already dead. Tajimamori gave half of his branches to Suinin's widow and offered the other half at the deceased emperor's tomb, then died himself, wailing with sadness. He also laments and recites a speech after learning of the Emperor's death. Worship The fruit Tajimamori brought back is suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tajima Province
was a Provinces of Japan, province of Japan in the area of northern Hyōgo Prefecture. Tajima bordered on Tango Province, Tango and Tanba Province, Tanba to the east, Harima Province, Harima to the south, and Inaba Province, Inaba to the west. Its abbreviated form name was . In terms of the Gokishichidō system, Tajimao was one of the provinces of the San'indō circuit. Under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, Tajima was ranked as one of the "superior countries" (上国) in terms of importance, and one of the "near countries" (近国) in terms of distance from the capital. The provincial capital was located in what is now the city of Toyooka, Hyōgo, Toyooka. The ''ichinomiya'' of the province is the Izushi Shrine also located in Toyooka. The area of the province was 2099.01 square kilometers. History Early history The early history of the Tajima region is uncertain. There appear to have been two power centers. The Tajima ''Kuni no miyatsuko'' ruled in eastern Tajima ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nihon Shoki
The or , sometimes translated as ''The Chronicles of Japan'', is the second-oldest book of classical Japanese history. It is more elaborate and detailed than the , the oldest, and has proven to be an important tool for historians and archaeologists as it includes the most complete extant historical record of ancient Japan. The was finished in 720 under the editorial supervision of Prince Toneri with the assistance of Ō no Yasumaro and presented to Empress Genshō. The book is also a reflection of Chinese influence on Japanese civilization. In Japan, the Sinicized court wanted written history that could be compared with the annals of the Chinese. The begins with the Japanese creation myth, explaining the origin of the world and the first seven generations of divine beings (starting with Kuninotokotachi), and goes on with a number of myths as does the , but continues its account through to events of the 8th century. It is believed to record accurately the latter reig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Emperor
The emperor of Japan is the hereditary monarch and head of state of Japan. The emperor is defined by the Constitution of Japan as the symbol of the Japanese state and the unity of the Japanese people, his position deriving from "the will of the people with whom resides sovereign power". The Imperial Household Law governs the line of imperial succession. Pursuant to his constitutional role as a national symbol, and in accordance with rulings by the Supreme Court of Japan, the emperor is personally immune from prosecution. By virtue of his position as the head of the Imperial House, the emperor is also recognized as the head of the Shinto religion, which holds him to be the direct descendant of the sun goddess Amaterasu. According to tradition, the office of emperor was created in the 7th century BC, but the first historically verifiable emperors appear around the 5th or 6th centuries AD. The role of the emperor of Japan has historically alternated between a largely cerem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |