|
Xiphos
The ''xiphos'' ( ; plural ''xiphe'', ) is a double-edged, one-handed Iron Age straight shortsword used by the ancient Greeks. It was a secondary battlefield weapon for the Greek armies after the dory or javelin. The classic blade was generally about long, although the Spartans supposedly preferred to use blades as short as around the era of the Greco-Persian Wars. Etymology Stone's ''Glossary'' has ''xiphos'' being a name used by Homer for a sword. The entry in the book says that the sword had a double-edged blade widest at about two-thirds of its length from the point, and ending in a very long point. The word is attested in Mycenaean Greek Linear B form as , '. A relation to Arabic '' saifun'' ('a sword') and Egyptian ''sēfet'' has been suggested, although this does not explain the presence of a labiovelar in Mycenaean. One suggestion connects Ossetic ''äxsirf'' "sickle", which would point to a virtual Indo-European ''*kwsibhro-''. Construction Most ''xiphe'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makhaira
The makhaira is a type of Ancient Greek bladed weapon and tool, generally a large knife or sword, similar in appearance to the modern day machete, with a single cutting edge. Terminology The Greek word μάχαιρα (''mákhaira'', plural ''mákhairai''), also transliterated ''machaira'' or ''machaera,'' is related to (''mákhē'') "a battle", (''mákhesthai'') "to fight". It derives from the Proto-Indo-European *''magh-.'' Homer mentions the makhaira, but as a domestic knife of no great size. In period texts, μάχαιρα has a variety of meanings, and can refer to virtually any knife or sword, even a surgeon's scalpel, but in a martial context it frequently refers to a type of one-edged sword; a sword designed primarily to cut rather than thrust. The Koine of the New Testament uses the word ''makhaira'' to refer to a sword generically, not making any particular distinction between native blades and the gladius of the Roman soldier. This ambiguity appears to have cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kopis
The term kopis () in Ancient Greece could describe a heavy knife with a forward-curving blade, primarily used as a tool for cutting meat, for ritual slaughter and animal sacrifice, or refer to a single edged cutting or "cut and thrust" sword with a similarly shaped blade. Etymology The term derives from the Greek word κοπίς (kopis), plural ''kopides'' from κόπτω – ''koptō'', "to cut, to strike". Alternatively a derivation from the Ancient Egyptian term ''khopesh'' for a cutting sword has been postulated. Characteristics The kopis sword was a one-handed weapon. Early examples had a blade length of up to 65 cm (25.6 inches), making it almost equal in size to the spatha. Later examples of the kopis from Macedonia tended to be shorter with a blade length of about 48 cm (18.9 inches). The kopis had a single-edged blade that pitched forward towards the point, the edge being concave on the part of the sword nearest the hilt, but swelling to convexity toward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age Sword
Swords made of iron (as opposed to bronze) appear from the Early Iron Age ( century BC), but do not become widespread before the 8th century BC. Early Iron Age swords were significantly different from later steel swords. They were work-hardened, rather than quench-hardened, which made them about the same or only slightly better in terms of strength and hardness to earlier bronze swords. This meant that they could still be bent out of shape during use. The easier production, however, and the greater availability of the raw material allowed for much larger scale production. Eventually smiths learned of processes to refine smelted iron and make steel. By quenching (making the steel hard and brittle) and tempering (removing the brittleness), swords could be made that would suffer much less damage, and would spring back into shape if bent. It took a long time, however, before this was done consistently, and even until the end of the early medieval period, many swords were still u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideogram
An ideogram or ideograph (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'idea' + 'to write') is a symbol that is used within a given writing system to represent an idea or concept in a given language. (Ideograms are contrasted with phonogram (linguistics), phonograms, which indicate sounds of speech and thus are independent of any particular language.) Some ideograms are more arbitrary than others: some are only meaningful assuming preexisting familiarity with some convention; others more directly resemble their signifieds. Ideograms that represent physical objects by visually illustrating them are called ''pictograms''. * Numeral system, Numerals and List of mathematical symbols, mathematical symbols are ideograms, for example ⟨1⟩ 'one', ⟨2⟩ 'two', ⟨+⟩ 'plus', and ⟨=⟩ 'equals'. * The ampersand ⟨&⟩ is used in many languages to represent the word ''and'', originally a stylized Ligature (writing), ligature of the Latin word . * Other typographical examples include ⟨§⟩ 'sect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gladius
''Gladius'' () is a Latin word properly referring to the type of sword that was used by Ancient Rome, ancient Roman foot soldiers starting from the 3rd century BC and until the 3rd century AD. Linguistically, within Latin, the word also came to mean "sword", regardless of the type used. Early ancient Roman swords were similar to those of the Greeks, called ''xiphos, xiphe'' (, : ''xiphos''). From the 3rd century BC, however, the Roman Republic, Romans adopted a weapon based on the sword of the Celtiberians of Hispania in service to Carthage during the Punic Wars, known in Latin as the ''gladius hispaniensis'', meaning "Hispania, Hispanic-type sword". The Romans improved the weapon and modified it depending on how their battle units waged war, and created over time new types of "''gladii''" such as the ''Mainz gladius'' and the ''Pompeii gladius''. Finally, in the third century AD the heavy Roman infantry replaced the ''gladius'' with the ''spatha'' (already common among Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Sword
Bronze Age swords appeared from around the 17th century BC, in the Black Sea and Aegean regions, as a further development of the dagger. They were replaced by iron swords during the early part of the 1st millennium BC. Typical Bronze Age swords were between 60 and 80 cm long, significantly shorter weapons are categorized as '' short swords'' or daggers. From an early time swords with lengths in excess of 100 cm were also produced. The necessary technology appears to have been developed in the Aegean around 1700 BC, using alloys of copper and tin or arsenic. Before about 1400 BC swords remained mostly limited to the Aegean and southeastern Europe. During the final centuries of the 2nd millennium BC their use spread to Central Europe and Britain, to the Near East, Central Asia, Northern India and to China. Predecessors Before bronze, stone (such as flint and obsidian) was used as the primary material for edged cutting tools and weapons. Stone, however, is too brittl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloids (such as arsenic or silicon). These additions produce a range of alloys some of which are harder than copper alone or have other useful properties, such as strength, ductility, or machinability. The archaeological period during which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age, which started about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in modern times. Because historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Tène Culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a Iron Age Europe, European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman Republic, Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and the Culture of Golasecca, Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences. La Tène culture's territorial extent corresponded to what is now Prehistory of France#The Iron Age, France, History of Belgium#Celtic and Roman periods, Belgium, Early history of Switzerland#Iron Age, Switzerland, History of Austria#Iron Age, Austria, History of England#Later Prehistory, England, History of Germany#Iron Age, Southern Germany, the History of the Czech lands#Iron Age, Czech Republic, Prehistoric Italy#Iron Age, Northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldric
A baldric (also baldrick, bawdrick, bauldrick as well as other rare or obsolete variations) is a belt worn over one shoulder that is typically used to carry a weapon (usually a sword) or other implement such as a bugle or drum. The word may also refer to any belt in general, but this usage is poetic or archaic. In modern contexts, military drum majors usually wear a baldric. Usage Baldrics have been used since ancient times, usually as part of military dress. The design offers more support for weight than a standard waist belt, without restricting movement of the arms, and while allowing easy access to the object carried. Alternatively, and especially in modern times, the baldric may fill a ceremonial role rather than a practical one. Most Roman tombstones in the third century had depictions of white baldrics. Design One end of the baldric was broad and finished in a straight edge, while the other was tapered to a narrow strip. The narrow end was brought through a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
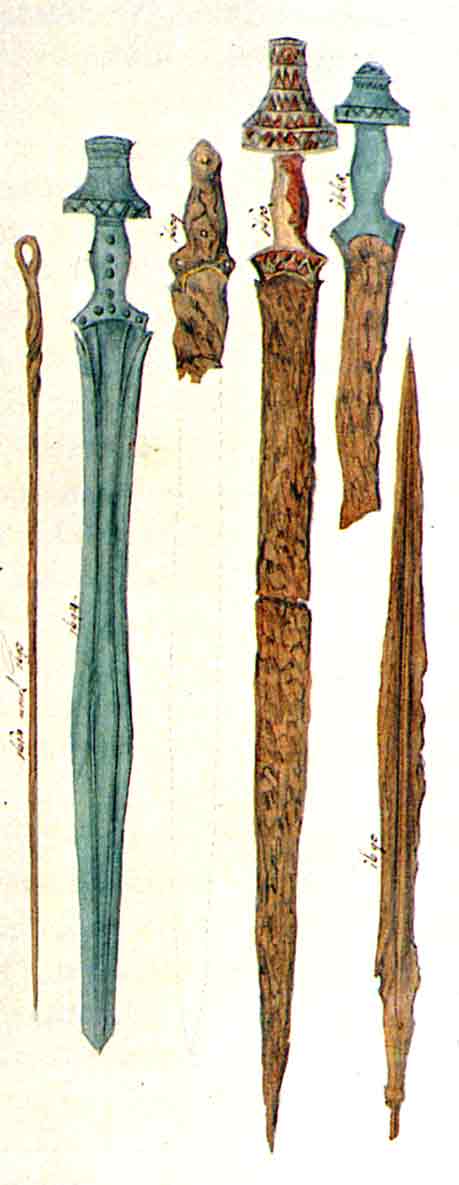
Two Xiphe, A Kopis And Spearheads From Thessaloniki Museum
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and the only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and Spirituality, spiritual significance in many Culture, cultures. Mathematics The number 2 is the second natural number after 1. Each natural number, including 2, is constructed by succession, that is, by adding 1 to the previous natural number. 2 is the smallest and the only even prime number A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a Product (mathematics), product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime ..., and the first Ramanujan prime. It is also the first superior highly composite number, and the first colossally abundant number. An integer is determined to be Parity (mathematics), even if it is Division (mathematics), divisible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |