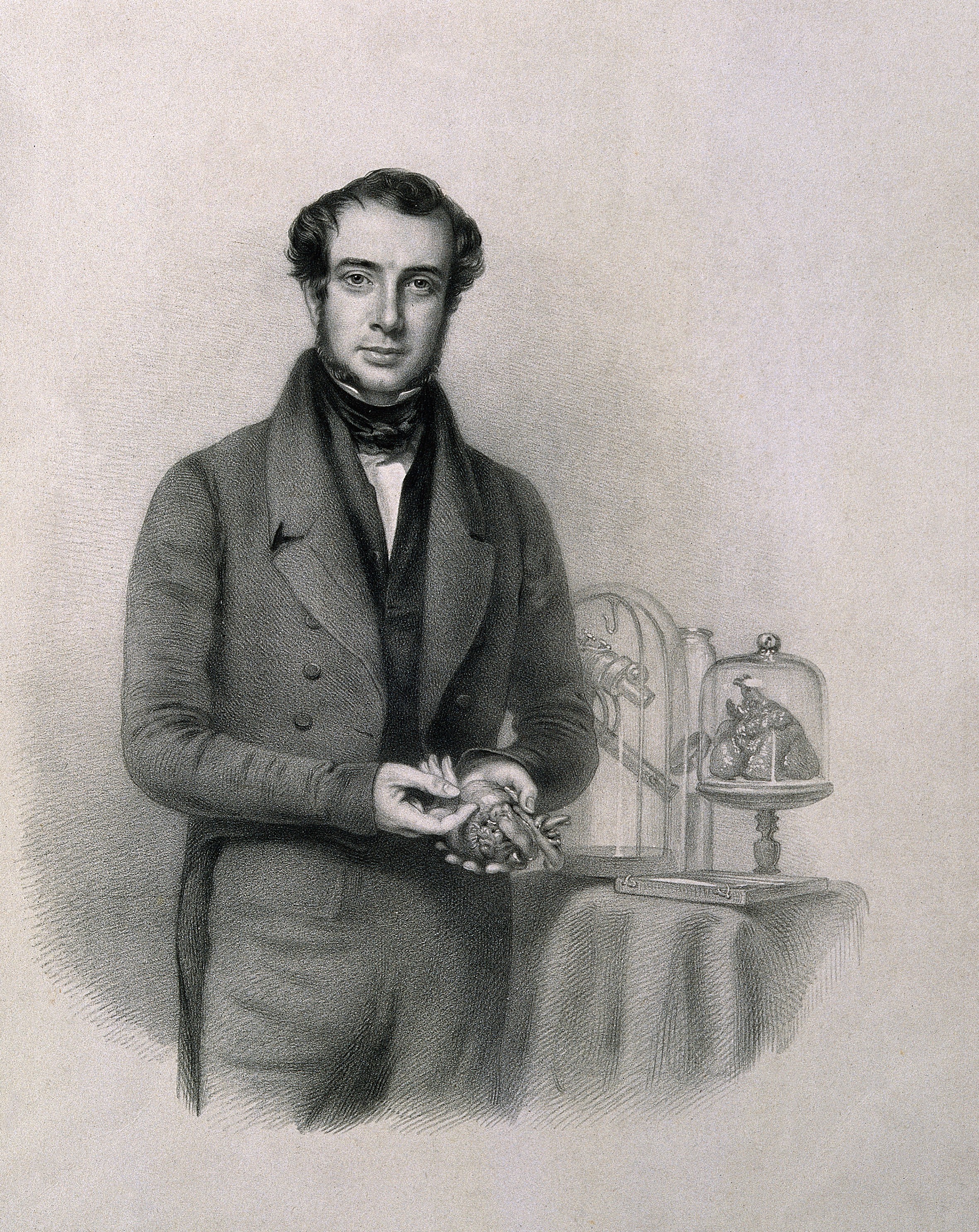|
William Coulson
William Coulson (1802 – 1877) was an English surgeon. Life The younger son of Thomas Coulson, master painter in Devonport dockyard, he was born at Penzance; Walter Coulson was an elder brother. His father was a close friend of Sir Humphry Davy; his mother was Catherine Borlase. After receiving some classical education at the local grammar school, Coulson spent two years in Brittany (1816–18), studying the French language and literature. Having first been apprenticed to a Penzance surgeon, he entered Edward Grainger's School of Anatomy in the Borough, and attended St. Thomas's Hospital, where he became dresser to Frederick Tyrrell. He then studied in Berlin, where he knew the poet Thomas Campbell, and spent some months in Paris. Coulson returned to London, and became a member of the Royal College of Surgeons on 26 September 1826. He helped found the Aldersgate Street School of Medicine with Tyrrell, Sir William Lawrence, and others, and acted for three years as demonstrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Coulson Maguire
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name should b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunterian Oration
The Hunterian Oration is a lecture of the Royal College of Surgeons of England. The oration was founded in 1813 by the executors of the will of pioneering surgeon John Hunter, his nephew Dr Matthew Baillie and his brother-in-law Sir Everard Home, who made a gift to the College to provide an annual oration and a dinner for Members of the Court of Assistants and others. In 1853, the oration and dinner became biennial; it is held on alternate years in rotation with the Bradshaw Lecture. It is delivered by a Fellow or Member of the college on 14 Feb, Hunter's birthday, ''"such oration to be expressive of the merits in comparative anatomy, physiology, and surgery, not only of John Hunter, but also of all persons, as should be from time to time deceased, whose labours have contributed to the improvement or extension of surgical science"''. The RCS Oration is not to be confused with the Hunterian Society Oration given at the Hunterian Society. Orators 19th century *1813 Sir Will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Birmingham Costello
William Birmingham Costello (1800–1867) was an Irish surgeon, alienist and medical author. Life Costello was born near Dublin, and was educated there. He then spent the 1820s in Paris, a student of surgery under Jean Civiale, Guillaume Dupuytren and Charles Louis Stanislas Heurteloup. In 1829 Costello set up himself in London as a surgeon, specialising in the stone and lithotrity. He wrote journal articles, and lectured in the transient Brewer Street medical school, with John Epps and Michael Ryan. Subsequently, he became medical superintendent of Wyke House Asylum, near Isleworth. In later life Costello lived in Paris, working mostly as a writer. He died there on 15 August 1867. Works Costello edited the ''Cyclopædia of Practical Surgery, including a copious bibliography''; of which 12 parts were published in London, 1841–3. Contributors included Walter Hayle Walshe, and John Gay John Gay (30 June 1685 – 4 December 1732) was an English poet and dramatist and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Armstrong Lane
Samuel Armstrong Lane FRCS (1802 – 2 August 1892) was an English surgeon, consulting surgeon to St Mary's Hospital. In 1840 while practicing in London England, Samuel Armstrong Lane, aided by consultant Dr. Blundell, performed the first successful whole Blood transfusion in an attempt to treat hemophilia. In 1843 he was elected one of the original 300 Fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons Fellowship of the Royal Colleges of Surgeons (FRCS) is a professional qualification to practise as a senior surgeon in Ireland or the United Kingdom. It is bestowed on an intercollegiate basis by the four Royal Colleges of Surgeons (the Royal ... References * http://livesonline.rcseng.ac.uk/biogs/E002474b.htm * * http://www.bloodbook.com/trans-history.html {{DEFAULTSORT:Lane, Samuel Armstrong English surgeons Transfusion medicine 1802 births 1892 deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Cooper (surgeon)
Samuel Cooper FRS (September 1780 – 2 December 1848) was an English surgeon and medical writer. He published a ''Surgical Dictionary'' which went through many editions. Biography Cooper was born in September 1780. His father, who had made a fortune in the West Indies, died when his three sons were still young. The eldest, George, became a judge of the supreme court in Madras, and was knighted. The second, Samuel, was educated by Dr. Charles Burney at Greenwich, and in 1800 entered St. Bartholomew's Hospital. In 1803 he became a Member of the Royal College of Surgeons, and settled in Golden Square. In 1806 he gained the Jacksonian prize at the College of Surgeons for the best essay on ''Diseases of the Joints''. He then began writing about surgery, for which he achieved a reputation, with his books going to several editions. His book (1840) "First Lines of Theory and Practice of Surgery" was the first formal acknowledgement of advanced melanoma as untreatable. He stated that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Newman
Francis Newman (circa 1605 – 18 November 1660) was an English colonist in America. He served as Governor of the New Haven Colony from 1658 to 1659. Early life and career Newman was born in England in 1605 and married Mary Newman Street Leete in 1630 when he was twenty-five. He emigrated to New Hampshire in 1634, but shortly thereafter moved to the Connecticut valley. Newman was prominent in the affairs of the colony at New Haven, becoming ensign in the trained band in June, 1642. He was made surveyor of roads and bridges on 21 October 1644. He rose to Deputy and Lieutenant of Artillery on 31 March 1645; interim secretary on 10 March 1646; and Deputy for Jurisdiction and Secretary on 18 October 1647. He became Magistrate on 25 May 1653. In 1653, he was one of the commissioners sent from the Connecticut River towns to Manhattan to demand reparation of Peter Stuyvesant, Governor of New Netherland, for injuries sustained by the English colonists at the hands of the Dutch. In July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Harris Barham
Richard Harris Barham (6 December 1788 – 17 June 1845) was an English cleric of the Church of England, a novelist and a humorous poet. He was known generally by his pseudonym Thomas Ingoldsby and as the author of ''The Ingoldsby Legends''. Life Richard Harris Barham was born in Canterbury. When he was seven years old his father died, leaving him a small estate, part of which was the manor of Tappington, in Denton, Kent, mentioned frequently in his later work ''The Ingoldsby Legends''. At nine he was sent to St Paul's School, but his studies were interrupted by an accident that partly crippled his arm for life. Deprived of vigorous bodily activity, he became a great reader and diligent student. During 1807 he entered Brasenose College, Oxford, intending at first to study for the law, but deciding on a clerical career instead. In 1813 he was ordained and found a country curacy. He married the next year and in 1821 he gained a minor canonry at London's St. Paul's Cathedral, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill (20 May 1806 – 7 May 1873) was an English philosopher, political economist, Member of Parliament (MP) and civil servant. One of the most influential thinkers in the history of classical liberalism, he contributed widely to social theory, political theory, and political economy. Dubbed "the most influential English-speaking philosopher of the nineteenth century", he conceived of liberty as justifying the freedom of the individual in opposition to unlimited state and social control. Mill was a proponent of utilitarianism, an ethical theory developed by his predecessor Jeremy Bentham. He contributed to the investigation of scientific methodology, though his knowledge of the topic was based on the writings of others, notably William Whewell, John Herschel, and Auguste Comte, and research carried out for Mill by Alexander Bain. He engaged in written debate with Whewell. A member of the Liberal Party and author of the early feminist work ''The Subjection o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Carlyle
Thomas Carlyle (4 December 17955 February 1881) was a Scottish essayist, historian and philosopher. A leading writer of the Victorian era, he exerted a profound influence on 19th-century art, literature and philosophy. Born in Ecclefechan, Dumfriesshire, Carlyle attended the University of Edinburgh where he excelled in mathematics, inventing the Carlyle circle. After finishing the arts course, he prepared to become a minister in the Burgher Church while working as a schoolmaster. He quit these and several other endeavours before settling on literature, writing for the ''Edinburgh Encyclopædia'' and working as a translator. He found initial success as a disseminator of German literature, then little-known to English readers, through his translations, his ''Life of'' ''Friedrich Schiller'' (1825), and his review essays for various journals. His first major work was a novel entitled ''Sartor Resartus'' (1833–34). After relocating to London, he became famous with his ''French Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Useful Knowledge Society
The Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) was founded in London in 1826, mainly at the instigation of Whig MP Henry Brougham, with the object of publishing information to people who were unable to obtain formal teaching or who preferred self-education. It was a largely Whig organisation, and published inexpensive texts intended to adapt scientific and similarly high-minded material for the rapidly-expanding reading public over twenty years until it was disbanded in 1846. Origins Henry Brougham considered that mass education was an essential prerequisite for political reform. In October 1824 he contributed an article on "scientific education of the people" to the Whig ''Edinburgh Review'', in which he argued that popular education would be greatly enhanced by the encouragement of cheap publications to complement the numerous recently founded provincial mechanics' institutes. The following year a version of this article was issued as a pamphlet entitled ''Practi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (11 May 1752 – 22 January 1840) was a German physician, naturalist, physiologist, and anthropologist. He is considered to be a main founder of zoology and anthropology as comparative, scientific disciplines. He was also important as a race theorist. He was one of the first to explore the study of the human being as an aspect of natural history. His teachings in comparative anatomy were applied to his classification of human races, of which he claimed there were five, Caucasian, Mongolian, Malayan, Ethiopian, and American. He was a member of what modern historians call the Göttingen School of History. Blumenbach's peers considered him one of the great theorists of his day, and he was a mentor or influence on many of the next generation of German biologists, including Alexander von Humboldt. Early life and education Blumenbach was born at his family house in Gotha. His father was Heinrich Blumenbach, a local school headmaster; his mother was Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Milne-Edwards
Henri Milne-Edwards (23 October 1800 – 29 July 1885) was an eminent French zoologist. Biography Henri Milne-Edwards was the 27th child of William Edwards, an English planter and colonel of the militia in Jamaica and Elisabeth Vaux, a Frenchwoman. Henri was born in Bruges, in present-day Belgium, where his parents had retired; Bruges was then a part of the newborn French Republic. His father had been jailed for several years for helping some Englishmen in their escape to their country. Henri spent most of his life in France. He was brought up in Paris by his older brother Guillaume Frederic Edwards (1777–1842), a distinguished physiologist and ethnologist. His father was released after the fall of Napoleon. The whole family then moved to Paris. At first he turned his attention to medicine, in which he graduated as an MD at Paris in 1823. His passion for natural history soon prevailed, and he gave himself up to the study of the lower forms of animal life. He became a stude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |