|
Washington Shirley, 5th Earl Ferrers
Vice Admiral Washington Shirley, 5th Earl Ferrers, FRS (26 May 1722 – 1 October 1778) was a British Royal Navy officer, peer, freemason and amateur astronomer. Biography Shirley was the second son of Hon. Laurence Shirley (himself the fourth son of Robert Shirley, 1st Earl Ferrers) and his wife, Anne. , he joined the Royal Navy and rose through the ranks as a Second Lieutenant in 1741, First Lieutenant in 1746 and Post-Captain soon after. Two weeks after the execution of his brother, Laurence Shirley, 4th Earl Ferrers in 1760, Shirley took his seat in the House of Lords (as the new Earl Ferrers). Ferrers was appointed a deputy lieutenant of Staffordshire on 28 August 1761. In 1763, George III granted him the family estates, previously forfeit by his brother as a felon (much to the surprise of Casanova, then visiting London) and he began to transform the family seat of Staunton Harold in Leicestershire. He was later promoted as a Rear Admiral in 1771 and Vice-Admiral in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to many eminent scientists throughout history, including Isaac Newton (1672), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Winston Churchill (1941), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955) and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellowship has been awarded to Stephen Hawking (1974), David Attenborough (1983), Tim Hunt (1991), Elizabeth Blackburn (1992), Tim Berners-Lee (2001), Venki Ramakrishn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Temple
HMS ''Temple'' was a 68-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 3 November 1758 at Blaydes Yard in Hull. Commissioned in January 1759 under the command of Washington Shirley, she saw service at the Battle of Quiberon Bay in November. The following year, in March 1760, she sailed for the West Indies under Captain Lucius O'Brien. With the aid of the cutter ''Griffin'', in September of that year she recaptured the sloop ''Virgin'' off Grenada. ''Temple'' operated as part of the fleet at the capture of Havana in 1762, under the command of Julian Legge. From June to September she was commanded by Chaloner Ogle Admiral of the Fleet Sir Chaloner Ogle KB (1681 – 11 April 1750) was a Royal Navy officer and politician. After serving as a junior officer during the Nine Years' War, a ship he was commanding was captured by three French ships off Ostend i ... and thereafter by Thomas Collingwood. On 18 December of that year, en route home to England, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Lieutenant
First lieutenant is a commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces; in some forces, it is an appointment. The rank of lieutenant has different meanings in different military formations, but in most forces it is sub-divided into a senior (first lieutenant) and junior (second lieutenant) rank. The NATO equivalent rank for land force officers is OF-1 rank. In navies, while certain rank insignia may carry the name lieutenant, the term may also be used to relate to a particular post or duty, rather than a rank. Indonesia In Indonesia, "first lieutenant" is known as ''Letnan Satu'' (''Lettu''), Indonesian National Armed Forces uses this rank across all three of its services. It is just above the rank of second lieutenant and just below the rank of captain. Israel In the Israel Defense Forces, the rank above second lieutenant is simply lieutenant. The rank of (קצין מקצועי אקדמאי (קמ"א (''katsín miktsoí akademai'' or "kama"), a professional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces, comparable to NATO OF-1 rank. Australia The rank of second lieutenant existed in the military forces of the Australian colonies and Australian Army until 1986. In the colonial forces, which closely followed the practices of the British military, the rank of second lieutenant began to replace ranks such as ensign and cornet from 1871. New appointments to the rank of second lieutenant ceased in the regular army in 1986. Immediately prior to this change, the rank had been effectively reserved for new graduates from the Officer Cadet School, Portsea which closed in 1985. (Graduates of the Australian Defence Force Academy (ADFA) and the Royal Military College, Duntroon (RMC-D) are commissioned as lieutenants.). The rank of second lieutenant is only appointed to officers in special appointments such as training institutions, university regiments and while under probation during training. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Shirley, 1st Earl Ferrers
Robert Shirley, 1st Earl Ferrers PC (20 October 1650 – 25 December 1717)—known as Sir Robert Shirley, 7th Baronet, from 1669 to 1677 and Robert Shirley, 14th Baron Ferrers of Chartley, from 1677 to 1711—was an English peer and courtier. Shirley was born at East Sheen, the third son of Sir Robert Shirley, 4th Baronet and his wife Catherine Okeover. He was educated at Christ Church, Oxford. In March 1669, he inherited his baronetcy from his infant nephew, and received an M.A. from Oxford in 1669. Shirley was suggested as a candidate for Lichfield in 1677 by Thomas Thynne, husband of his second cousin Frances, but he preferred to accept a seat in the House of Lords, the barony of Ferrers of Chartley being called out of abeyance for him in December. He was also appointed a deputy lieutenant of Staffordshire shortly thereafter. In 1683, he was appointed high steward of Stafford, replacing the Duke of Monmouth. On 18 February 1684, Lord Ferrers was appointed Master of the Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honourable
''The Honourable'' (British English) or ''The Honorable'' (American English; see spelling differences) (abbreviation: ''Hon.'', ''Hon'ble'', or variations) is an honorific style that is used as a prefix before the names or titles of certain people, usually with official governmental or diplomatic positions. Use by governments International diplomacy In international diplomatic relations, representatives of foreign states are often styled as ''The Honourable''. Deputy chiefs of mission, , consuls-general and consuls are always given the style. All heads of consular posts, whether they are honorary or career postholders, are accorded the style according to the State Department of the United States. However, the style ''Excellency'' instead of ''The Honourable'' is used for ambassadors and high commissioners. Africa The Congo In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the prefix 'Honourable' or 'Hon.' is used for members of both chambers of the Parliament of the Democratic R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either observational (by analyzing the data) or theoretical astronomy. Examples of topics or fields astronomers study include planetary science, solar astronomy, the origin or evolution of stars, or the formation of galaxies. A related but distinct subject is physical cosmology, which studies the Universe as a whole. Types Astronomers usually fall under either of two main types: observational and theoretical. Observational astronomers make direct observations of celestial objects and analyze the data. In contrast, theoretical astronomers create and investigate models of things that cannot be observed. Because it takes millions to billions of years for a system of stars or a galaxy to complete a life cycle, astronomers must observe sna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freemasonry
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups: * Regular Freemasonry insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member profess belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics be banned. * Continental Freemasonry consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions. The basic, local organisational unit of Freemasonry is the Lodge. These private Lodges are usually supervised at the regional level (usually coterminous with a state, province, or national border) by a Grand Lodge or Grand Orient. There is no international, worldwide Grand Lodge that supervises all of Freemasonry; each Grand Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peerage
A peerage is a legal system historically comprising various hereditary titles (and sometimes non-hereditary titles) in a number of countries, and composed of assorted noble ranks. Peerages include: Australia * Australian peers Belgium * Belgian nobility Canada * British peerage titles granted to Canadian subjects of the Crown * Canadian nobility in the aristocracy of France China * Chinese nobility France * Peerage of France * List of French peerages * Peerage of Jerusalem Japan * Peerage of the Empire of Japan * House of Peers (Japan) Portugal * Chamber of Most Worthy Peers Spain * Chamber of Peers (Spain) * List of dukes in the peerage of Spain * List of viscounts in the peerage of Spain * List of barons in the peerage of Spain * List of lords in the peerage of Spain United Kingdom Great Britain and Ireland * Peerages in the United Kingdom ** Hereditary peer, holders of titles which can be inherited by an heir ** Life peer, members of the peerage of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, education and public engagement and fostering international and global co-operation. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by King Charles II as The Royal Society and is the oldest continuously existing scientific academy in the world. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the Society's President, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. The members of Council and the President are elected from and by its Fellows, the basic members of the society, who are themselves elected by existing Fellows. , there are about 1,700 fellows, allowed to use the postnominal title FRS (Fellow of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
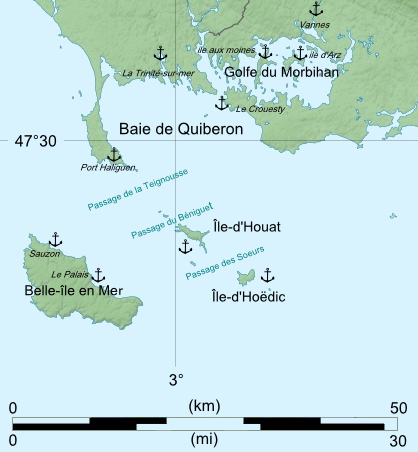
Battle Of Quiberon Bay
The Battle of Quiberon Bay (known as ''Bataille des Cardinaux'' in French) was a decisive naval engagement during the Seven Years' War. It was fought on 20 November 1759 between the Royal Navy and the French Navy in Quiberon Bay, off the coast of France near St. Nazaire. The battle was the culmination of British efforts to eliminate French naval superiority, which could have given the French the ability to carry out their planned invasion of Great Britain. A British fleet of 24 ships of the line under Sir Edward Hawke tracked down and engaged a French fleet of 21 ships of the line under Marshal de Conflans. After hard fighting, the British fleet sank or ran aground six French ships, captured one and scattered the rest, giving the Royal Navy one of its greatest victories, and ending the threat of French invasion for good. The battle signalled the rise of the Royal Navy in becoming the world's foremost naval power, and, for the British, was part of the Annus Mirabilis of 1759 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |