|
Waltham Cross Railway Station
Waltham Cross railway station is on the West Anglia Main Line, serving the suburban town of Waltham Cross in Hertfordshire, and the neighbouring Waltham Abbey in Essex, England. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street and is situated between and . Its three-letter station code is WLC and it is in Travelcard zone 7. The station and all trains serving it are operated by Greater Anglia. The station has 4 Oyster card readers rather than ticket barriers. During the 2012 Olympic Games, Waltham Cross and Cheshunt provided the main rail access to the Lee Valley White Water Centre. History Early years (1840-1862) The first station, together with the railway line from Stratford to Broxbourne, was opened by the Northern & Eastern Railway (N&ER) on 15 September 1840. Originally called Waltham and later renamed to Waltham Cross, it was originally on a site to the north of the road between Waltham Cross and Waltham Abbey. Following on from negotiations in 1843, the Eastern Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Anglia (train Operating Company)
Greater Anglia (legal name Abellio East Anglia Limited) is a train operating company in Great Britain owned as a joint venture by Abellio, the international arm of the state-owned Dutch national rail operator Nederlandse Spoorwegen, and the Japanese trading company Mitsui & Co. It operates the East Anglia franchise, providing the commuter and intercity services from its Central London terminus at London Liverpool Street to Essex, Suffolk, Norfolk and parts of Hertfordshire and Cambridgeshire as well as many regional services throughout the East of England. Abellio began operating the franchise, then known as the Greater Anglia franchise, in February 2012. Initially, it traded under the same name until it rebranded as Abellio Greater Anglia in December 2013. Shortly after taking over operations, the company initiated a series of projects to improve service levels, including the procurement of new trains and the launch of the 'Norwich in 90' programme to reduce travel times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Counties Railway
The Eastern Counties Railway (ECR) was an English railway company incorporated in 1836 intended to link London with Ipswich via Colchester, and then extend to Norwich and Yarmouth. Construction began in 1837 on the first nine miles at the London end. Construction was beset by engineering and other problems, leading to severe financial difficulties. As a result, the project was truncated at Colchester in 1843 but through a series of acquisitions (including the Eastern Union Railway who completed the link between Colchester and Norwich) and opening of other lines, the ECR became the largest of the East Anglian railways. In 1862 ECR was merged with a number of other companies to form the Great Eastern Railway. Opening In 1835 a surveyor called Henry Sayer presented a plan for a new railway from London to York via Cambridge to London solicitors Dimes & Boyman. Together with John Clinton Robertson who was to become the first secretary of the ECR and engineers John Braithwaite it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Anglia Franchise Railway Stations
Greater may refer to: *Greatness, the state of being great *Greater than, in inequality * ''Greater'' (film), a 2016 American film *Greater (flamingo), the oldest flamingo on record * "Greater" (song), by MercyMe, 2014 *Greater Bank, an Australian bank *Greater Media Greater Media, Inc., known as Greater Media, was an American media company that specialized in radio stations. The markets where they owned radio stations included Boston, Detroit, Philadelphia, Charlotte, and the state of New Jersey. The compa ..., an American media company See also * * {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Great Eastern Railway Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Hertfordshire
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lea Valley Lines
The Lea Valley lines are two commuter lines and two branches in north-east London, so named because they run along the Lower Lea Valley of the River Lea. They were part of the Great Eastern Railway, now part of the ''Anglia Route'' of Network Rail. On 31 May 2015, services between London Liverpool Street to Chingford, Cheshunt and Enfield Town were transferred to London Overground; services from London Liverpool Street and Stratford via Tottenham Hale to Hertford East and Bishops Stortford remain with Greater Anglia. History The first section was opened by the Eastern Counties Railway (ECR) on 20 June 1839 from the London end at Devonshire Street to Romford, extended on 1 July 1840 to Bishopsgate (London end) and Brentwood. The Northern and Eastern Railway (N&ER) opened its first section from that line at Stratford to Broxbourne on 15 September 1840, and to Harlow in 1841; though it remained a separate entity, its line was leased to the ECR from 1 January 1844. A branch f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishops Stortford Railway Station
Bishop's Stortford railway station is on the West Anglia Main Line serving the town of Bishop's Stortford in Hertfordshire, England. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street and is situated between and stations. Its three-letter station code is BIS. The station and all trains serving it are operated by Greater Anglia, including the half-hourly Stansted Express service. History The station was opened by the Northern and Eastern Railway as a temporary terminus on 16 May 1842, and became a through station on 30 July 1845 when the line was extended through to Norwich. In 1843 the train from London to Bishop's Stortford was timetabled to run at , exclusive of stops - the fastest booked run on any English railway at the time. The station site included a large goods yard occupying the land now used for car parking as well as sidings running as far west as the riverside wharves of the Stort Navigation. To the east, a small turntable and engine sheds lay on land recently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
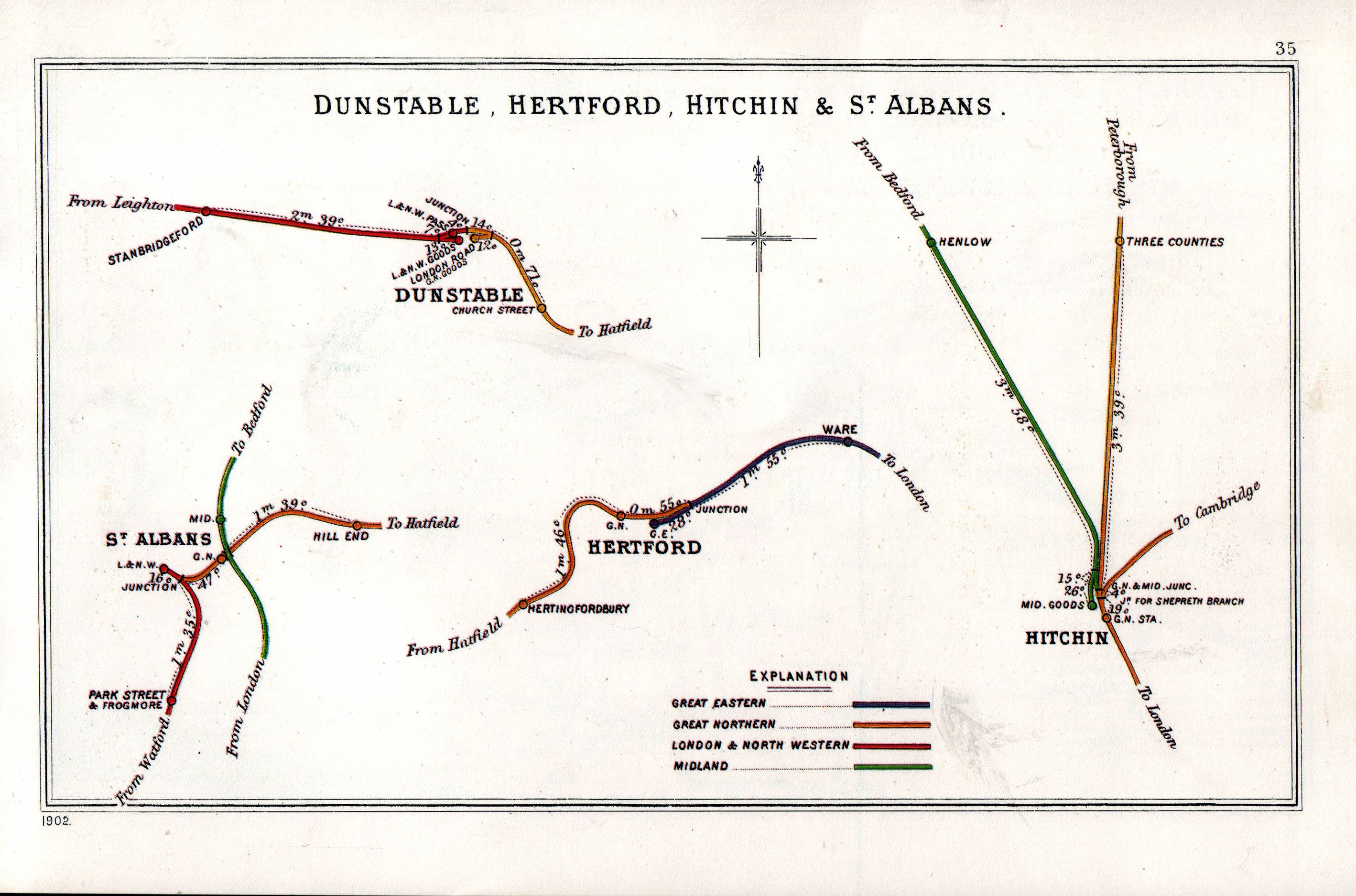
Hertford East Railway Station
Hertford East railway station is the northern terminus of the Hertford East branch line off the West Anglia Main Line in the east of England, and is located in the town of Hertford in Hertfordshire. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street and is one of two stations in the town, the other being on the Hertford Loop Line. Its three-letter station code is HFE. The station and all trains calling are operated by Greater Anglia. There are two platforms, although platform number one is generally only used during peak times, during times of disruption and primarily for trains to and from Stratford station. History The first station opened on 31st October 1843 sited to the east of the present station. The current station, designed by W. N. Ashbee, was opened by the Great Eastern Railway on 27 February 1888, replacing the first station. The station was listed in 1974 as a Grade II* listed building; in 1996 the buffer stop lights on platform 1 were separately listed in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tottenham Hale Station
Tottenham Hale is a National Rail and London Underground interchange station located in Tottenham Hale in north London, England. On the National Rail network it is on the West Anglia Main Line, from London Liverpool Street, and is served by Greater Anglia and Stansted Express. On the Underground it is on the Victoria line between and . The station is in Travelcard Zone 3. The station was opened in 1840, with Underground services added in 1968. A new station building is under construction, and an additional platform is being added as part of a regeneration scheme. History 19th century Locations served by Tottenham Hale trains in previous years included London St Pancras (via the Tottenham and Hampstead Joint Railway), North Woolwich via the low level platforms at (after the Palace Gates Line service was cut back) and York (via Cambridge and the Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Railway). Until recently, the next station served to the south on the line to was , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oyster Card
The Oyster card is a payment method for public transport in London (and certain areas around it) in England, United Kingdom. A standard Oyster card is a blue credit-card-sized stored-value contactless smart card. It is promoted by Transport for London (TfL) and can be used on travel modes across London including London Buses, London Underground, the Docklands Light Railway (DLR), London Overground, Tramlink, some river boat services, and most National Rail services within the London fare zones. Since its introduction in June 2003, more than 86 million cards have been used. Oyster cards can hold period tickets; travel permits and; most commonly, credit for travel ("Pay as you go"), which must be added to the card before travel. Passengers touch it on an electronic reader when entering and leaving the transport system in order to validate it and deduct funds from the stored credit. Cards may be "topped-up" by continuous payment authority, by online purchase, at credit card ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waltham Cross Railway Station
Waltham Cross railway station is on the West Anglia Main Line, serving the suburban town of Waltham Cross in Hertfordshire, and the neighbouring Waltham Abbey in Essex, England. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street and is situated between and . Its three-letter station code is WLC and it is in Travelcard zone 7. The station and all trains serving it are operated by Greater Anglia. The station has 4 Oyster card readers rather than ticket barriers. During the 2012 Olympic Games, Waltham Cross and Cheshunt provided the main rail access to the Lee Valley White Water Centre. History Early years (1840-1862) The first station, together with the railway line from Stratford to Broxbourne, was opened by the Northern & Eastern Railway (N&ER) on 15 September 1840. Originally called Waltham and later renamed to Waltham Cross, it was originally on a site to the north of the road between Waltham Cross and Waltham Abbey. Following on from negotiations in 1843, the Eastern Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 125
The British Rail Class 125 was a design of three car Diesel Multiple Unit built by BR Derby at Derby Works in 1958. They were almost identical in appearance to the Class 116. History The Class 125 was built in 1958 at Derby Works as high capacity suburban railcars specifically for the Lea Valley Lines near Stratford. They were fitted with powerful Rolls-Royce engines, allowing them to have comparable performance to contemporary EMUs.They bore a close resemblance to the similar class 116, which were also built by British Rail at Derby. The Class 125 had a unique multiple working code (orange star), due to their unique pneumatic, rather than electric, engine control system. They also had a non-standard jumper cable arrangement and were therefore incompatible with other British Rail diesel multiple unit classes. They were withdrawn in 1977 and like many other first generation DMUs, never wore their Class 125 TOPS classifications. Operational history The class 125 entered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_p13_-_Our_Starting_Train.jpg)