|
Wallia
Wallia or Walha (Spanish: ''Walia'', Portuguese ''Vália''), ( 385 – 418) was king of the Visigoths from 415 to 418, earning a reputation as a great warrior and prudent ruler. He was elected to the throne after Athaulf and then Sigeric were assassinated in 415. Biography Early on, Wallia made peace with Emperor Honorius and accepted a treaty with the Roman Empire. He also returned Honorius' sister Galla Placidia to him. As gains from these arrangements, Wallia was granted Aquitaine in 417 as a region where the Visigoths would be based as official allies or ''foederati''. He established his court in Toulouse, which became the Visigothic capital for the rest of the fifth century. In 418 he honored the alliance by invading Hispania, where his army destroyed the Siling Vandals and so reduced the numbers of Alans living there that the survivors placed themselves under the rule of Gunderic, king of the Asding Vandals. Some historical sources say that he was related to Alaric only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alejo Vera
Alejo Vera y Estaca (14 July 1834, Viñuelas – 4 February 1923, Madrid) was a Spanish painter in the Romantic style who specialized in history painting. Biography At an early age, his teachers in the public school noticed that he had an aptitude for drawing, so they got together to request a study grant from the government of Guadalajara Province. It was given, and he began his studies at the Escuela de Bellas Artes de San Fernando in Madrid. Later, he obtained a position in the workshop of Federico de Madrazo Federico de Madrazo y Kuntz (9 February 181510 June 1894) was a Spanish painter. Biography Born in Rome, he was the son of José de Madrazo y Agudo, the painter and former Director of the Prado Museum. Federico's grandfather on his mother side .... With the help of a local banker, he went to Italy, where he became fascinated by the ruins of Pompeii; an influence that can be readily perceived in his later works. One of his first major works there was the "E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divided into two new provinces, Baetica and Lusitania, while Hispania Citerior was renamed Hispania Tarraconensis. Subsequently, the western part of Tarraconensis was split off, first as Hispania Nova, later renamed "Callaecia" (or Gallaecia, whence modern Galicia). From Diocletian's Tetrarchy (AD 284) onwards, the south of the remainder of Tarraconensis was again split off as Carthaginensis, and all of the mainland Hispanic provinces, along with the Balearic Islands and the North African province of Mauretania Tingitana, were later grouped into a civil diocese headed by a ''vicarius''. The name Hispania was also used in the period of Visigothic rule. The mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Warriors
Gothic or Gothics may refer to: People and languages *Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes **Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths **Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken by the Crimean Goths, also extinct ** Gothic alphabet, one of the alphabets used to write the Gothic language **Gothic (Unicode block), a collection of Unicode characters of the Gothic alphabet Art and architecture *Gothic art, a Medieval art movement *Gothic architecture *Gothic Revival architecture (Neo-Gothic) **Carpenter Gothic ** Collegiate Gothic **High Victorian Gothic Romanticism *Gothic fiction or Gothic Romanticism, a literary genre Entertainment * ''Gothic'' (film), a 1986 film by Ken Russell * ''Gothic'' (series), a video game series originally developed by Piranha Bytes Game Studios ** ''Gothic'' (video game), a 2001 video game developed by Piranha Bytes Game Studios Modern culture and lifestyle * Goth subculture, a music-cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balt Dynasty
The Balts or Baltic peoples ( lt, baltai, lv, balti) are an ethno-linguistic group of peoples who speak the Baltic languages of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. One of the features of Baltic languages is the number of conservative or archaic features retained. Among the Baltic peoples are modern-day Lithuanians and Latvians (including Latgalians) — all Eastern Balts — as well as the Old Prussians, Yotvingians and Galindians — the Western Balts — whose languages and cultures are now extinct. Etymology Medieval German chronicler Adam of Bremen in the latter part of the 11th century AD was the first writer to use the term "Baltic" in reference to the sea of that name.Bojtár page 9. Before him various ancient places names, such as Balcia, were used in reference to a supposed island in the Baltic Sea. Adam, a speaker of German, connected ''Balt-'' with ''belt'', a word with which he was familiar. In Germanic languages there was some form of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
418 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 418 ( CDXVIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Honorius and Theodosius (or, less frequently, year 1171 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 418 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Honorius bribes Wallia, king of the Visigoths, into regaining Hispania for the Roman Empire. His victory over the Vandals in 416 forces them to retire to Andalusia. The Visigothic territory in Gaul now extends from the Garonne to the Loire, and becomes known as the Visigothic Kingdom. * Theodoric I becomes king of the Visigoths. He completes the settlements in Gallia Aquitania and expands his military power to the south. By topic Religion * December 28 – Pope Boniface I succeeds Zosimus as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Of Aquitaine
Walter or Walther of Aquitaine is a king of the Visigoths in Germanic heroic legend. Epic poetry Walter figures in several epic poems and narratives dealing with Germanic heroic legend in medieval languages: * ''Waldere'', a fragment of an Old English epic of which just over sixty lines survive. * ''Waltharius'', a 10th-century Latin epic written by the monk Ekkehard I of St Gall. * ''Chronicon Novaliciense'' ("Chronicle of Novalesa"), a Latin prose chronicle composed ''c.''1060, at Novalesa Abbey: Abbazia de Novalesa website Waltarius figures in chapters 7-13. * '''', a |
Burgundians
The Burgundians ( la, Burgundes, Burgundiōnes, Burgundī; on, Burgundar; ang, Burgendas; grc-gre, Βούργουνδοι) were an early Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared in the middle Rhine region, near the Roman Empire, and were later moved into the empire, in the western Alps and eastern Gaul. They were possibly mentioned much earlier in the time of the Roman Empire as living in part of the region of Germania that is now part of Poland. The Burgundians are first mentioned together with the Alamanni as early as the 11th panegyric to emperor Maximian given in Trier in 291, and referring to events that must have happened between 248 and 291, and they apparently remained neighbours for centuries. By 411 a Burgundian group had established themselves on the Rhine, between Franks and Alamanni, holding the cities of Worms, Speyer, and Strasbourg. In 436, Aëtius defeated the Burgundians on the Rhine with the help of Hunnish forces, and then in 443, he re-settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gundioc
Gondioc (died 473), also called ''Gunderic'' and ''Gundowech'', was a King of the Burgundians, succeeding his putative father Gunther in 436. In 406, the Burgundians under King Gundahar (Gundihar, Guntiar) at Mainz had crossed the Rhine and then settled with the permission of the Roman emperor Honorius on the Rhine. Gundahar's violent attempts to expand his empire to the west brought the Burgundians into conflict with the Romans 30 years later. In 435, a Burgundian army was defeated by Hunnic auxiliary troops under the Roman Aetius and finally destroyed. The Burgundian capital Worms was destroyed by the Huns. Most of the surviving Burgundians joined the Romans as auxiliary troops under their new King Gondioc. Aetius settled them in 443 as ' 'foederati' ' in western Switzerland and the Sapaudia (today's Savoy) as a buffer against the growing strength of the Alamanni. This settlement was the beginning of a Burgundian kingdom, with its capital at Geneva. In 451, Gondioc join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ricimer
Flavius Ricimer ( , ; – 18/19 August 472) was a Romanized Germanic general who effectively ruled the remaining territory of the Western Roman Empire from 461 until his death in 472, with a brief interlude in which he contested power with Anthemius. Deriving his power from his position as ''magister militum'' of the Western Empire, Ricimer exercised political control through a series of puppet emperors. Ricimer's military office and his dominance over the empire led some historians to conclude that he was a link between previous ''magistri militum'', such as the Vandal Flavius Stilicho, and the dux of Italy, Flavius Odoacer. Lineage The date of Ricimer's birth is unknown. Some scholars have dated it as late as the early 430s, which would have made him unusually young when he rose to power. A birthdate of around 418 is more likely. The names of his parents are also unknown. In his panegyric to Anthemius, given in 468, the poet Sidonius Apollinaris claimed that Ricimer was S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suevi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names such as the Marcomanni, Quadi, Hermunduri, Semnones, and Lombards. New groupings formed later, such as the Alamanni and Bavarians, and two kingdoms in the Migration Period were simply referred to as Suebian. Although Tacitus specified that the Suebian group was not an old tribal group itself, the Suebian peoples are associated by Pliny the Elder with the Irminones, a grouping of Germanic peoples who claimed ancestral connections. Tacitus mentions Suebian languages, and a geographical "Suevia". The Suevians were first mentioned by Julius Caesar in connection with the invasion of Gaul by the Germanic king Ariovistus during the Gallic Wars. Unlike Tacitus he described them as a single people, distinct from the Marcomanni, within the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
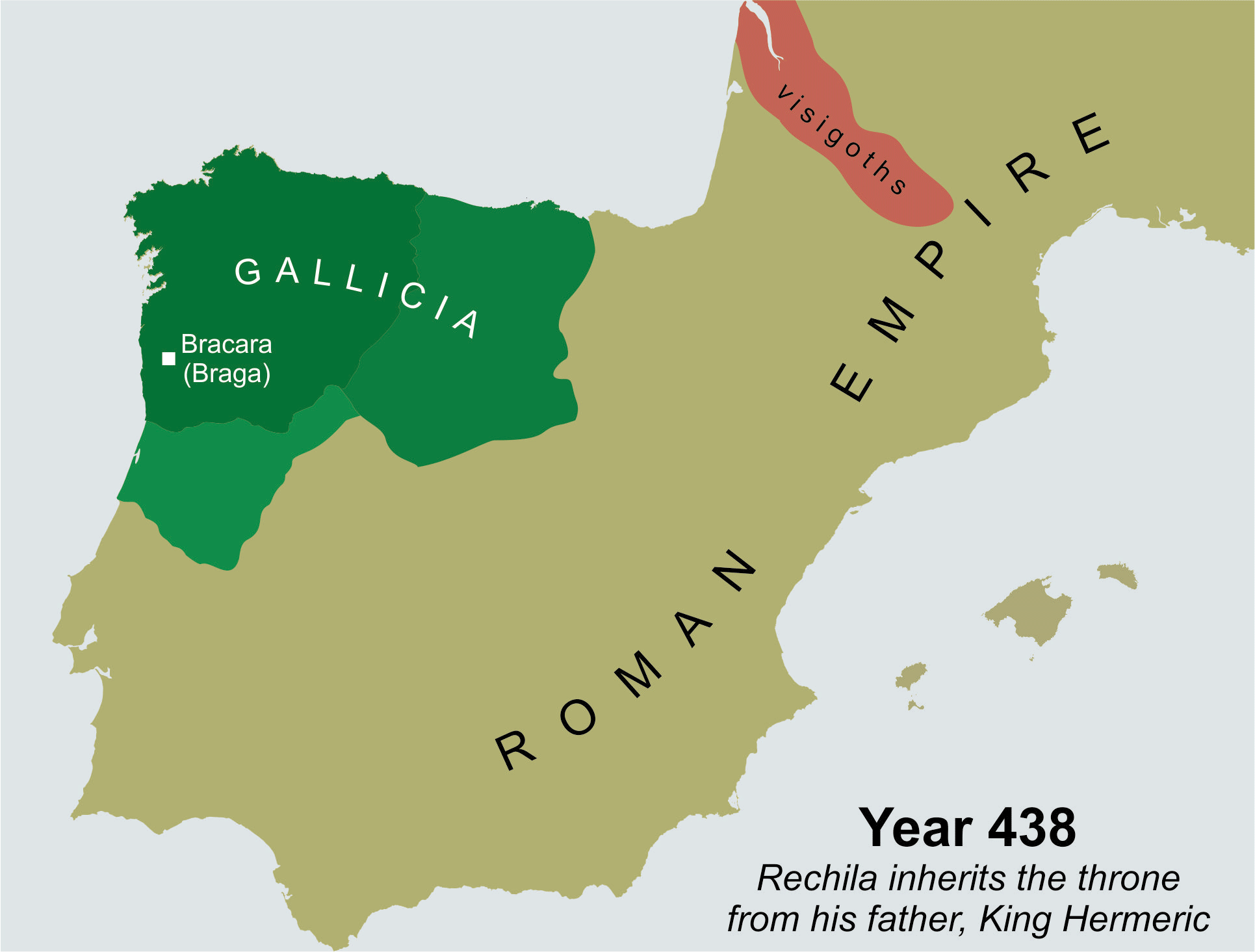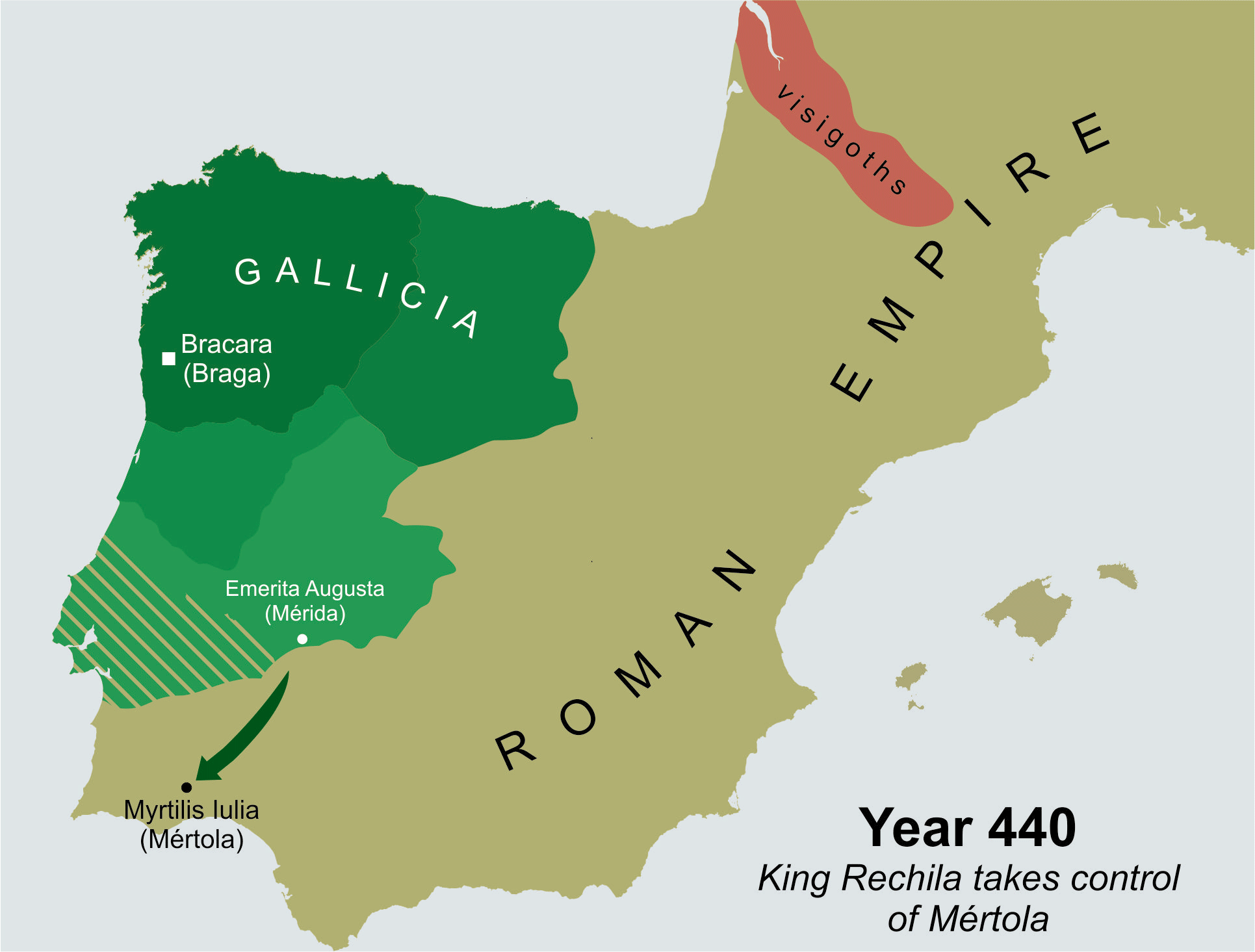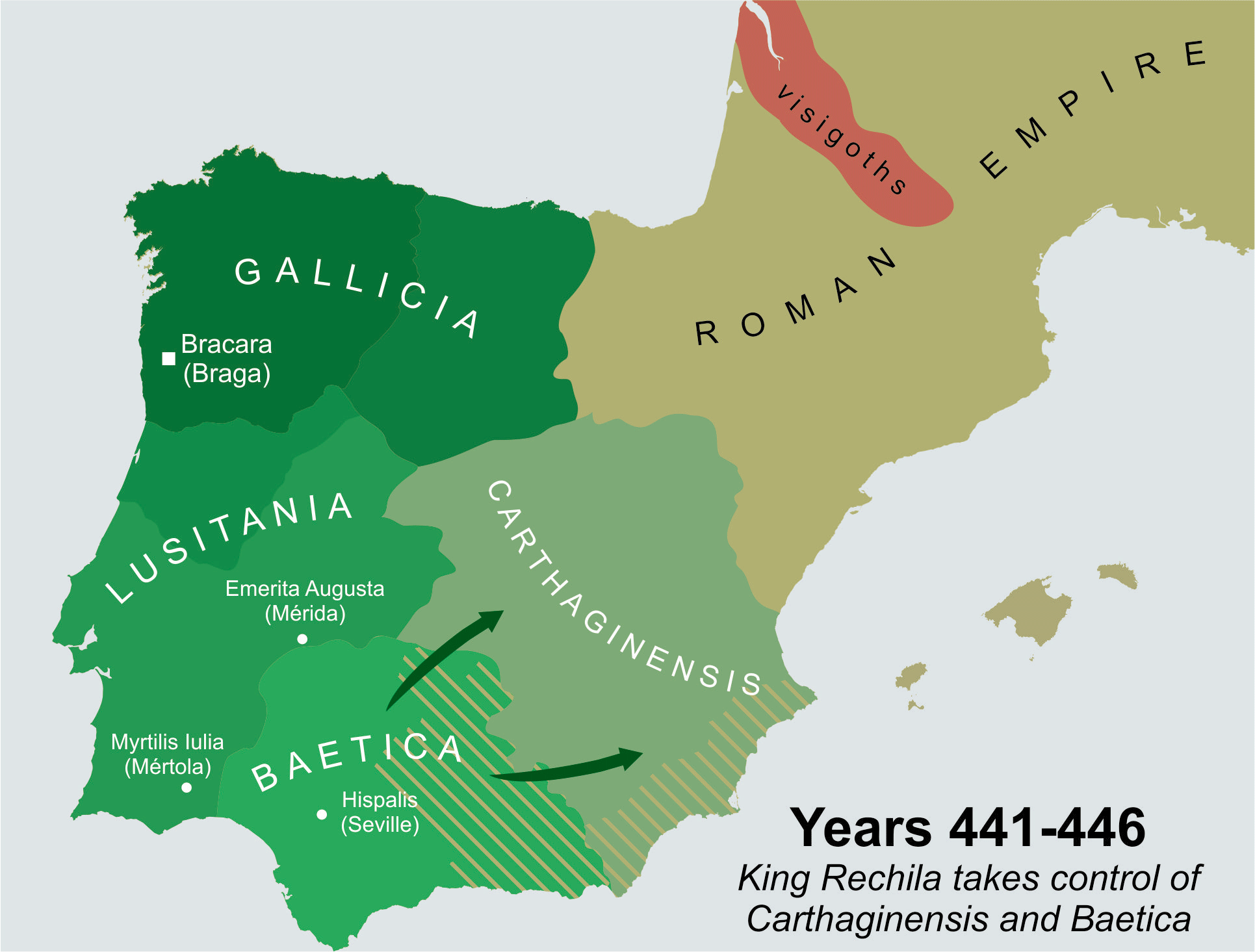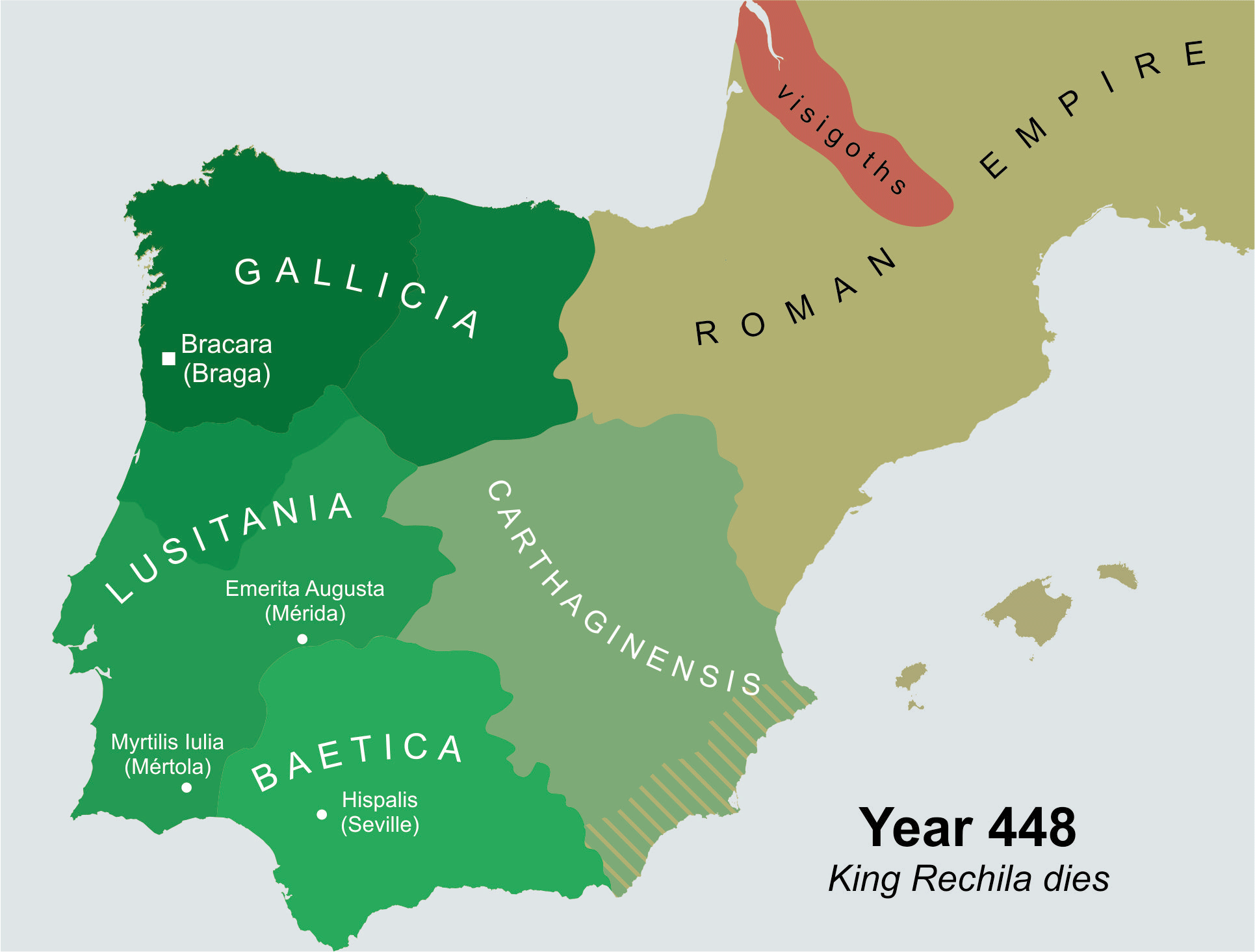
Rechila
Rechila (died 448) was the Suevic king of Galicia from 438 until his death. There are few primary sources for his life, but Hydatius was a contemporary Christian (non- Arian) chronicler in Galicia. When his father, Hermeric, turned ill in 438, he retired from active political life (dying in 441) and handed the reins of government and the royal title over to his son. He endeavoured to expand the Suevic kingdom to fill the vacuum left by the retiring Vandals and Alans. In 438 he defeated Andevotus, the '' comes Hispaniarum'', on the river Genil (Singillio). The Roman position in Iberia became so tenuous that three ''magistri utriusque militiae'' (masters of both services) were sent to the peninsula between 441 and 446. Invading southern Iberia, Rechila took the provincial capitals of Mérida in 439 and Seville in 441. These conquests were extremely significant, but nothing of the sequence of events leading to them is known. The provinces of Lusitania, Baetica, and Carthaginiens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaric I
Alaric I (; got, 𐌰𐌻𐌰𐍂𐌴𐌹𐌺𐍃, , "ruler of all"; c. 370 – 410 AD) was the first king of the Visigoths, from 395 to 410. He rose to leadership of the Goths who came to occupy Moesia—territory acquired a couple of decades earlier by a combined force of Goths and Alans after the Battle of Adrianople. Alaric began his career under the Gothic soldier Gainas and later joined the Roman army. Once an ally of Rome under the Roman emperor Theodosius, Alaric helped defeat the Franks and other allies of a would-be Roman usurper. Despite losing many thousands of his men, he received little recognition from Rome and left the Roman army disappointed. After the death of Theodosius and the disintegration of the Roman armies in 395, he is described as king of the Visigoths. As the leader of the only effective field force remaining in the Balkans, he sought Roman legitimacy, never quite achieving a position acceptable to himself or to the Roman authorities. He operated m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_02.jpg)