|
Württemberg Ts 4
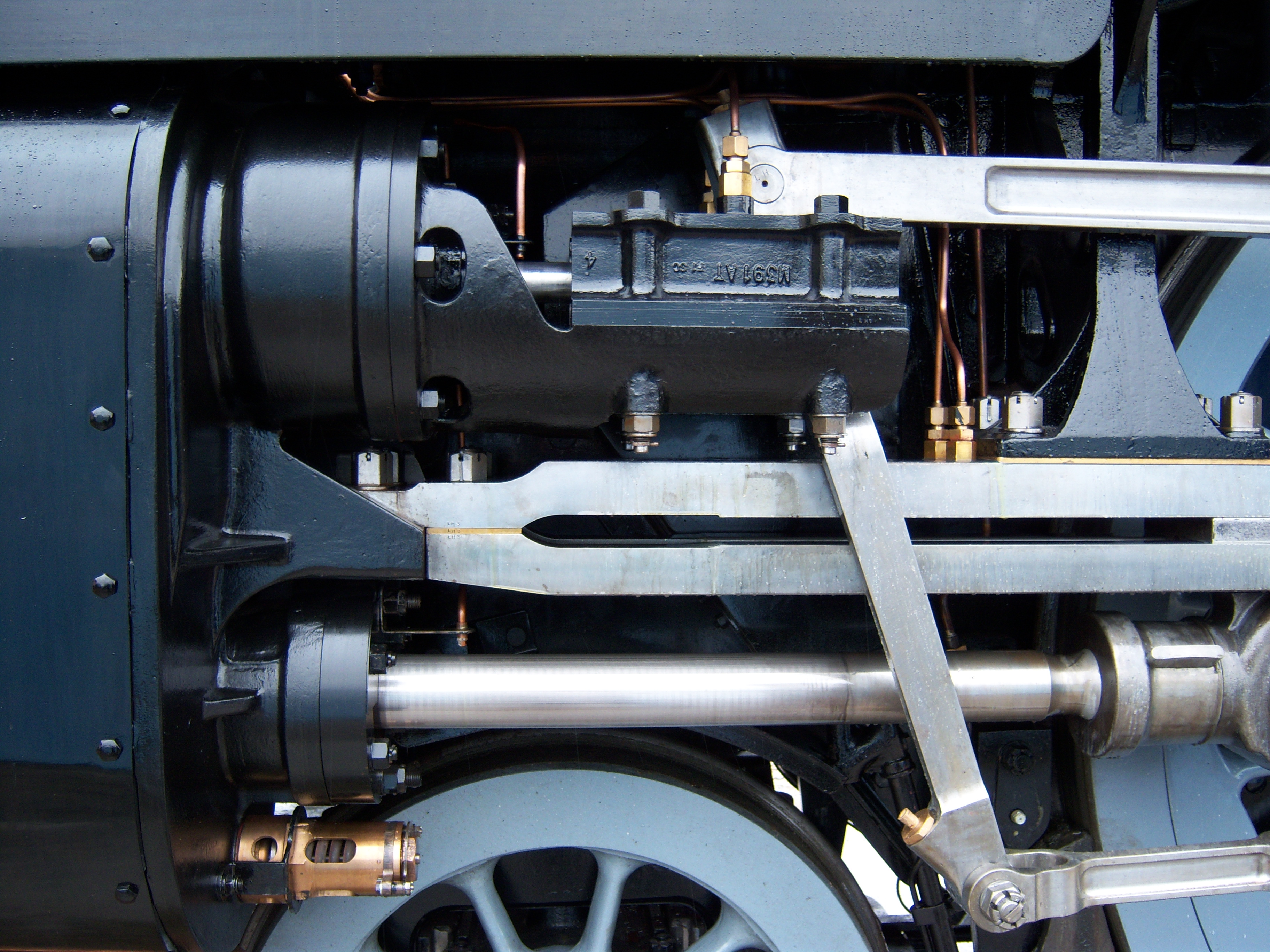
The DRG Class 99.17, formerly the Württemberg Ts 4 of the Royal Württemberg State Railways were German narrow gauge steam locomotives bought for working the 15.11 kilometre long route between the towns of Altensteig and Nagold. The three tank locomotives had an outer frame and a ''Klose'' drive. The first and third axles were steered by the third, radially-sliding axle by means of a system of levers. The second axle was driven by the inside cylinder and had no wheel flanges. Overall the system was very reliable, but nevertheless also very maintenance-intensive. The engines were delivered in 1891, 1892 and 1899, and later all taken over by the Reichsbahn. There they were given numbers 99 171–99 173. They also had the names ''Altensteig, Berneck'' and ''Ebhausen'' See also *Royal Württemberg State Railways *List of Württemberg locomotives and railbuses This list covers the locomotives and railbuses operated by the Royal Württemberg State Railways (''Königlich Württembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maschinenfabrik Esslingen
Maschinenfabrik Esslingen (ME) was a German engineering firm that manufactured locomotives, tramways, railway wagons, roll-blocks, technical equipment for the railways, (turntable (rail), turntables and traverser (railway), traversers), bridges, steel structures, pumps and boilers. Founding It was founded by Emil Kessler on 11 March 1846 in Stuttgart, as a result of an initiative of the Kingdom of Württemberg to create a railway industry that was not dependent on foreign manufacturers. Emil Kessler brought vital experience from his time with the Maschinenbau-Gesellschaft Karlsruhe, engineering works in Karlsruhe, where he had been a member of the board since 1837 and the sole director since 1842. The foundation stone of the new factory was laid at Esslingen am Neckar on 4 May 1846. One year later, in October 1847, the first locomotive ordered by the Royal Württemberg State Railways (''Königlich Württembergische Staats-Eisenbahnen'') or ''K.W.St. E.'' was delivered. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsbahn
The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' (), also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the German national railway system created after the end of World War I from the regional railways of the individual states of the German Empire. The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' has been described as "the largest enterprise in the capitalist world in the years between 1920 and 1932"; nevertheless, its importance "arises primarily from the fact that the Reichsbahn was at the center of events in a period of great turmoil in German history". Overview The company was founded on 1 April 1920 as the ("German Imperial Railways") when the Weimar Republic, which still used the nation-state term of the previous monarchy, (German Reich, hence the usage of the in the name of the railway; the monarchical term was ), took national control of the German railways, which had previously been run by the German states ('' Länderbahnen''). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1891
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and freight transport globally, thanks to its energy efficiency and potentially high speed.Rolling stock on rails generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, allowing rail cars to be coupled into longer trains. Power is usually provided by diesel or electric locomotives. While railway transport is capital-intensive and less flexible than road transport, it can carry heavy loads of passengers and cargo with greater energy efficiency and safety. Precursors of railways driven by human or animal power have existed since antiquity, but modern rail transport began with the invention of the steam locomotive in the United Kingdom at the beginning of the 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esslingen Locomotives
Esslingen may refer to: Places * Esslingen (district), a district (''Landkreis'') of Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany * Esslingen am Neckar, capital city of the district of Esslingen * Esslingen, Switzerland, a village in Switzerland * Eßlingen, a municipality in western Germany Other * Maschinenfabrik Esslingen Maschinenfabrik Esslingen (ME) was a German engineering firm that manufactured locomotives, tramways, railway wagons, roll-blocks, technical equipment for the railways, (turntable (rail), turntables and traverser (railway), traversers), bridges, s ..., a former locomotive manufacturing company based in Esslingen am Neckar See also * Esslinger (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotives Of Württemberg
A locomotive is a rail vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, push–pull operation has become common, and in the pursuit for longer and heavier freight trains, companies are increasingly using distributed power: single or multiple locomotives placed at the front and rear and at intermediate points throughout the train under the control of the leading locomotive. Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin 'from a place', ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing motion', and is a shortened form of the term ''locomotive engine'', which was first used in 1814 to distinguish between self-propelled and stationary steam engines. Classifications Prior to locomotives, the motive force for railways had been generated by various lower-technology methods such as human power, horse power, gravity or stationary engines that drove cable systems. Few such systems are still i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre-gauge Steam Locomotives
Metre-gauge railways ( US: meter-gauge railways) are narrow-gauge railways with track gauge of or 1 metre. Metre gauge is used in around of tracks around the world. It was used by several European colonial powers including France, Britain and Germany in their colonies. In Europe, large metre-gauge networks remain in use in Switzerland, Spain and many European towns with urban trams, but most metre-gauge local railways in France, Germany and Belgium closed down in the mid-20th century, although some still remain. With the revival of urban rail transport, metre-gauge light metros were built in some cities. The slightly-wider gauge is used in Sofia, Bulgaria. Another similar gauge is . __TOC__ Examples of metre-gauge See also * Italian metre gauge * Narrow-gauge railways A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge (distance between the rails) narrower than . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and . Since narrow-gaug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrow-gauge Steam Locomotives Of Germany
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge (distance between the rails) narrower than . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and . Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structure gauges, and lighter rails; they can be less costly to build, equip, and operate than standard- or broad-gauge railways (particularly in mountainous or difficult terrain). Lower-cost narrow-gauge railways are often used in mountainous terrain, where engineering savings can be substantial. Lower-cost narrow-gauge railways are often built to serve industries as well as sparsely populated communities where the traffic potential would not justify the cost of a standard- or broad-gauge line. Narrow-gauge railways have specialised use in mines and other environments where a small structure gauge necessitates a small loading gauge. In some countries, narrow gauge is the standard: Japan, Indonesia, Taiwan, New Zealand, South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Württemberg Locomotives And Railbuses
This list covers the locomotives and railbuses operated by the Royal Württemberg State Railways (''Königlich Württembergische Staats-Eisenbahnen''), the national railway company of Württemberg, a state in southwest Germany that was part of the German Empire. In 1920 the Royal Württemberg State Railways, along with the other German state railways (Länderbahnen), were merged into the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft, Deutsche Reichsbahn. Locomotive classification The Württemberg state railway first divided its locomotives into classes in 1845. This first categorisation into classes I to VII was based on the order in which individual vehicles were procured. The scheme proved to be unworkable in practice, so in 1858 a new system was introduced as follows: * A - Light express train, express and fast-stopping train locomotives * B - Heavy express and fast-stopping train locomotives * C - Light passenger train locomotives * D - Heavy passenger train locomotives * E - Light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (locomotive)
The cylinder is the power-producing element of the steam engine powering a steam locomotive. The cylinder (engine), cylinder is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were initially cast iron, but later made of steel. The cylinder casting includes other features such as (in the case of Stephenson's Rocket) valve ports and mounting feet. The last big American locomotives incorporated the cylinders as part of huge one-piece steel castings that were the Locomotive frame, main frame of the locomotive. Renewable wearing surfaces were needed inside the cylinders and provided by cast-iron bushings. The way the valve controlled the steam entering and leaving the cylinder was known as steam distribution and shown by the shape of the indicator diagram. What happened to the steam inside the cylinder was assessed separately from what happened in the boiler and how much friction the moving machinery had to cope wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klose Locomotive
Klose is a surname of German, Silesian, and West Slavic origins, and may refer to * Adolf Klose (1844–1923), German railroad engineer and inventor * Alfred Klose (1895–1953), German mathematician * Anastasia Klose (born 1978), Australian artist * Annika Klose (born 1992), German politician * Bob Klose (born 1945), British musician and photographer * Friedrich Klose (1862–1942), German composer * Hans-Ulrich Klose (1937–2023), German politician (SPD) * Hyacinthe Klosé (1808–1880), French composer and inventor of the Böhm clarinet system * Jann Klose, German-born singer, songwriter, producer * Josef Klose (born 1947), Polish football player * Kevin Klose (born 1940), American public radio CEO * Kirsten Klose (born 1977), German hammer thrower * Margarete Klose (1899–1968), German opera singer (contralto) * Miroslav Klose (born 1978), German footballer * Samuel Gottlieb Klose, German Lutheran missionary - see German Australians#German missionaries * Timm Klose (born 1988 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Klose
Adolf Klose (21 May 1844 – 2 September 1923) was the chief engineer of the Royal Württemberg State Railways in southern Germany from June 1885 to 1896. Klose was born in Bernstadt auf dem Eigen, in Saxony. Before his taking up his post in Stuttgart he had been the technical inspector of the United Swiss Railways (''Vereinigten Schweizerbahnen''). After a period of depending on Prussian prototypes between 1865 and 1885, a new engineering direction followed under Klose's time in office. It was stamped by numerous home-grown ideas and discoveries. In particular he promoted the introduction of compound working for steam locomotives in Württemberg. The patented Klose steering (''Klose-Lenkwerk'') carries his name. This was a multipartite and complex device for steam locomotives, which controlled the radial setting of leading and trailing wheelsets in order to improve curve running. Unfortunately, its costly maintenance and tendency to develop faults meant that his invention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |