|
Writings Of BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh
The writings of BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh are the corpus of texts written or narrated by BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh, which are regarded as sacred scripture in the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith. BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh was the founder of the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith; he was born in Persia and later exiled for being a follower of the BĂĄb, who in 1844 had declared himself to be a Manifestation of God and forerunner of " Him Whom God shall make manifest". BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh first announced his claim to be a Manifestation of God in 1863 and spent the rest of his life as a prisoner of the Ottoman Empire, exiled first to Baghdad, followed by Istanbul, Edirne, where he began proclaiming his mission, and finally Acre. His teachings revolve around the principles of unity and religious renewal, ranging from moral and spiritual progress to world governance. Overview BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh's writings, also referred to as Tablets, were written over a forty-year period beginning before he declared his mission in 1863. Almost 20,000 separate works with a total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh
BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh (, born កusayn-Ê»AlĂ; 12 November 1817 â 29 May 1892) was an Iranian religious leader who founded the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith. He was born to an aristocratic family in Iran and was exiled due to his adherence to the messianic BĂĄbism. In 1863, in Iraq, he first announced his claim to a revelation from God in the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith, God and spent the rest of his life in further imprisonment in the Ottoman Empire. His teachings revolved around the principles of unity and religious renewal, ranging from moral and spiritual progress to world governance. BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh was raised with no formal education but was well-read and devoutly religious. His family was considerably wealthy, and at the age of 22 he turned down a position in the government, instead managing family properties and donating time and money to charities. At the age of 27 he accepted the claim of the BĂĄb and became one of the most outspoken supporters of the new religious movement which advocated, among o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. The texts include instructions, stories, poetry, prophecies, and other genres. The collection of materials accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text varies. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible, called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning 'five books') in Greek. The second-oldest part was a collection of narrative histories and prophecies (the Nevi'im). The third co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidden Words
''The Hidden Words'' (, , ) is a book written by BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh, the founder of the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith, around 1858. He composed it while walking along the banks of the Tigris river during his exile in Baghdad. The book is written partly in Arabic and partly in Persian. ''The Hidden Words'' is written in the form of a collection of 153 short aphorisms, 71 in Arabic and 82 in Persian, in which BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh says he has taken the basic essence of certain spiritual truths and written them in brief form. Ê»Abdu'l-BahĂĄ, BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh's son and the authorized interpreter of his teachings, advised BahĂĄÊŒĂs to read them every day and every night and to implement their latent wisdom into their daily lives. He also said that ''The Hidden Words'' is "a treasury of divine mysteries" and that when one ponders its contents, "the doors of the mysteries will open". History There is a ShiÊ»a Muslim tradition called " Mushaf of Fatimah" (), which speaks of Fatimah upon the passing of her f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
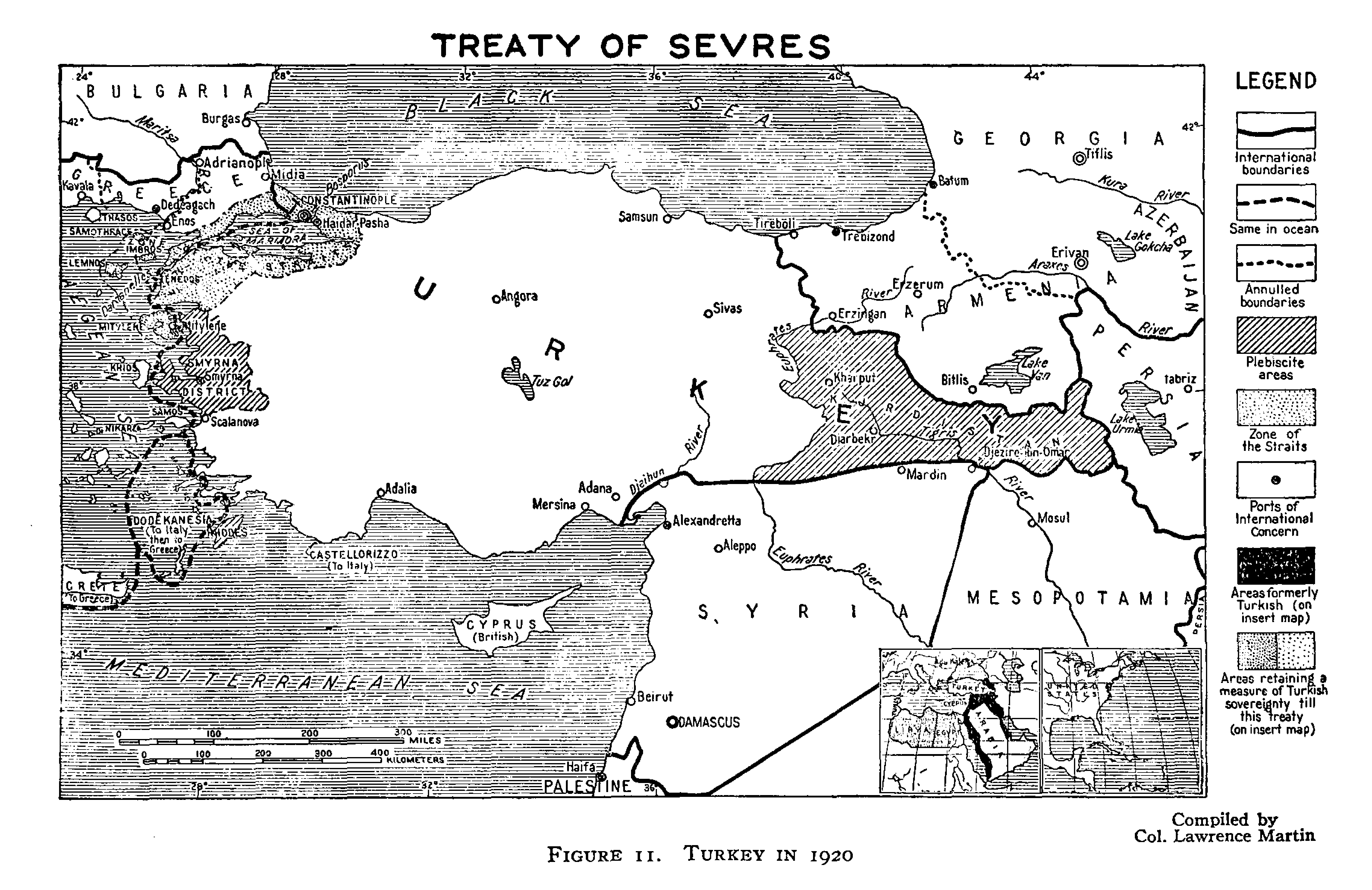
Kurdistan
Kurdistan (, ; ), or Greater Kurdistan, is a roughly defined geo- cultural region in West Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, languages, and national identity have historically been based. Geographically, Kurdistan roughly encompasses the northwestern Zagros and the eastern Taurus mountain ranges. Kurdistan generally comprises the following four regions: southeastern Turkey ( Northern Kurdistan), northern Iraq ( Southern Kurdistan), northwestern Iran ( Eastern Kurdistan), and northern Syria ( Western Kurdistan). Some definitions also include parts of southern Transcaucasia. Certain Kurdish nationalist organizations seek to create an independent nation state consisting of some or all of these areas with a Kurdish majority, while others campaign for greater autonomy within the existing national boundaries. The delineation of the region remains disputed and varied, with some maps greatly exaggerating its boundaries. Histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulaymaniyah
Sulaymaniyah or Slemani (; ), is a city in the east of the Kurdistan Region of Iraq and is the capital of the Sulaymaniyah Governorate. It is surrounded by the Azmar (Ezmer), Goizha (Goyje) and Qaiwan (Qeywan) Mountains in the northeast, Baranan Mountain in the south and the Tasluja Hills in the west. The city has a semi-arid climate with very hot dry summers and cold wet winters. The modern city of Slemani was founded in 1784 by the Ottoman-Kurdish prince Ibrahim Pasha Baban in Collaboration with Azim Beg and Haji Aziz Bey Aghal Dwanze Swarey Meriwane Jawamer Agha Rangena, who named it after his father Sulayman Pasha. Slemani was the capital of the historic Kurdish principality of Baban from 1784 to 1850. History The region of Slemani was known as '' Zamwa'' prior to the foundation of the modern city in 1784. The capital of the Kurdish Baban principality (1649â1850), before Slemani, was a territory named "Qelaçiwalan". At the time of the Babani's rule there were ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KitĂĄb-i-Aqdas
The ''KitĂĄb-i-Aqdas'' () is the central religious text of the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith, written by BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh, the founder of the religion, in 1873. Though it is the main source of BahĂĄÊŒĂ laws and practices, much of the content deals with other matters, like foundational principles of the religion, the establishment of BahĂĄÊŒĂ institutions, mysticism, ethics, social principles, and prophecies. In BahĂĄÊŒĂ literature it is described as "the Mother-Book" of the BahĂĄÊŒĂ teachings, and the "Charter of the Future World Civilization". BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh had manuscript copies sent to BahĂĄÊŒĂs in Iran some years after its writing in 1873, and in 1890â91 (1308 AH, 47 BE) he arranged for its first publication in Bombay, India. Parts of the text were translated into English by Shoghi Effendi, which, along with a ''Synopsis and Codification,'' were published in 1973 by the Universal House of Justice on the centennial anniversary of its writing. The full authoritative English translat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoghi Effendi
ShoghĂ Effendi (; ;1896 or 1897 â 4 November 1957) was Guardian of the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith from 1922 until his death in 1957. As the grandson and successor of Ê»Abdu'l-BahĂĄ, he was charged with guiding the development of the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith, including the creation of its global administrative structure and the prosecution of BahĂĄÊŒĂ teaching plans, a series of teaching plans that oversaw the expansion of the religion to a number of new countries. As the authorized interpreter of the BahĂĄÊŒĂ writings, BahĂĄÊŒĂ Writings his translations of the primary written works of the Faith's central figures, provided unity of understanding about essential teachings of the Faith and safeguarded its followers from division. Upon his death in 1957, leadership passed to the Hands of the Cause, and in 1963 the BahĂĄÊŒĂs of the world elected the Universal House of Justice, an institution which had been described and planned by BahĂĄÊŒuâllah. Effendi, an AfnĂĄn, was born ShoghĂ RabbĂĄnĂ i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MĂrzĂĄ YahyĂĄ
Subh-i-Azal (1831â1912, born MÄ«rzÄ YahyÄ NĆ«rÄ«) was an Iranian religious leader and writer who was the second head of the BÄbÄ« movement after the execution of its founder, the BÄb, in 1850. He was named the leader of the movement after being the BÄb's chief deputy shortly before its execution, and became a generally-acknowledged head of the community after their expulsion to Baghdad in 1852. The BÄb believed Subh-i-Azal had an ability to write divinely-inspired verses and saw him as a mirror, providing the ability to explain the unexplained, in the time before the appearance of the messiah, known in the BÄbÄ« religion as He whom God shall make manifest (). However, not all BÄbÄ«s followed his authority, and some of them also made claims of their own, including those to the position of the messiah. After his later conflict with his half-brother BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh, who became Subh-i-Azal's leading intermediary and later claimed the messianic status, over leadership of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rasháž„-i-Ê»AmĂĄ
''RasÍháž„-i-Ê»AmĂĄ'' (''"The Clouds of the Realms Above"'' or ''"Sprinkling of the Cloud of Unknowing"'') is the first known tablet written by BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh, founder of the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith, in 1852. It is also the only known tablet of BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh written in Qajar dynasty Persia. It is a poem of 20 couplets in Persian, written when BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh was imprisoned in the SĂyĂĄh-ChĂĄl in Tehran. In February 2019 an authorized translation was published by the BahĂĄÊŒĂ World Centre in the collection ''The Call of the Divine Beloved''.BWNS. A collection of BahaÊŒu'llĂĄh's mystical writings published'' 6 February 2019. Notes Further reading * Cole, Juan. "Baha'u'llah and the Naqshbandi Sufis in Iraq, 1854-1856", from Iran East and West: Studies in Babi and Baha'i History, vol. 2' (edited, with Moojan Momen Moojan Momen (b. 1950) is a retired physician and historian specializing in BahĂĄÊŒĂ studies who has published numerous books and articles about the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SĂyĂĄh-ChĂĄl
The SĂyĂĄh-ChĂĄl ( literally "black pit") was a subterrenean dungeon southeast of Golestan Palace in Tehran. It carries a significant role in the history of the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith, because its founder, BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh was held there for four months in 1852, and it is where he claimed to have received a revelation. The SĂyĂĄh-ChĂĄl is regarded as the second holiest place in Iran to BahĂĄÊŒĂs, after the house of the BĂĄb, in Shiraz. The pit was a discarded cistern converted into a dungeon. It had three flights of steep stairs descending into an area that received no light. There was no functioning latrine, and the small area was filled with up to 150 men. On 15 August 1852, a radical group of BĂĄbĂs attempted to assassinate Naser al-Din Shah Qajar and failed. The group of BĂĄbĂs linked with the plan were rounded up and executed, but notwithstanding the assassins' claim that they were working alone, the entire BĂĄbĂ community was blamed, precipitating a pogrom against the BĂ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Pius IX
Pope Pius IX (; born Giovanni Maria Battista Pietro Pellegrino Isidoro Mastai-Ferretti; 13 May 1792 â 7 February 1878) was head of the Catholic Church from 1846 to 1878. His reign of nearly 32 years is the longest verified of any pope in history; if including unverified reigns, his reign was second to that of Peter the Apostle. He was notable for convoking the First Vatican Council in 1868 and for permanently losing control of the Papal States in 1870 to the Kingdom of Italy. Thereafter, he refused to leave Vatican City, declaring himself a "prisoner in the Vatican". At the time of his election, he was a liberal reformer, but his approach changed after the Revolutions of 1848. Upon the assassination of his prime minister, Pellegrino Rossi, Pius fled Rome and excommunicated all participants in the short-lived Roman Republic (1849â1850), Roman Republic. After its suppression by the French army and his return in 1850, his policies and doctrinal pronouncements became increasingl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prayer In The BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith
There are two types of prayer in the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith: ''obligatory prayer'' and ''general'' or ''devotional prayer''. Both types of prayer are composed of reverent words which are addressed to God, and the act of prayer is one of the most important BahĂĄÊŒĂ laws for individual discipline. The purpose of prayer in the BahĂĄÊŒĂ Faith is to grow closer to God and his Manifestations and to help better one's own conduct and to request divine assistance. BahĂĄÊŒĂs between the ages of 15 and 70 are required to perform one of three prescribed obligatory prayers daily and individually, according to a set form and in accordance with specific laws. In addition to the daily obligatory prayer, BahĂĄÊŒĂ scripture directs believers daily to offer devotional prayer as well as to meditate and study sacred scripture. There is no set form for devotions and meditations. There is a large corpus of devotional prayers written by the BĂĄb, BahĂĄÊŒu'llĂĄh, Ê»Abdu'l-BahĂĄ, the central figures of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |