|
Windsor, Nova Scotia
Windsor is a community located in Hants County, Nova Scotia, Hants County, Nova Scotia, Canada. It is a service centre for the western part of the county and is situated on Nova Scotia Highway 101, Highway 101. The community has a history dating back to its use by the Mi'kmaq people, Mi'kmaq Nation for several millennia prior to European colonization. When the Acadians lived in the area, the town was raided by New England forces in 1704. The area was central to both Father Le Loutre's War and the Expulsion of the Acadians during the Bay of Fundy Campaign (1755), Bay of Fundy Campaign in 1755. The town promotes itself as the birthplace of ice hockey and was the home of Canada's first internationally best-selling author, Thomas Chandler Haliburton. On April 1, 2020, the Town of Windsor amalgamated with the District of West Hants to become the West Hants Regional Municipality. History Having migrated from Habitation at Port-Royal, Port Royal, Nova Scotia, the Acadians were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
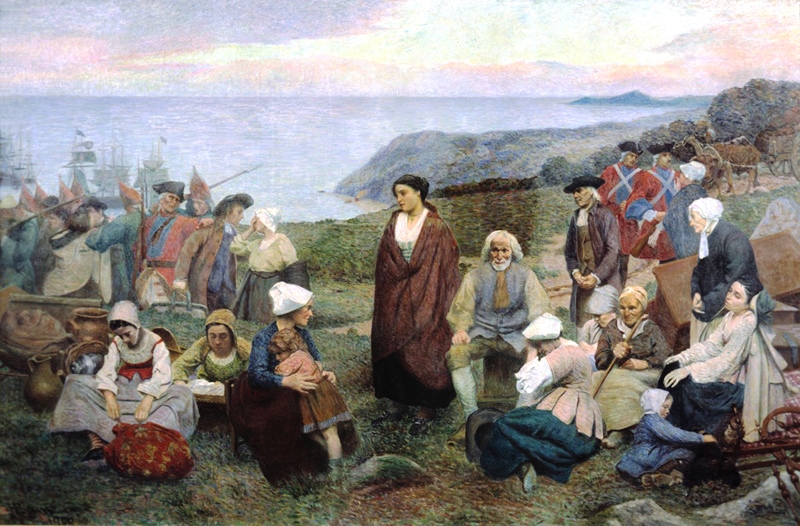
Acadians
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French colonial empire, French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern American Acadia (region), region of Acadia, where descendants of Acadians who escaped the Expulsion of the Acadians (a.k.a. The Great Upheaval / ''Le Grand Dérangement'') re-settled, or in Louisiana, where thousands of Acadians moved in the late 1700s. Descendants of the Louisiana Acadians are most commonly known as Cajuns, the anglicized term of "Acadian". Acadia was one of the five regions of New France, located in what is now Eastern Canada's The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, as well as parts of Quebec and present-day Maine to the Kennebec River. It was ethnically, geographically and administratively different from the other French colonies such as the Canada (New France), French colony of Canada. As a result, the Acadians developed a dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raid On Deerfield
The Raid on Deerfield, also known as the Deerfield Massacre, occurred during Queen Anne's War on February 29, 1704, when French and Native American raiders under the command of Jean-Baptiste Hertel de Rouville attacked the English colonial settlement of Deerfield, Massachusetts Bay, just before dawn. They burned parts of the town and killed 47 colonists. The raiders left with 112 colonists as captives, whom they took overland the nearly 300 miles to Montreal; some died or were killed along the way because they were unable to keep up. Roughly 60 colonists were later ransomed by their associates, while others were adopted by Mohawk families at Kahnawake and became assimilated into the tribe. In this period, English colonists and their Indian allies were involved in similar raids against French villages along the northern area between the spheres of influence. Typical of the small-scale frontier conflict in Queen Anne's War, the French-Indian forces consisted of French soldie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, second-largest country by total area, with the List of countries by length of coastline, world's longest coastline. Its Canada–United States border, border with the United States is the world's longest international land border. The country is characterized by a wide range of both Temperature in Canada, meteorologic and Geography of Canada, geological regions. With Population of Canada, a population of over 41million people, it has widely varying population densities, with the majority residing in List of the largest population centres in Canada, urban areas and large areas of the country being sparsely populated. Canada's capital is Ottawa and List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various indigenous First Nations in Canada, First Nations that comprised the Wabanaki Confederacy, the Acadian people and other French people, French settlers. The first capital of Acadia was established in 1605 as Port-Royal (Acadia), Port-Royal. Soon after, English forces of Captain Argall, an English ship's captain employed by the Virginia Company of London attacked and burned down the Port-Royal National Historic Site, fortified habitation in 1613. A new centre for Port-Royal was established nearby, and it remained the longest-serving capital of French Acadia until the British Siege of Port Royal (1710), siege of Port Royal in 1710. There were six colonial wars in a 74-year period in which British interests tried to capture Acadia, starting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wabanaki Confederacy
The Wabanaki Confederacy (''Wabenaki, Wobanaki'', translated to "People of the Dawn" or "Easterner"; also: Wabanakia, "Dawnland") is a North American First Nations and Native American confederation of five principal Eastern Algonquian nations: the Abenaki, Mi'kmaq, Wolastoqiyik, Passamaquoddy (''Peskotomahkati'') and Penobscot. There were more tribes, along with many bands, that were once part of the Confederation. Native tribes such as the Nanrantsouak, Alemousiski, Pennacook, Sokoki, and Canibas, through massacres, tribal consolidation, and ethnic label shifting were absorbed into the five larger national identities. Members of the Wabanaki Confederacy, the Wabanakiyak, are located in and named for the area which they call Wabanaki ("Dawnland"), roughly the area that became the French colony of Acadia. The territory boundaries encompass present-day Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, in the United States, and New Brunswick, mainland Nova Scotia, Cape Breton Island, Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War (1702–1713) or the Third Indian War was one in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In the United States, it is often studied as a standalone conflict under this name, although it is also viewed as the American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession. In France, it was known as the Second Intercolonial War. The war was primarily a conflict between French, Spanish and English colonial ambitions for control of the North American continent while the War of the Spanish Succession was being fought in Europe. Each side drew in various Indigenous communities as allies, and it was fought on four fronts. In the south, Spanish Florida and the English Province of Carolina attacked one another, and English colonists engaged French colonists based at Old Mobile Site, Fort Louis de la Louisiane (near present-day Mob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
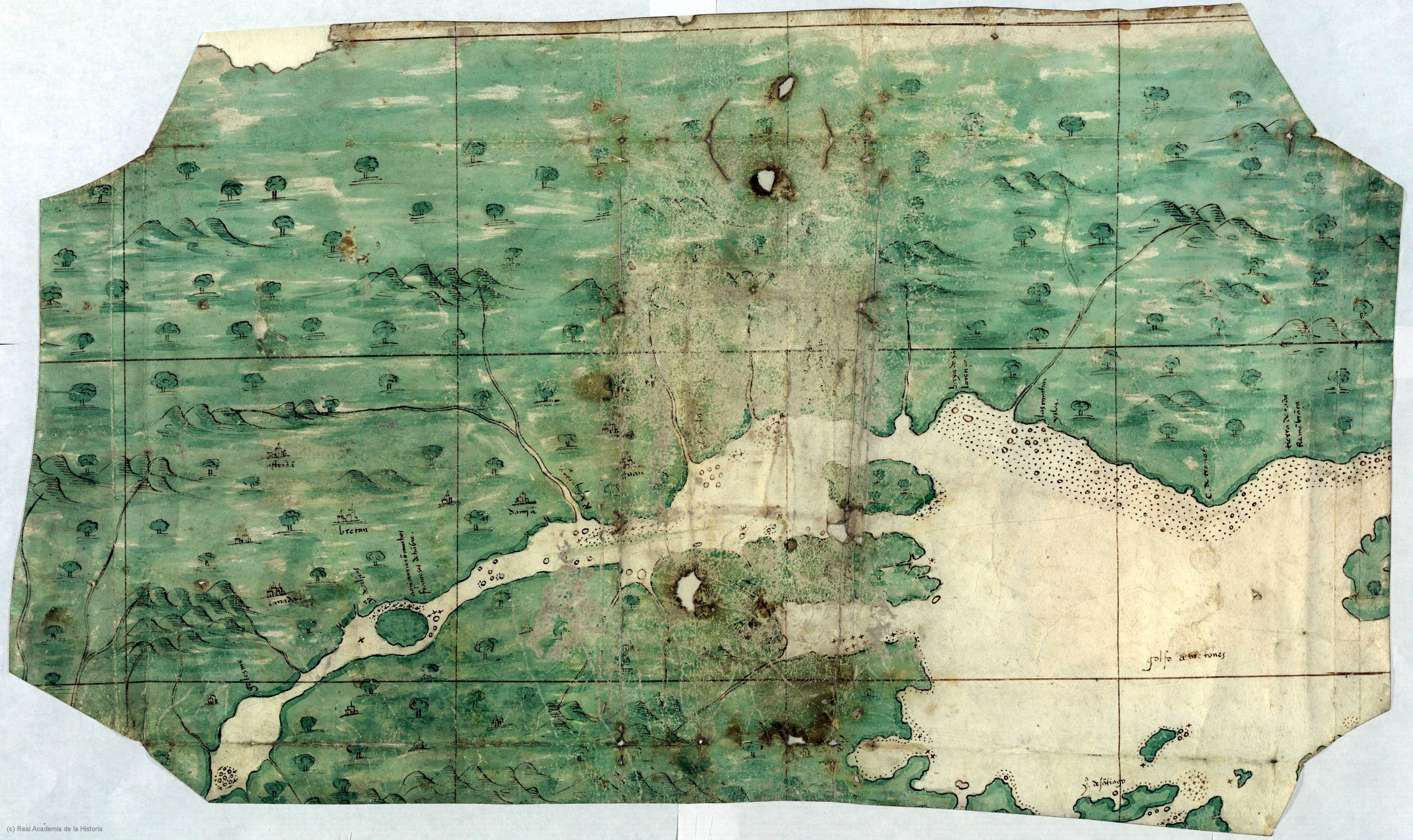
Pisiguit
Pisiguit is the pre- expulsion-period Acadian region located along the banks of the Avon River (known as the Pisiquit River to the Acadians) from its confluence with the Minas Basin of Acadia, which is now Nova Scotia, including the St. Croix River drainage area. Settlement in the region commenced simultaneous to the establishment of Grand-Pré. Many villages (Rivet, Foret, Babin, Landry, Thibodeau, Vincent, etc.) spread rapidly eastward along the river banks. These settlements became known as ''Pisiguit'' or (''Pisiquit'', ''Pigiguit'', ''Pisiquid'', ''Pisiguid''). The name is from the Mi'kmaq ''Pesaquid'', meaning "Junction of Waters". In 1714, there were 351 people (in 56 families) there.From Acadian-Cajun Genealogy & History: Exile Destination: Pisiguit Population By the mid-18th century, a memoire from 1748 noted that there were 2,700 people in Pisiguit compared to 2,400 in the Grand Pré and Canard area. But the area lost its population rather quickly. Pisiguit was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitation At Port-Royal
Port-Royal National Historic Site is a National Historic Site located on the north bank of the Annapolis Basin in Granville Ferry, Nova Scotia, Canada. The site is the location of the Habitation at Port-Royal, which was the centre of activity for the New France colony of Port Royal in Acadia from 1605 to 1613, when it was destroyed by English forces from the Colony of Virginia. History The French colony of Port Royal, centered on the habitation, was the first successful attempt by Europeans to establish a permanent settlement in what is today known as Canada. The habitation's active period was from 1605 to 1613. Although the European settlement of Port Royal persevered, with some interruptions, the habitation's role as the focus of the colony ended with its destruction in 1613. In 1629, Charles Fort, now Fort Anne, was established by Scottish settlers. The founding of the new fort permanently shifted the Port Royal colony's centre of activity. The settlement around the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Hants
West Hants, officially named the West Hants Regional Municipality, is a regional municipality in Hants County, Nova Scotia, Canada. It occupies the western half of Hants County, running from the Minas Basin to the boundary with Halifax County, sharing this boundary with the Municipality of the District of East Hants. The Municipality of the District of West Hants amalgamated with Windsor on April 1, 2020, becoming the Region of Windsor and West Hants Municipality. It was renamed as West Hants Regional Municipality on October 6, 2020. Demographics In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, the West Hants Regional Municipality had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021. Famous people The poet George Elliot Clarke is from West Hants. His poem, "West Hants County" tells of the difficult condition of black workers in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Chandler Haliburton
Thomas Chandler Haliburton (17 December 1796 – 27 August 1865) was a Nova Scotian politician, judge, and author who was the first international best-selling fiction author from what is now Canada, and who served as a Conservative Member of Parliament in England. He was the father of the British civil servant Lord Haliburton and of the anthropologist Robert Grant Haliburton. Life Thomas Chandler Haliburton was born on 17 December 1796, in Windsor, Nova Scotia, to William Hersey Otis Haliburton, a judge and politician, and Lucy Chandler Grant. His mother died when he was a small child. When Thomas was seven, his father married Susanna Davis, the daughter of Michael Francklin, who had been Nova Scotia's Lieutenant Governor. He attended University of King's College in Windsor, from which he graduated in 1815 to become a lawyer who practiced at Annapolis Royal. Between 1826 and 1829, Haliburton represented Annapolis County in the Nova Scotia House of Assembly. Haliburton's f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |