|
Windrow
A windrow is a row of cut (mown) hay or small grain crop. It is allowed to dry before being baled, combined, or rolled. For hay, the windrow is often formed by a hay rake, which rakes hay that has been cut by a mowing machine or by scythe into a row, or it may naturally form as the hay is mown. For small grain crops which are to be harvested, the windrow is formed by a swather which both cuts the crop and forms the windrow. By analogy, the term may also be applied to a row of any other material such as snow, earth or materials for collection. * Snow windrows are created by snow plows when clearing roads of snow; where this blocks driveways the windrow may require removal. Snow windrowed to the centre of the street can be removed by a snow blower and truck. In preparing a pond or lake for ice cutting, the snow on top of the ice, which slows freezing, might be scraped off and windrowed. * Earth windrows may be formed by graders when grading earthworks or dirt roads * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windrow Composting
In agriculture, windrow composting is the production of compost by piling organic matter or biodegradable waste, such as animal manure and crop residues, in long rows – windrow. As the process is aerobic, it is also known as Open Windrow Composting (OWC) or Open Air Windrow Composting (OAWC). This method is suited to producing large volumes of compost. These rows are generally turned to improve porosity and oxygen content, mix in or remove moisture, and redistribute cooler and hotter portions of the pile. Windrow composting is a commonly used farm scale composting method. Composting process control parameters include the initial ratios of carbon and nitrogen rich materials, the amount of bulking agent added to assure air porosity, the pile size, moisture content, and turning frequency. The temperature of the windrows must be measured and logged constantly to determine the optimum time to turn them for quicker compost production. Compost windrow turners Compost windrow turner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hay Rake
A hay rake is an agricultural rake (tool), rake used to collect cut hay or straw into windrows for later collection (e.g. by a baler or a loader wagon). It is also designed to fluff up the hay and turn it over so that it may dry. It is also used in the evening to protect the hay from morning dew. The next day a Tedder (machine), tedder is used to spread it again, so that the hay dries more quickly. Types A hay rake may be mechanized, drawn by a tractor or draft animals, or it may be a hand tool. The earliest hay rakes were nothing more than tree branches, but rake (tool), wooden hand rakes with wooden teeth, similar in design to a garden rake but larger, were prevalent in the 19th and early 20th centuries, and still are used in some locations around the world. Hay rakes were among the first agricultural tools to become popular in the shift from human manual labor to animal labor in the 19th century. The typical early horse-drawn hay rake was a ''dump rake'', a wide two-wheel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swather
A swather (North America), or windrower (Australia and rest of world), is a farm implement that cuts hay or small grain crops and forms them into a windrow for drying. They may be self-propelled with an engine, or drawn by a tractor and power take-off powered. A swather uses a reciprocating sickle bar or rotating discs to sever the crop stems. The reel helps cut crop fall neatly onto a canvas or auger conveyor which deposits it into a windrow with stems aligned and supported above the ground by the stubble. A swather does the same task for hay crops as hand scything, cradling and swathing, or mowing and raking. Horizontal rollers behind the cutters may be used to crimp or condition the stems of hay crops to decrease drying time. For grains, as combines replaced threshing machines, the swather introduced an optional step in the harvesting process to provide for the drying time that binding formerly afforded. Swathing is still more common in the northern United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langmuir Circulation
In physical oceanography, Langmuir circulation consists of a series of shallow, slow, counter-rotating vortices at the ocean's surface aligned with the wind. These circulations are developed when wind blows steadily over the sea surface. Irving Langmuir discovered this phenomenon after observing windrows of seaweed in the Sargasso Sea in 1927. Langmuir circulations circulate within the mixed layer; however, it is not yet so clear how strongly they can cause mixing at the base of the mixed layer. Theory The driving force of these circulations is an interaction of the mean flow with wave averaged flows of the surface waves. Stokes drift velocity of the waves stretches and tilts the vorticity of the flow near the surface. The production of vorticity in the upper ocean is balanced by downward (often turbulent) diffusion \nu_T. For a flow driven by a wind \tau characterized by friction velocity u_* the ratio of vorticity diffusion and production defines the Langmuir number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermicompost
Vermicompost (vermi-compost) is the product of the decomposition process using various species of worms, usually red wigglers, white worms, and other earthworms, to create a mixture of decomposing vegetable or food waste, bedding materials, and vermicast. This process is called vermicomposting, with the rearing of worms for this purpose is called vermiculture. Vermicast (also called worm castings, worm humus, worm poop, worm manure, or worm faeces) is the end-product of the breakdown of organic matter by earthworms. These excreta have been shown to contain reduced levels of contaminants and a higher saturation of nutrients than the organic materials before vermicomposting. Vermicompost contains water-soluble nutrients which may be extracted as vermiwash and is an excellent, nutrient-rich organic fertilizer and soil conditioner.Coyne, Kelly and Erik Knutzen. ''The Urban Homestead: Your Guide to Self-Sufficient Living in the Heart of the City.'' Port Townsend: Process Self Relia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
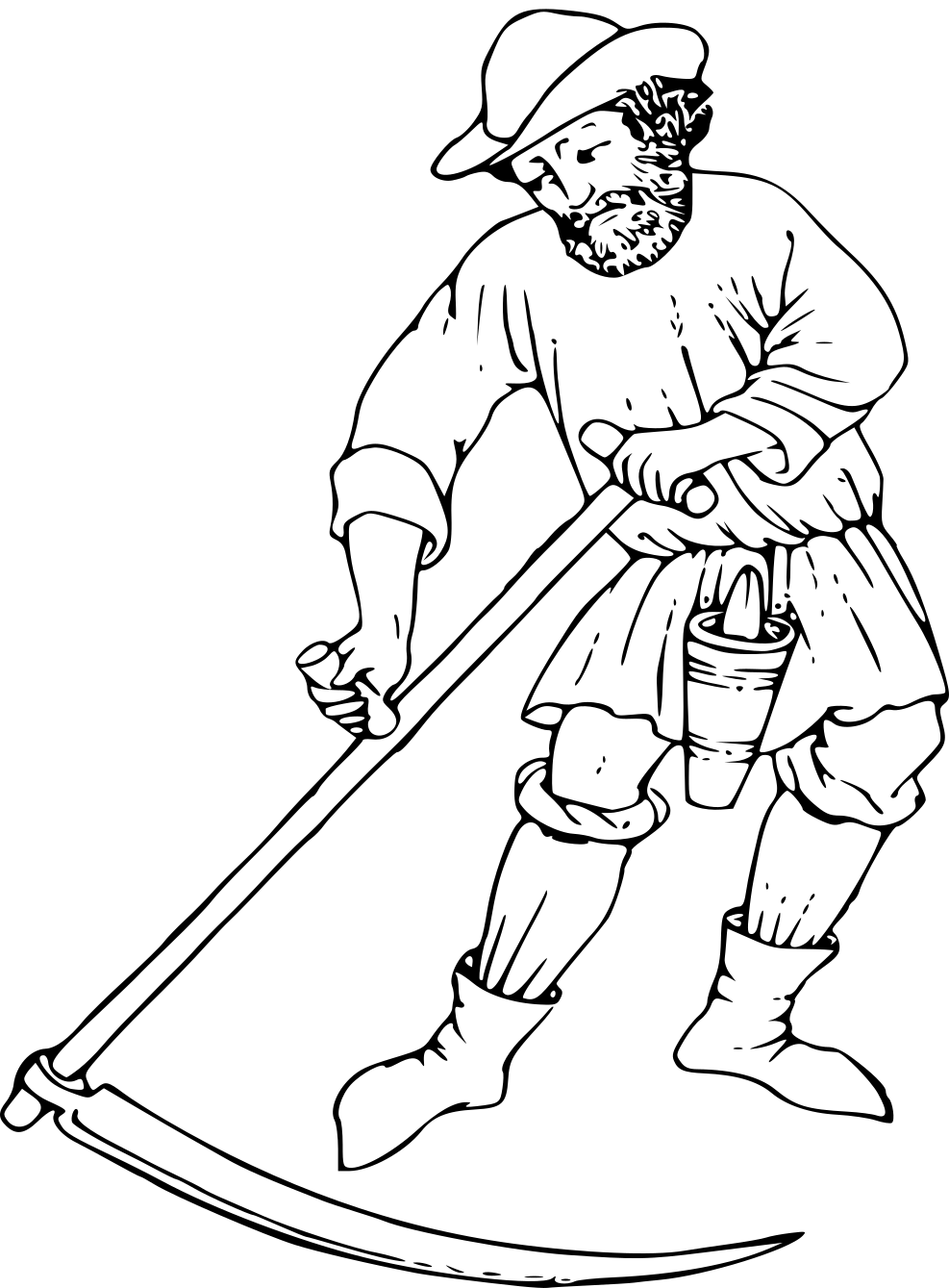
Scythe
A scythe (, rhyming with ''writhe'') is an agriculture, agricultural hand-tool for mowing grass or Harvest, harvesting Crop, crops. It was historically used to cut down or reaping, reap edible grain, grains before they underwent the process of threshing. Horse-drawn and then tractor machinery largely replaced the scythe, but it is still used in some areas of Europe and Asia. Reapers are bladed machines that automate the cutting action of the scythe, and sometimes include subsequent steps in preparing the grain or the straw or hay. The word "scythe" derives from Old English ''siðe''. In Middle English and later, it was usually spelled ''sithe'' or ''sythe''. However, in the 15th century some writers began to use the ''sc-'' spelling as they thought (wrongly) that the word was related to the Latin (meaning "to cut"). Nevertheless, the ''sithe'' spelling lingered, and notably appears in Noah Webster's dictionaries. A scythe consists of a shaft about long called a ''snaith'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baler
A baler or hay baler is a piece of farm machinery used to compress a cut and raked crop (such as hay, cotton, flax straw, salt marsh hay, or silage) into compact bales that are easy to handle, transport, and store. Often, bales are configured to dry and preserve some intrinsic (e.g. the nutritional) value of the plants bundled. Different types of balers are commonly used, each producing a different type of balerectangular or cylindrical, of various sizes, bound with twine, strapping, netting, or wire. Industrial balers are also used in material recycling facilities, primarily for baling metal, plastic, or paper for transport. History Before the 19th century, hay was cut by hand and most typically stored in haystacks using hay forks to rake and gather the scythed grasses into optimally sized heapsneither too large, promoting conditions favorable for spontaneous combustion, nor too small, which would mean much of the pile is susceptible to rotting. These haystacks lift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mower
A mower is a person or machine that cuts (mows) grass or other plants that grow on the ground. Usually mowing is distinguished from reaping, which uses similar implements, but is the traditional term for harvesting grain crops, e.g. with reapers and combines. A smaller mower used for lawns and sports grounds (playing fields) is called a ''lawn mower'' or ''grounds mower'', which is often self-powered, or may also be small enough to be pushed by the operator. Grounds mowers have reel or rotary cutters. Larger mowers or '' mower-conditioners'' are mainly used to cut grass (or other crops) for hay or silage and often place the cut material into rows, which are referred to as ''windrows''. '' Swathers'' (or ''windrowers'') are also used to cut grass (and grain crops). Prior to the invention and adoption of mechanized mowers, (and today in places where use a mower is impractical or uneconomical), grass and grain crops were cut by hand using scythes or sickles. Mower configurati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combine Harvester
The modern combine harvester, also called a combine, is a machine designed to harvest a variety of cultivated seeds. Combine harvesters are one of the most economically important labour-saving inventions, significantly reducing the fraction of the population engaged in agriculture. Among the crops harvested with a combine are wheat, rice, oats, rye, barley, Maize, corn (maize), sorghum, millet, soybeans, flax (linseed), sunflowers and rapeseed (canola). The separated straw (consisting of stems and any remaining leaves with limited nutrients left in it) is then either chopped onto the field and ploughed back in, or laid out in rows, ready to be Baler, baled and used for bedding and cattle feed. The name of the machine is derived from the fact that the harvester combined multiple separate harvesting operations – Reaper, reaping, threshing or winnowing and gathering – into a single process around the start of the 20th century. A combine harvester still performs its functions ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windrow Formation
The Windrow Formation is a geologic formation in Minnesota named after Windrow Bluff on Fort McCoy, Monroe County, Wisconsin. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cretaceous period Period may refer to: Common uses * Period (punctuation) * Era, a length or span of time *Menstruation, commonly referred to as a "period" Arts, entertainment, and media * Period (music), a concept in musical composition * Periodic sentence (o .... See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Minnesota * Paleontology in Minnesota References * Cretaceous Minnesota Geologic formations of Minnesota {{Cretaceous-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Cutting
Ice cutting is a winter task of collecting surface ice from lakes and rivers for storage in ice houses and use or sale as a cooling method. Rare today, it was common (see ice trade) before the era of widespread mechanical refrigeration and air conditioning technology. History The work was done as a winter chore by many farmers and as a winter occupation by icemen. Kept insulated, the ice was preserved for cold food storage during warm weather, either on the farm or for delivery to residential and commercial customers with ice boxes. A large ice trade existed in the 19th and early 20th centuries, until mechanical refrigeration displaced it. Due to its harvesting and trade, ice was considered a "crop". Ice harvesting generally involved waiting until approximately a foot of ice had built up on the water surface in the winter. The ice would then be cut with either a handsaw or a powered saw blade into long continuous strips and then cut into large individual blocks for transport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champs DSC01390
Champs may refer to: Music * The Champs, a U.S. instrumental music group * Champs (Brazilian band), a Brazilian boy band * Champs (British band), a British folk- and indie rock-influenced band * The Fucking Champs, a U.S. progressive heavy metal band previously known as The Champs * "Champs", a song on Wire's 1977 album ''Pink Flag'' Places in France * Champs, Aisne, in the Aisne ''département'' * Champs, Orne, in the Orne ''département'' * Champs, Puy-de-Dôme, in the Puy-de-Dôme ''département'' * Champs-Romain, in the Dordogne ''département'' * Champs-sur-Marne, in the Seine-et-Marne ''département'' * Champs-sur-Tarentaine-Marchal, in the Cantal ''département'' * Champs-sur-Yonne, in the Yonne ''département'' * Les Champs-de-Losque, in the Calvados ''département'' * Champs-Élysées, literally the "Elysian fields", a broad avenue in Paris Sport * Champs (brand), a Brazilian sporting goods manufacturer * Champs Sports, a subsidiary of Foot Locker, Inc. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |