|
Wilkowyja, Gniezno County
Wilkowyja (; German: ''Neu Paulsdorf'') is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Kłecko, within Gniezno County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It lies approximately west of Kłecko, north-west of Gniezno, and north-east of the regional capital Poznań. In the years 1975-1998, the village administratively belonged to the Poznań Voivodeship. According to the 2021 National Census, Wilkowyja was inhabited by 387 inhabitants, of which 48.8% were women and 51.2% men. The main part of the village with single-family buildings is located by the district road 2154P connecting Wilkowyja with Polska Wieś and the provincial road No. 190. In the village, historic buildings from the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries, including a former manor house and school building, an old distillery and a historic Evangelical cemetery. History Wilkowyja was a knightly village owned by the Junosza family. The first mention of the village dates back to 1580, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
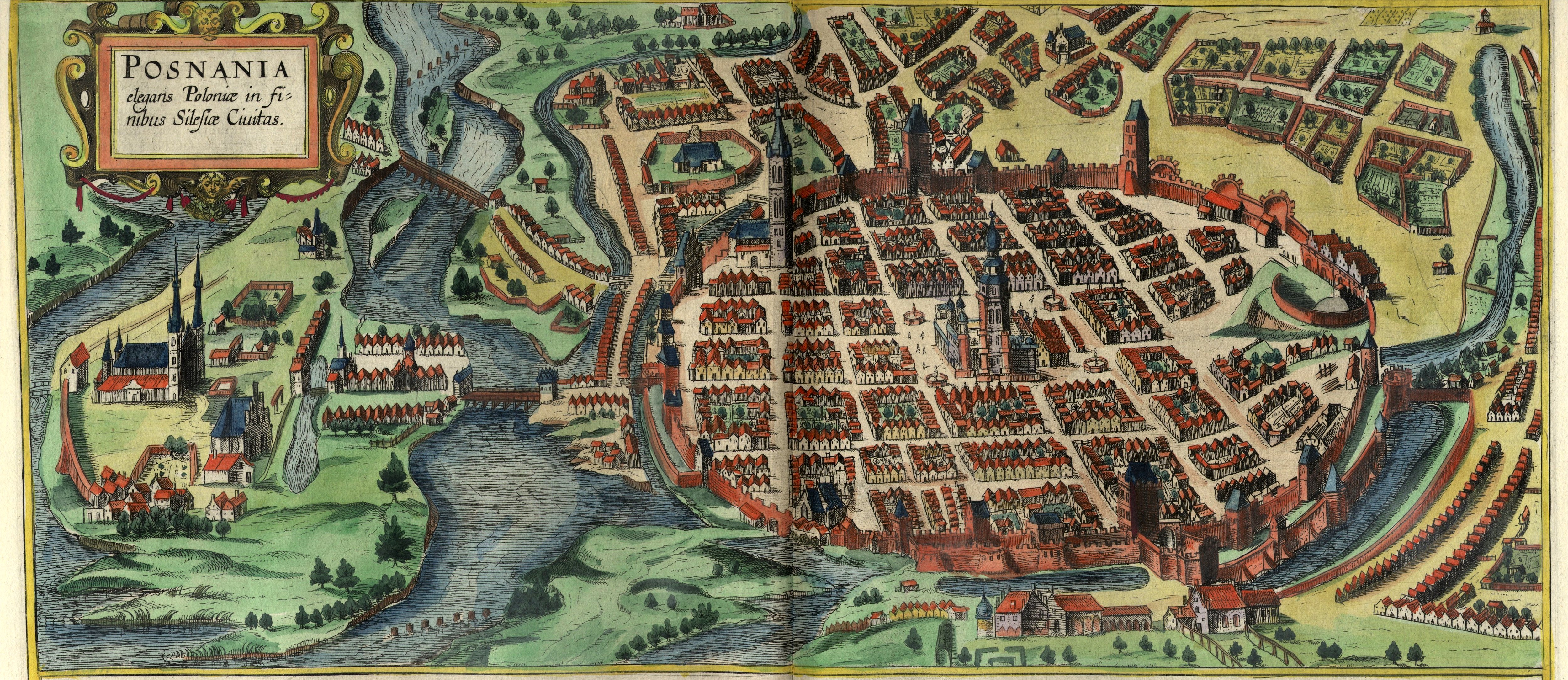
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair, Poznań, Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional St. Martin's croissant, Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance Old Town, Poznań Town Hall, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest List of cities and towns in Poland#Cities, city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rawicz
Rawicz (; ) is a town in west-central Poland with 21,398 inhabitants as of 2004. It is situated in the Greater Poland Voivodeship (since 1999); previously it was in Leszno Voivodeship (1975–1998). It is the capital of Rawicz County. History The town was founded by Adam Olbracht Przyjemski of Rawa coat of arms, Rawicz coat of arms for Protestant refugees from Silesia during the Thirty Years' War. In 1638 King Władysław IV Vasa granted Rawicz town rights and confirmed the town's coat of arms. Rawicz was built as a precisely planned town and developed at a rapid pace. It was located on the trade route connecting Poznań and Wrocław. In 1640, a cloth guild was founded. Cloth production became a leading branch of the local industry, and by the end of the 18th century Rawicz was the leading weaving town of the whole region of Greater Poland. Rawicz was a private town of szlachta, Polish nobility, administratively located in the Kościan County in the Poznań Voivodeship (14th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarnowa, Rawicz
Sarnowa (), formerly a town in its own right, is a historic neighbourhood and administrative district in Rawicz, Poland, located in the northeastern part of the town. History It was mentioned intermittently in various documents over the course of its history, with the first mention of a settlement was as far back as 1065, with another mention in 1110. It was mentioned in the Innocent II's papal ''Bull of Gniezno'' in 1136. In 1248 and 1262 it was mentioned in royal documentation, with the latter on 7 June the first mention of Sarnowa as a town, but formally received Magdeburg rights much later, in 1407. Until 1 January 1973, when it became part of Rawicz by the decision of the Council of Ministers, it was a separate town in its own right. Landmarks The historic landmarks of Sarnowa include the old Town Hall, the Baroque Saint Andrew the Apostle church, and the Eclectic manor house. Sports The local football Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miejska Górka
Miejska Górka is a town in Rawicz County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, Poland. With 3,190 inhabitants (2010), it lies approximately north-east of Rawicz and south of the regional capital Poznań. History Miejska Górka was granted town rights before 1406. It was a private town, administratively located in the Kościan County in the Poznań Voivodeship in the Greater Poland Province of the Kingdom of Poland. Following the joint German-Soviet invasion of Poland, which started World War II in September 1939, Miejska Górka was occupied by Germany until 1945. The occupiers operated a subcamp of the Nazi prison in Rawicz, dedicated to prisoners suffering from tuberculosis. On 22 May 1941, the Germans perpetrated a public execution of 25 Poles in the town (see ''Nazi crimes against the Polish nation''). The command of the ''Miejscowa Organizacja Podziemna'' Polish resistance organization was operating in Miejska Górka, and eventually became part of the larger Home Army The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Poland Uprising (1918–1919)
Greater Poland Uprising (also Wielkopolska Uprising or Great Poland Uprising) may refer to a number of armed rebellions in the region of Greater Poland Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; ), is a Polish Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city in Poland. The bound ...: * Greater Poland Uprising (1794) * Greater Poland Uprising (1806) * Greater Poland Uprising (1846) * Greater Poland Uprising (1848) * Greater Poland Uprising (1918–1919) See also * Greater Poland (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tithe
A tithe (; from Old English: ''teogoþa'' "tenth") is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Modern tithes are normally voluntary and paid in money, cash, cheques or via online giving, whereas historically tithes were required and paid in kind, such as agricultural produce. Church tax linked to the tax system are used in many countries to support their national church. Donations to the church beyond what is owed in the tithe, or by those attending a congregation who are not members or adherents, are known as offering (Christianity), offerings, and often are designated for specific purposes such as a building program, debt retirement, or mission work. Many Christian denominations hold Jesus in Christianity, Jesus taught that tithing must be done in conjunction with a deep concern for "justice, mercy and faithfulness" (cf. Matthew 23:23). Tithing was taught at early Christian Church Council, church counc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junosza Coat Of Arms
Junosza is a Polish coat of arms. Notable bearers Notable bearers of this coat of arms include: * House of Borawski Pawel 1849 * Franciszek Bieliński * House of Borkowski * House of Karnkowski ** Stanisław Karnkowski ** Jan Karnkowski * House of Koła ** Barbara Kolanka * House of Ojrzanowski / Oyrzanowski * House of Sobański * Hieronim Radziejowski * Józef Zaliwski * House of Załuski ** Marcin Załuski ** Paweł Antoni Załuski ** Louis Bartholomew Załuski ** Andrzej Chryzostom Załuski * Konstanty Felicjan Szaniawski, bishop Gallery image:POL COA Borkowski hrabia.svg, Counts Borkowski image:Borkowski Hrabia POL COA.svg, Counts Borkowski image:Borowiec POL COA.svg, Borowiec (odm.) See also * Polish heraldry * Heraldic family * List of Polish nobility coats of arms Polish heraldry is typical to the Polish nobility/szlachta, which has its origins in Middle Ages knights/warriors clans that provided military support to the king, dukes or overlords. Exception ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polska Wieś, Gniezno County
Polska Wieś (; German: ''Paulsdorf'') is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Kłecko, within Gniezno County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It lies approximately west of Kłecko, north-west of Gniezno, and north-east of the regional capital Poznań. In the years 1975-1998, the village administratively belonged to the Poznań Voivodeship. According to the 2021 National Census, Polska Wieś was inhabited by 242 inhabitants, of which 49.6% were women and 50.4% men. History Polska Wieś was one of the few villages located in the Middle Ages under the so-called Polish law (at that time, a location based on Magdeburg law was much more popular). The village probably existed before 1523 and was part of the Kłecko starosty, created as a result of the division of the Środa starosty. In the years 1580 - 1620 the village belonged to the Czarnkowski family. In 1771 the village paid a sheaf tithe to the parish priests of St. George in Gniezno, and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poznań Voivodeship
Poznań Voivodeship was the name of several former administrative regions (''województwo'', rendered as ''voivodeship'' and usually translated as "province") in Poland, centered on the city of Poznań, although the exact boundaries changed over the years. Poznań Voivodeship was incorporated into the Greater Poland Voivodeship after the Polish local government reforms of 1998. 14th century to 1793 Poznań Voivodeship () was established in 1320 and was part of the Greater Poland Voivodeship, until it was annexed by Prussia in 1793. It was in the rule of the Garczynski family for much of the 17th and 18th century. A notable voïvodie includes Stefan Garczyński (1690–1756), author, who was opposed to serfdom, amongst other social norms of the time. 1793 to 1921 Between 1793 and 1921, the territory formerly contained in Poznań Voivodeship was part of the following territories: South Prussia, the Poznań Department of the Duchy of Warsaw, the Grand Duchy of Posen, and the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gniezno
Gniezno (; ; ) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. The city is the administrative seat of Gniezno County (''powiat''). One of the Piast dynasty's chief cities, it was the first historical capital of Poland in the 10th century and early 11th century, and afterwards remained one of the main cities of the historic region of Greater Poland. Gniezno is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Gniezno, the country's oldest archdiocese, founded in 1000, and its archbishop is the primate (bishop), primate of Poland, making the city the country's ecclesiastical capital. The Gniezno Cathedral is one of the most historically important churches in Poland, and as such is a designated Historic Monument (Poland), Historic Monument of Poland. Other sights include the Old Town and the Museum of the Origins of the Polish State. Geography Gniezno is one of the histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeships Of Poland
A voivodeship ( ; ; plural: ) is the highest-level Administrative divisions of Poland, administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province". The administrative divisions of Poland, Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, which went into effect on 1 January 1999, reduced the number of voivodeships to sixteen. These 16 replaced the 49 subdivisions of the Polish People's Republic, former voivodeships that had existed from 1 July 1975, and bear a greater resemblance (in territory, but not in name) to the voivodeships that existed between 1950 and 1975. Today's voivodeships are mostly named after historical and geographical regions, while those prior to 1998 generally took their names from the cities on which they were centered. The new units range in area from under (Opole Voivodeship) to over (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |