|
Wilhelm Radziwiłł
Prince Fryderyk Wilhelm Paweł Mikolaj Radziwiłł (19 March 1797 – 5 August 1870) was a Polish nobleman and Prussian general who was the founding president of the Berlin Numismatic Society. Early life Radziwiłł was born on 19 March 1797 in Berlin. He was the eldest son of Prince Antoni Henryk Radziwiłł, the ''Duke-Governor'' (, ) of the Grand Duchy of Poznań, an autonomous province of the Kingdom of Prussia, and Princess Louise of Prussia (1770–1836). Among his surviving siblings were Prince Ferdynand Fryderyk Radziwiłł (who died unmarried); Princess Eliza Fryderyka Radziwiłł (the desired bride of Prince William of Prussia, who later became William I, German Emperor, but they were not allowed to marry); Prince Bogusław Fryderyk Radziwiłł (who married Countess Leontyna von Clary und Aldringen); Prince Władysław Radziwiłł (who died unmarried); and Princess Wanda Augusta Wilhelmina Radziwiłł (who married their first cousin, Prince Adam Czartoryski). His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
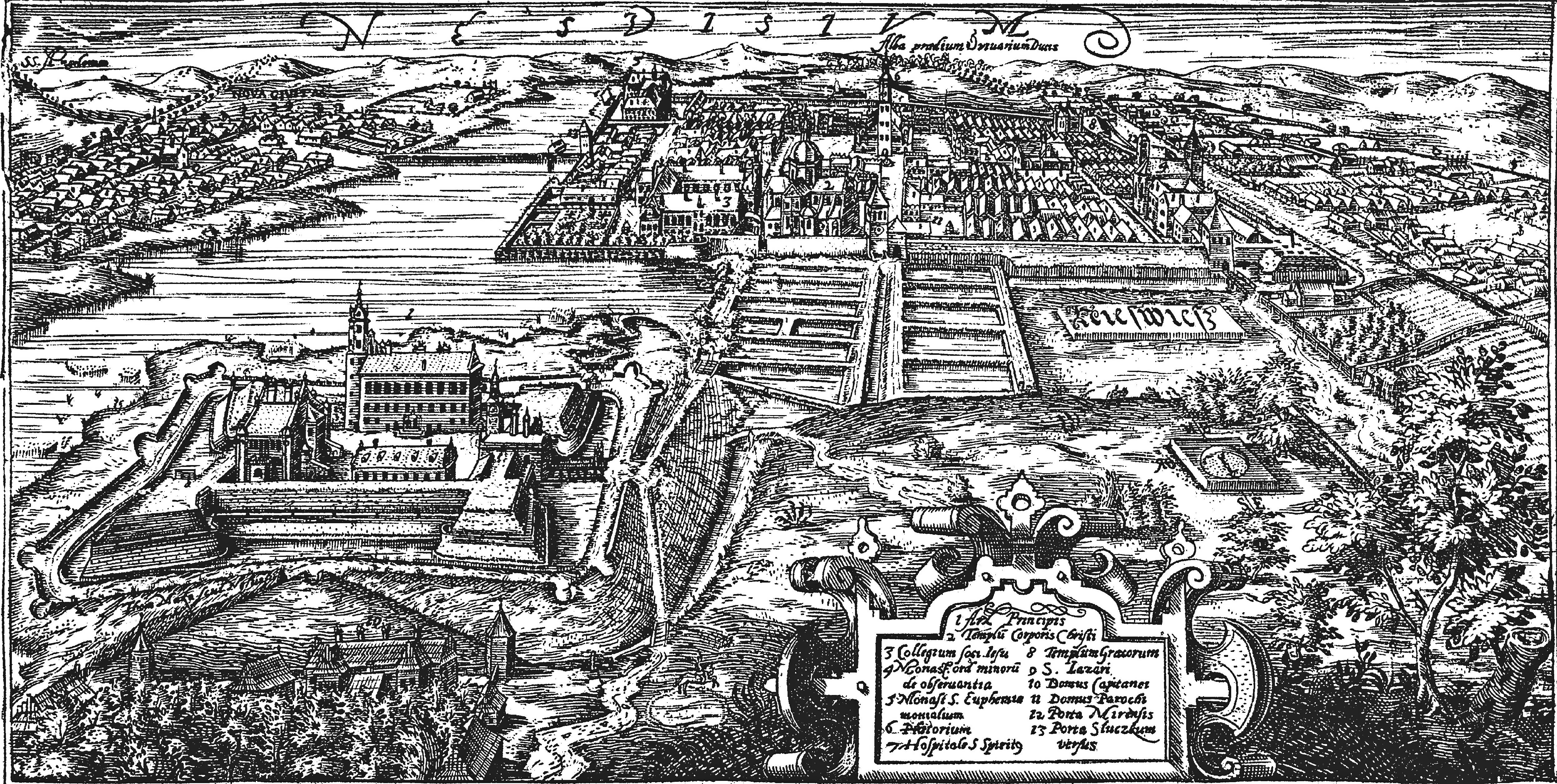
Nyasvizh
Nyasvizh or Nesvizh is a town in Minsk Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative centre of Nyasvizh District. Nyasvizh is the site of Nesvizh Castle, a World Heritage Site. In 2009, its population was 14,300. As of 2025, it has a population of 15,909. History Nesvizh was first documented in 1223. It was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania until 1793, but the Grand Duchy was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth since 1569. In the 15th century, while still a minor town, it belonged to the Kiszka family and later to the Radziwiłł family, and remained the family's seat until 1813. In 1561 or 1562 Maciej Kawęczyński founded the print works of the Polish Brethren. The first Belarusian language book printed in Latin script, a catechism by Symon Budny, was published in Nesvizh in 1562. The ''Nieśwież Bible'' ('' Biblia nieświeska''), one of the oldest Polish translations of the Bible, also by Budny, was completed there in 1571 and published in 1572. Nesvizh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdynand Radziwiłł
Prince Ferdynand Fryderyk Radziwiłł (1834 in Berlin – 1926 in Rome) was a Polish nobleman and Polish-German politician. Early life He was the son of Bogusław Fryderyk Radziwiłł and Leontyna von Clary und Aldringen. Through his paternal grandmother, Princess Louise of Prussia, he was a cousin of the German Emperors. He was educated in Berlin and received a law degree. Career During the Franco-Prussian War, he served as a soldier in the German army for one year. For much of his life he lived in the German Empire, where he was a member of the German parliament ( Reichstag) from 1874 to 1918. He was known as an important leader of the Polish minority and opponent of the Germanization and Kulturkampf policies. Prior to 1885, his political concerns fell mostly with the relation of the Church to the Kulturkampf. In 1901, he gave a speech at the Reichstag to protest the treatment of Polish school children in Września. In the speech, he denounced the alleged use o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
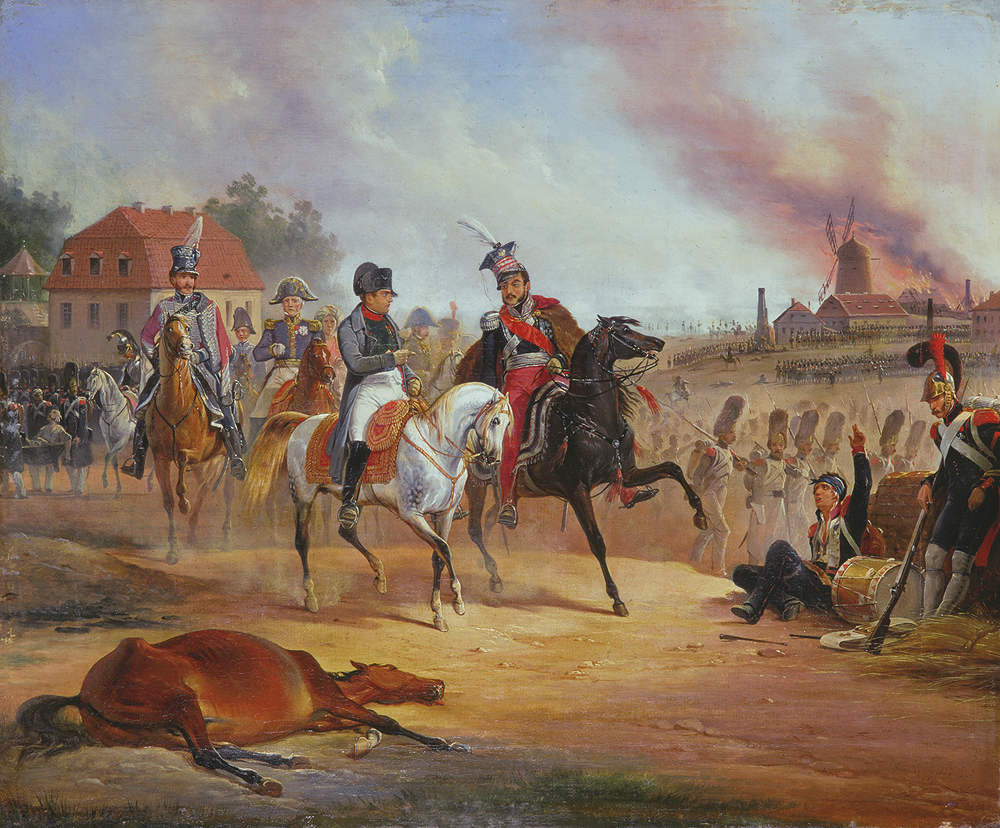
Battle Of Laon
The Battle of Laon, fought on March 9–10, 1814, was a pivotal engagement during the waning months of the Napoleonic Wars. Prelude Following his costly success at the Battle of Craonne, Napoleon sought to exploit the disarray within General Blücher's Army of Silesia. Blücher had retreated to the fortified hilltop town of Laon, where he consolidated his forces, reinforced by Prussian and Russian contingents. Laon's strategic significance lay in its role as a key road junction, dominating the terrain and offering natural defensive advantages. Napoleon, aware of the urgent need to halt Blücher's advance toward Paris, assembled a smaller but determined French force, weakened by casualties and stretched supply lines. Despite his strategic acumen, Napoleon faced a formidable challenge: a well-prepared, numerically superior Allied force under an experienced and resolute commander. The French approach to Laon was fraught with difficulties. Napoleon's troops were exhausted from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Leipzig
The Battle of Leipzig, also known as the Battle of the Nations, was fought from 16 to 19 October 1813 at Leipzig, Saxony. The Coalition armies of Austria, Prussia, Sweden, and Russia, led by Tsar Alexander I, Karl von Schwarzenberg, and Gebhard von Blücher decisively defeated the ''Grande Armée'' of French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. Napoleon's army also contained Polish and Italian troops, as well as Germans from the Confederation of the Rhine (mainly Saxony and Württemberg). The battle was the culmination of the German campaign of 1813 and involved about 560,000 soldiers, 2,200 artillery pieces, the expenditure of 400,000 rounds of artillery ammunition, and 133,000 casualties, making it the largest battle of the Napoleonic Wars, and the largest battle in Europe prior to World War I. Decisively defeated, Napoleon was compelled to return to France while the Sixth Coalition kept up its momentum, dissolving the Confederation of the Rhine and invading France early the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Wilhelm Freiherr Von Bülow
Friedrich Wilhelm Freiherr von Bülow, Graf von Dennewitz (16 February 175525 February 1816) was a Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian general of the Napoleonic Wars. Early life Bülow was born in Falkenberg (Wische), Falkenberg, in the Altmark, and was the elder brother of Freiherr Dietrich Heinrich von Bülow. A member of the noble Bülow family, he received an excellent education, and entered the Prussian army in 1768, becoming ensign (rank), ensign in 1772, and second lieutenant in 1775. He took part in the War of the Bavarian Succession of 1778, and subsequently devoted himself to the study of his profession and of the sciences and arts. Throughout his life, Bülow was devoted to music, his great musical ability bringing him to the notice of King Frederick William II of Prussia, and c. 1790 he was conspicuous in the most fashionable circles of Berlin. He did not, however, neglect his military studies, and in 1792 he was made military instructor to the young Prince Louis Ferdinand o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernhard Von Poten
Karl Georg Heinrich Bernhard von Poten (8 August 1828 – 22 November 1909), known as Bernhard von Poten, was a royal Prussian colonel best known for his military writing. Family and life Poten was born in Celle into a bourgeois family of officers from the Kingdom of Hanover. His parents were the Hannoversche Major Georg Poten (1799–1882) and Juliane Dorothea Kannengießer (1804–1841). His uncle Friedrich Poten (1779–1845), Hanoverian lieutenant colonel, was made hereditary baron in 1827 by Grand Duke Ludwig I of Baden. His nephew continued the baronial lineage. In 1861, Poten married Anna Sophie Elisabeth Behncke (1837–1905) in Celle. They had a son Heinrich Georg Wilhelm Alexander von Poten (1863–1920) also a Prussian major general and commander of the Cuirassiers in Brandenburg. Poten died in Berlin on 22 November 1909. Career Berhard von Poten served from 1847 to 1866 in the Hanover Military services. In 1847, he was a second lieutenant, and was promoted to fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnasium (school)
''Gymnasium'' (and Gymnasium (school)#By country, variations of the word) is a term in various European languages for a secondary school that prepares students for higher education at a university. It is comparable to the US English term ''University-preparatory school, preparatory high school'' or the British term ''grammar school''. Before the 20th century, the gymnasium system was a widespread feature of educational systems throughout many European countries. The word (), from Greek () 'naked' or 'nude', was first used in Ancient Greece, in the sense of a place for both physical and intellectual education of young men. The latter meaning of a place of intellectual education persisted in many European languages (including Albanian language, Albanian, Bulgarian language, Bulgarian, Czech language, Czech, Dutch language, Dutch, Estonian language, Estonian, Greek language, Greek, German language, German, Hungarian language, Hungarian, Macedonian language, Macedonian, Montene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Wilhelm Gymnasium
The Friedrich Wilhelm Gymnasium (or Friedrich-Wilhelms-Gymnasium) was a secondary school ( ''Gymnasium'') in Berlin. History The school originated from a Realschule founded by the Pietist Johann Julius Hecker in 1747, the first secondary school in Berlin. On its 50th anniversary in 1797, the school was renamed after Friedrich Wilhelm III, who had succeeded his father as King of Prussia earlier in that year, and wanted to improve the successful secondary school. He gave additional funds for an additional building to house the expanded school. The Friedrich Wilhelm Gymnasium buildings were located on Kochstrasse in Berlin's Friedrichstadt district. The grammar school was located on Kochstrasse at the corner of Friedrichstrasse 41 until 1890 (demolished) when it was relocated to a new building at Kochstrasse 13 (south side), built according to plans by building officer Friedrich Schulze from 1888 to 1890. The Realgymnasium and Elisabeth School were located at Kochstrasse 66 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
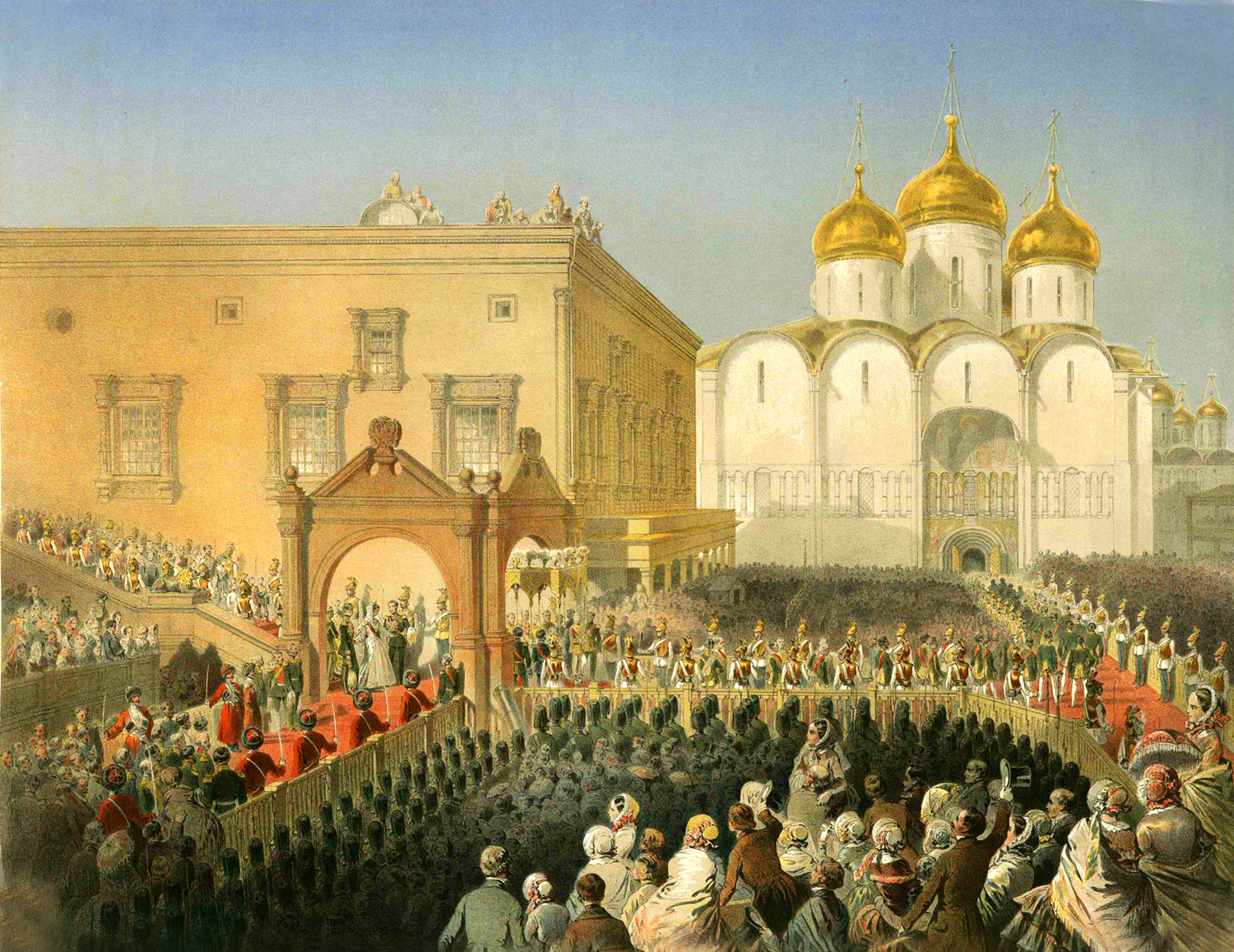
Alexander II Of Russia
Alexander II ( rus, Алекса́ндр II Никола́евич, Aleksándr II Nikoláyevich, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ftɐˈroj nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ; 29 April 181813 March 1881) was Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Finland from 2 March 1855 until Assassination of Alexander II of Russia, his assassination in 1881. Alexander's most significant reform as emperor was the emancipation reform of 1861, emancipation of Serfdom in Russia, Russia's serfs in 1861, for which he is known as Alexander the Liberator ( rus, Алекса́ндр Освободи́тель, r=Aleksándr Osvobodítel, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ɐsvəbɐˈdʲitʲɪlʲ). The tsar was responsible for other Liberalism, liberal reforms, including reorganizing the judicial system, setting up elected local judges, abolishing corporal punishment, promoting local self-government through the ''zemstvo'' system, imposing universal military service, ending some privileges of the nobility, and promot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George I Of Great Britain
George I (George Louis; ; 28 May 1660 – 11 June 1727) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 1 August 1714 and ruler of the Electorate of Hanover within the Holy Roman Empire from 23 January 1698 until his death in 1727. He was the first British monarch of the House of Hanover. Born in Hanover to Ernest Augustus, Elector of Hanover, Ernest Augustus and Sophia of Hanover, George inherited the titles and lands of the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg from his father and uncles. In 1682, he married his cousin Sophia Dorothea of Celle, with whom he had two children; he also had three daughters with his mistress Melusine von der Schulenburg. George and Sophia Dorothea divorced in 1694. A succession of European wars expanded George's German domains during his lifetime; he was ratified as prince-elector of Hanover in 1708. As the senior Protestant descendant of his great-grandfather James VI and I, George inherited the British throne following the deaths in 1714 of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick William I Of Prussia
Frederick William I (; 14 August 1688 – 31 May 1740), known as the Soldier King (), was King in Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg from 1713 until his death in 1740, as well as Prince of Neuchâtel. Born in Berlin, he was raised by the Huguenot governess Marthe de Roucoulle. His political awakening occurred during the Great Northern War's plague outbreak in Prussia, leading to his challenge against corruption and inefficiency in government. He initiated reforms, especially in the military, doubling the Prussian Army and increased the officer corps to 3,000. A believer in absolute monarchy, he focused on state development and financial reorganization, imposing taxes and stringent regulations on public servants. He made efforts to reduce crime and centralized his authority during his 27 years' reign, cementing Prussia as a regional power. Despite his effective rule, he had a harsh nature, exacerbated by his health issues. He engaged in colonial affairs, but prioritized militar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |