|
Wilderness First Aid
A wilderness medical emergency is a medical emergency that takes place in a wilderness or remote setting affinitive care (hospital, clinic, etc.). Such an emergency can require specialized skills, treatment techniques, and knowledge in order to manage the patient for an extended period of time before and during evacuation. Types Injury and illnesses * Arthropod bites and stings * Appendicitis (leading to peritonitis folkloric "what if" for long-distance sailing) * Ballistic trauma (gunshot wound when hunting) * Eye injuries (such as from branches) * Flail chest associated with ice climbing and snowclimbing falls * Hyperthermia (heat stroke or sunstroke) ** Malignant hyperthermia * Hypothermia * Frostbite * Poisoning ** Food poisoning associated with warm weather expeditions ** Venom (poison), Venomous animal bite ** Botanical from mushrooms or "wild greens"" * Severe Burn (injury), burn (forest fire) * Spreading wound infection * Suspected Vertebra, spinal injury from falls, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Emergency
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified person, as some of these emergencies, such as cardiovascular (heart), respiratory, and gastrointestinal cannot be dealt with by the victim themselves.AAOS 10th Edition Orange Book Dependent on the severity of the emergency, and the quality of any treatment given, it may require the involvement of multiple levels of care, from first aiders through emergency medical technicians, paramedics, emergency physicians and anesthesiologists. Any response to an emergency medical situation will depend strongly on the situation, the patient involved, and availability of resources to help them. It will also vary depending on whether the emergency occurs whilst in hospital under medical care, or outside medical care (for instance, in the street or alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venom (poison)
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a stinger, in a process called '' envenomation''. Venom is often distinguished from ''poison'', which is a toxin that is passively delivered by being ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, and '' toxungen'', which is actively transferred to the external surface of another animal via a physical delivery mechanism. Venom has evolved in terrestrial and marine environments and in a wide variety of animals: both predators and prey, and both vertebrates and invertebrates. Venoms kill through the action of at least four major classes of toxin, namely necrotoxins and cytotoxins, which kill cells; neurotoxins, which affect nervous systems; myotoxins, which damage muscles; and haemotoxins, which disrupt blood clotting. Venomous animals ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
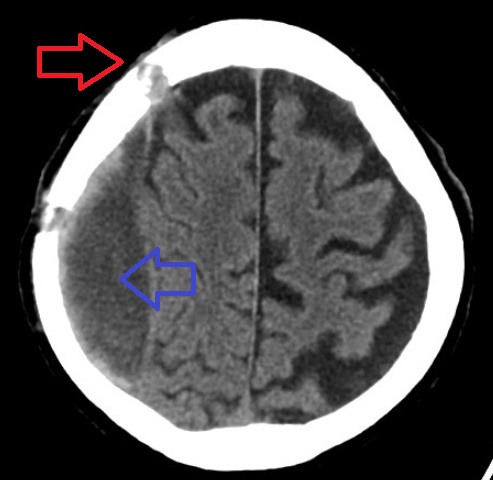
Subdural Hematoma
A subdural hematoma (SDH) is a type of bleeding in which a collection of blood—usually but not always associated with a traumatic brain injury—gathers between the inner layer of the dura mater and the arachnoid mater of the meninges surrounding the brain. It usually results from rips in bridging veins that cross the subdural space. Subdural hematomas may cause an increase in the pressure inside the skull, which in turn can cause compression of and damage to delicate brain tissue. Acute subdural hematomas are often life-threatening. Chronic subdural hematomas have a better prognosis if properly managed. In contrast, epidural hematomas are usually caused by rips in arteries, resulting in a build-up of blood between the dura mater and the skull. The third type of brain hemorrhage, known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), causes bleeding into the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. SAH are often seen in trauma settings, or after rupture of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of bacillus (shape), rod-shaped, (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two known species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' is the type species and is further divided into six subspecies that include over 2,650 serotypes. ''Salmonella'' was named after Daniel Elmer Salmon (1850–1914), an American veterinary surgeon. ''Salmonella'' species are non-Endospore, spore-forming, predominantly motility, motile enterobacteriaceae, enterobacteria with cell diameters between about 0.7 and 1.5 micrometre, μm, lengths from 2 to 5 μm, and peritrichous flagella (all around the cell body, allowing them to move). They are chemotrophs, obtaining their energy from Redox, oxidation and reduction reactions, using organic sources. They are also facultative aerobic organism, facultative anaerobes, capable of generating adenosine triphosphate with oxygen ("aerobically") ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. It was historically referred to as hydrophobia ("fear of water") because its victims panic when offered liquids to drink. Early symptoms can include fever and abnormal sensations at the site of exposure. These symptoms are followed by one or more of the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, violent movements, uncontrolled excitement, fear of water, an inability to move parts of the body, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Once symptoms appear, the result is virtually always death. The time period between contracting the disease and the start of symptoms is usually one to three months but can vary from less than one week to more than one year. The time depends on the distance the virus must travel along Peripheral nervous system, peripheral nerves to reach the central nervous system. Rabies is caused by lyssaviruses, including the rabies virus and Australian bat lyssavirus. It is spread when an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotizing Fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis (NF), also known as flesh-eating disease, is an infection that kills the body's soft tissue. It is a serious disease that begins and spreads quickly. Symptoms include red or purple or black skin, swelling, severe pain, fever, and vomiting. The most commonly affected areas are the limb (anatomy), limbs and perineum. Bacterial infection is by far the most common cause of necrotizing fasciitis. Despite being called a "flesh-eating disease", bacteria do not eat human tissue. Rather, they release toxins that cause tissue death. Typically, the infection enters the body through a break in the skin such as a cut or burn. Risk factors include recent trauma or surgery and immunodeficiency, a weakened immune system due to diabetes or cancer, obesity, alcoholism, intravenous drug use, and peripheral artery disease. It does not usually spread between people. The disease is classified into four types, depending on the infecting organisms. Medical imaging is often helpfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration
Exploration is the process of exploring, an activity which has some Expectation (epistemic), expectation of Discovery (observation), discovery. Organised exploration is largely a human activity, but exploratory activity is common to most organisms capable of directed Animal locomotion, locomotion and the ability to learn, and has been described in, amongst others, social insects foraging behaviour, where feedback from returning individuals affects the activity of other members of the group. Types Geographical Geographical exploration, sometimes considered the default meaning for the more general term exploration, is the practice of discovering lands and regions of the planet Earth remote or relatively inaccessible from the origin of the explorer. The surface of the Earth not covered by water has been relatively comprehensively explored, as access is generally relatively straightforward, but underwater and subterranean areas are far less known, and even at the surface, much is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, Epileptic seizure, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected ''Anopheles'' mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial Immunity (medical), resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. The mosquitoes themselves are harmed by malaria, causing reduced lifespans in those infected by it. Malaria is caused by protozoa, single-celled microorganisms of the genus ''Plasmodium''. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a tick-borne disease caused by species of ''Borrelia'' bacteria, Disease vector, transmitted by blood-feeding ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. It is the most common disease spread by ticks in the Northern Hemisphere. Infections are most common in the spring and early summer. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and fatigue (medical), tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include Facial nerve paralysis, loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, arthritis, joint pains, Meningitis, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later, repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally, shootin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traumatic Brain Injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumatic brain injury. TBI can also be characterized based on mechanism (closed head injury, closed or penetrating head injury) or other features (e.g., occurring in a specific location or over a widespread area). Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional and behavioral symptoms, and outcomes can range from complete recovery to permanent disability or death. Causes include Falling (accident), falls, vehicle collisions, and violence. Brain trauma occurs as a consequence of a sudden acceleration or deceleration of the brain within the skull or by a complex combination of both movement and sudden impact. In addition to the damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an Disease#Terminology, illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune systems. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an Innate immune system, innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an Adaptive immune system, adaptive response. Treatment for infections depends on the type of pathogen involved. Common medications include: * Antibiotics for bacterial infections. * Antivirals for viral infections. * Antifungals for fungal infections. * Antiprotozoals for protozoan infections. * Antihelminthics for infections caused by parasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |