|
Western Division, Royal Artillery
The Western Division, Royal Artillery, was an administrative grouping of garrison units of the Royal Artillery, Militia (United Kingdom), Artillery Militia and Volunteer Force, Artillery Volunteers within the British Army's Western Command (United Kingdom), Western District from 1882 to 1902. Organisation Under General Order 72 of 4 April 1882 the Royal Artillery (RA) broke up its existing administrative brigades of garrison artillery (7th–11th Brigades, RA) and assigned the individual Battery (artillery), batteries to 11 new territorial divisions. These divisions were purely administrative and recruiting organisations, not field formations. Most were formed within the existing military districts into which the United Kingdom was divided, and for the first time associated the part-time Militia (United Kingdom), Artillery Militia with the regulars. Shortly afterwards the Volunteer Force, Artillery Volunteers were also added to the territorial divisions. The British Army, Regular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The British Army
A flag is a piece of textile, fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the Maritime flag, maritime environment, where Flag semaphore, semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as "vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
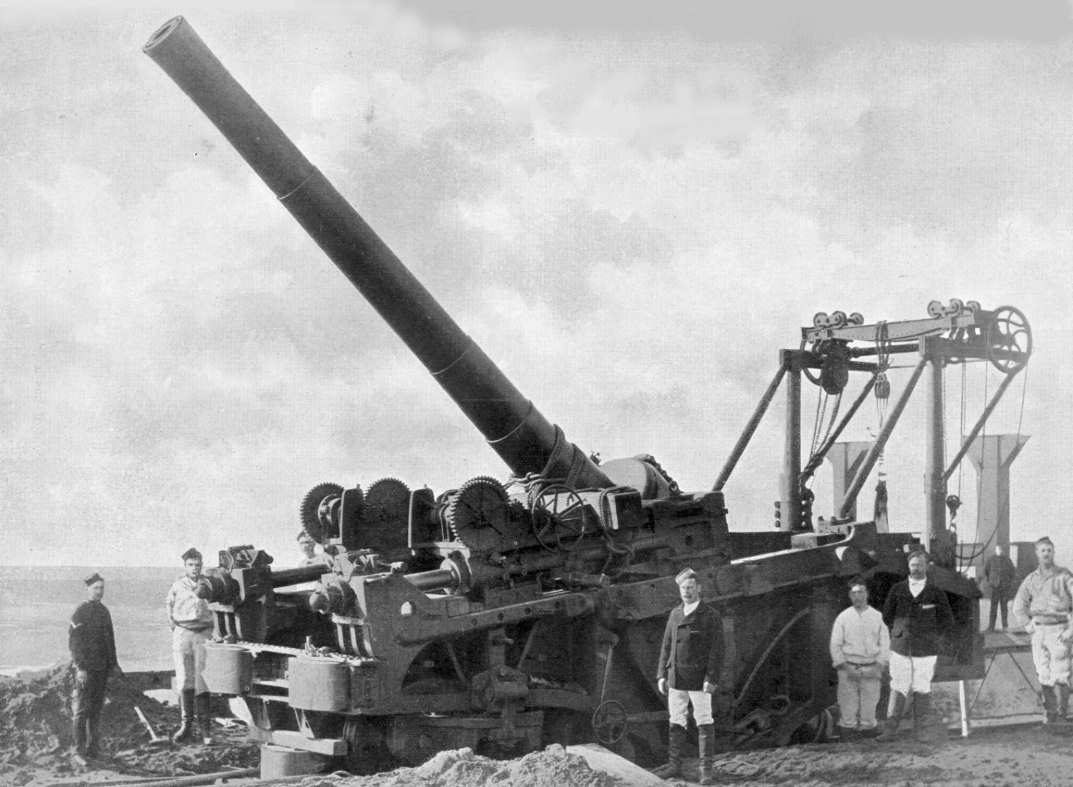
Camden Fort Meagher
Camden Fort Meagher is a Coastal defence and fortification, coastal defence fortification close to Crosshaven, County Cork, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Together with similar structures at Fort Mitchell (Spike Island, County Cork, Spike Island), Fort Davis (Whitegate, County Cork, Whitegate), and Templebreedy Battery (also close to Crosshaven), the fort was built to defend the mouth of Cork Harbour. Though originally constructed in the 16th century, the current structures of the fort date to the 1860s. Originally named ''Fort Camden'' and operated by the British Armed Forces, the fort (along with other Treaty Ports (Ireland), Treaty Port installations) was handed-over to the Irish Defence Forces in 1938. Renamed ''Fort Meagher'' in honour of Thomas Francis Meagher, it remained an Irish military installation until 1989 when the Irish Army handed the fort over to Cork County Council. It remained largely overgrown until 2010 when a group of local volunteers began restoration and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodmin
Bodmin () is a town and civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated south-west of Bodmin Moor. The extent of the civil parish corresponds fairly closely to that of the town so is mostly urban in character. It is bordered to the east by Cardinham parish, to the southeast by Lanhydrock parish, to the southwest and west by Lanivet parish, and to the north by Helland parish. Bodmin had a population of 14,736 as of the 2011 Census. It was formerly the county town of Cornwall until the Crown Courts moved to Truro which is also the administrative centre (before 1835 the county town was Launceston, Cornwall, Launceston). Bodmin was in the administrative North Cornwall District until local government reorganisation in 2009 abolished the District (''see also Politics of Cornwall, Cornwall Council''). The town is part of the North Cornwall (UK Parliament constituency), North Cornwall parliamentary constituency, which is represented by Ben Maguire MP. Bodmin Town Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
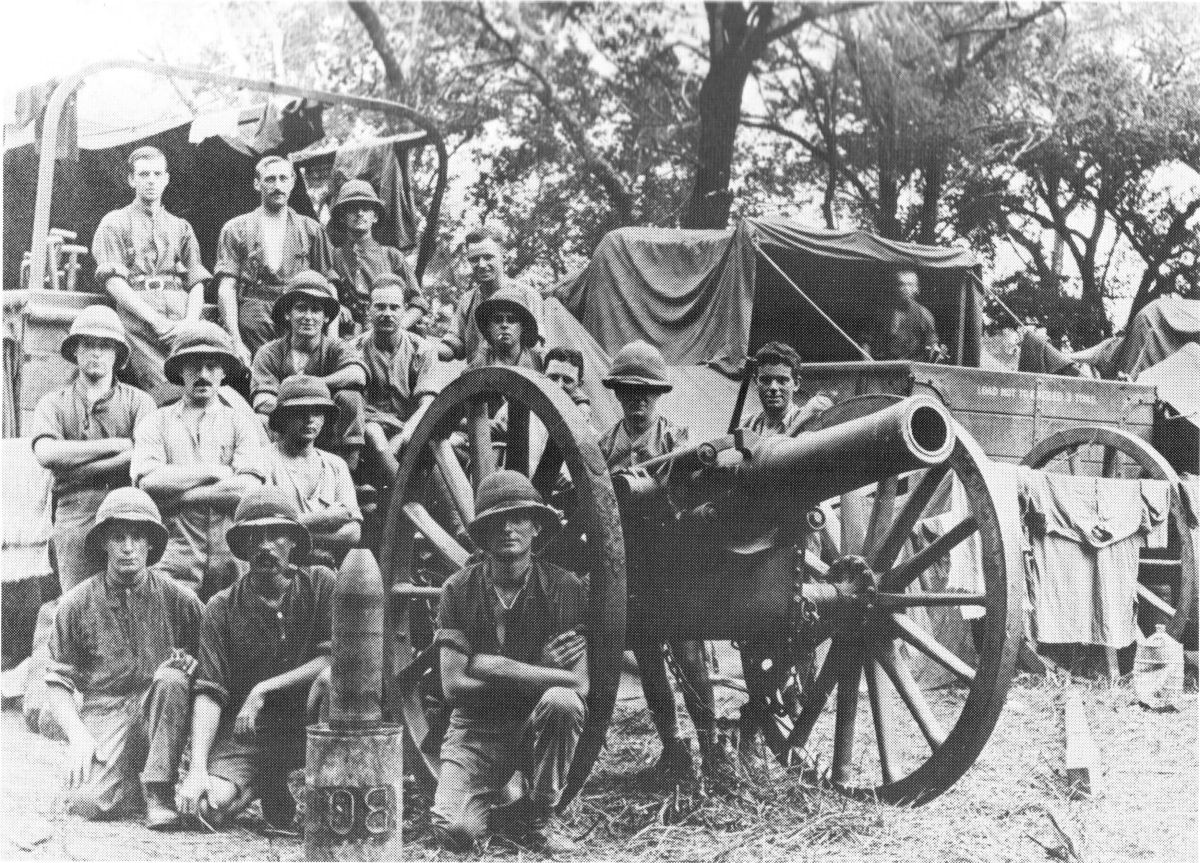
1st Cornwall (Duke Of Cornwall's) Artillery Volunteers
The 1st Cornwall (Duke of Cornwall's) Artillery Volunteers were formed in 1860 as a response to a French invasion threat. They served as a Coast Artillery unit during both World Wars, and also manned batteries serving overseas. The unit continued in existence until the dissolution of Coast Artillery in the UK in 1956. Artillery Volunteers 1859–1908 The Volunteer Force (Great Britain), Volunteer Force came into existence in 1859 as a result of an invasion scare and the consequent enthusiasm for joining local Rifle, Artillery and Engineer Volunteer Corps. By 24 May 1860 there were enough Artillery Volunteer Corps (AVCs) in Cornwall to form an Administrative Brigade with its Headquarters (HQ) at Bodmin to include all the AVCs in the county. From July 1861 the 1st Admin Brigade of Cornwall Artillery Volunteers appeared in the ''Army List'' under the title of The Duke of Cornwall's Artillery Volunteers, for which Queen Victoria gave special permission. The brigade had the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Devonshire Artillery Volunteers
The 2nd Devonshire Artillery Volunteers was a unit of the British Volunteer Force and Territorial Army. The unit and its successors defended Plymouth Dockyard and the Devon coast from 1861 to 1961. Origin The 2nd Administrative Brigade, Devonshire Artillery Volunteers was formed at Devonport, Plymouth on 3 January 1861 as a headquarters for a number of Artillery Volunteer Corps (AVCs) that had been raised in Devonshire in response to the invasion scare of 1859. A 1st Administrative Brigade had been formed the previous year, but the number of units in the county had continued to grow and they were split between the two headquarters. The 2nd Admin Brigade took the units in the western part of the county and was based at Devonport, Plymouth, with the following composition:Litchfield & Westlake, pp. 52–3.Frederick, p. 654.Maurice-Jones, pp. 164–5. * 6th ( Dartmouth) Devonshire AVC, raised 25 January 1860; transferred from 1st to 2nd Administrative Brigade in January 1861 * 10th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exeter
Exeter ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and the county town of Devon in South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol. In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal command of Vespasian. Exeter became a religious centre in the Middle Ages. Exeter Cathedral, founded in the mid 11th century, became Anglicanism, Anglican in the 16th-century English Reformation. Exeter became an affluent centre for the wool trade, although by the First World War the city was in decline. After the Second World War, much of the city centre was rebuilt and is now a centre for education, business and tourism in Devon and Cornwall. It is home to two of the constituent campuses of the University of Exeter: Streatham Campus, Streatham and St Luke's Campus, St Luke's. The administrative area of Exeter has the status of a non-metropolitan district under the administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Devonshire Artillery Volunteers
The 1st Devonshire Artillery Volunteers and its successor units served in the British Army's Army Reserve (United Kingdom), Reserve Forces from 1859 to 1961. During World War I it carried out garrison duty in British Raj, British India but went on to see active service in the Third Anglo-Afghan War. Converting to an air defence role before World War II its units participated in the Norwegian campaign and the Dunkirk evacuation, the Battle of Britain and then the campaigns in North African campaign, North Africa, Italian campaign (World War II), Italy, and Burma campaign, Burma Volunteer Force The Volunteer Force (Great Britain), Volunteer Force came into existence in 1859 as a result of an invasion scare and the consequent enthusiasm for joining local Rifle, Artillery and Engineer Volunteer Corps. By 8 August 1860 there were already enough Artillery Volunteer Corps (AVCs) in Devonshire to form an Administrative Brigade with its Headquarters (HQ) at Teignmouth:Frederick, p. 654.Litc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devon Artillery Militia
The North Devon Militia, later the Devon Artillery Militia, was a part-time military unit in the maritime county of Devonshire in the West of England. The Militia had always been important in the county, which was vulnerable to invasion, and from its formal creation in 1758 the regiment served in home defence in all Britain's major wars until 1909. Having always been an infantry regiment, the North Devon Militia was converted into an artillery unit in 1853, with a role in manning the forts that protected the vital naval base at Plymouth. Background The universal obligation to military service in the Shire levy was long established in England and its legal basis was updated by two acts of 1557 ( 4 & 5 Ph. & M. cc. 2 and 3), which placed selected men, the ' Trained Bands', under the command of Lords Lieutenant appointed by the monarch. This is seen as the starting date for the organised county militia in England. The Devon Trained Bands were divided into three 'Divisions' (East, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall And Devon Miners Artillery Militia
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, Devon to the east, and the English Channel to the south. The largest urban area is the Redruth and Camborne conurbation. The county is predominantly rural, with an area of and population of 568,210. After the Redruth-Camborne conurbation, the largest settlements are Falmouth, Cornwall, Falmouth, Penzance, Newquay, St Austell, and Truro. For Local government in England, local government purposes most of Cornwall is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, with the Isles of Scilly governed by a Council of the Isles of Scilly, unique local authority. The Cornish nationalism, Cornish nationalist movement disputes the constitutional status of Cornwall and seeks greater autonomy within the United Kingdom. Cornwall is the weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falmouth, Cornwall
Falmouth ( ; ) is a town, civil parish and port on the River Fal on the south coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. Falmouth was founded in 1613 by the Killigrew family on a site near the existing Pendennis Castle. It developed as a port on the Carrick Roads harbour, overshadowing the earlier town of Penryn, Cornwall, Penryn. In the 19th century after the arrival of the railways, tourism became important to its economy. In modern times, both industries maintain a presence in Falmouth and the town is also home to the National Maritime Museum Cornwall, a campus of Falmouth University and Falmouth Art Gallery. Etymology The name Falmouth is of English language, English origin, a reference to the town's situation on the mouth (river), mouth of the River Fal. The Cornish language name, or , is of identical meaning. History Early history In 1540, Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII built Pendennis Castle in Falmouth to defend Carrick Roads. The main town of the distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga, and St. Brandon (Cargados Carajos shoals). The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, along with nearby Réunion (a French overseas department), are part of the Mascarene Islands. The main island of Mauritius, where the population is concentrated, hosts the capital and largest city, Port Louis. The country spans and has an exclusive economic zone covering approximately . The 1502 Portuguese Cantino planisphere has led some historians to speculate that Arab sailors were the first to discover the uninhabited island around 975, naming it ''Dina Arobi''. Called ''Ilha do Cirne'' or ''Ilha do Cerne'' on early Portuguese maps, the island was visited by Portuguese sailors in 1507. A Dutch fleet, under the command of Admiral Van War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( ) is a rocky headland on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa. A List of common misconceptions#Geography, common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Africa, based on the misbelief that the Cape was the dividing point between the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic and Indian Ocean, Indian oceans. In fact, the southernmost point of Africa is Cape Agulhas about to the east-southeast. The currents of the two oceans meet at the point where the warm-water Agulhas current meets the cold-water Benguela current and turns back on itself. That oceanic meeting point fluctuates between Cape Agulhas and Cape Point (about east of the Cape of Good Hope). When following the western side of the African coastline from the equator, however, the Cape of Good Hope marks the point where a ship begins to travel more eastward than southward. Thus, the first modern rounding of the cape in 1487 by Portuguese discoveries, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |