|
Werner Tübke
Werner Tübke (30 July 1929 in Schönebeck, Germany – 27 May 2004 in Leipzig, Germany) was a German painter, best known for his monumental Early Bourgeois Revolution in Germany, Peasants' War Panorama located in Bad Frankenhausen. Associated with the Leipzig School (painting), Leipzig School, he is "one of the few East German artists who gained recognition in West Germany." History Tübke was born in 1929 into a merchant family. At the age of 17, Tübke spent 10 months in Soviet occupation zone of Germany, Soviet occupation authorities' prison without charge. He learned the trade of a building painter in Schönebeck (Elbe) and Magdeburg. After completing his high school education late, Tübke studied from 1948 to 1950 at the Higher School of Graphic Arts and Book Design in Leipzig. From 1953 to 1954, he conducted research work at the Central House of Folk Art in Leipzig. From 1954 to 1956 and 1957 to 1963, he worked as an independent artist. From 1956 to 1957, he was a senior a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Honecker
Erich Ernst Paul Honecker (; 25 August 1912 – 29 May 1994) was a German communist politician who led the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) from 1971 until shortly before the fall of the Berlin Wall in November 1989. He held the posts of General Secretary of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) and National Defence Council of East Germany, Chairman of the National Defence Council; in 1976, he replaced Willi Stoph as State Council of East Germany, Chairman of the State Council, the official head of state. As the leader of East Germany, Honecker was viewed as a dictator. During his leadership, the country had close ties to the Soviet Union, which maintained Group of Soviet Forces in Germany, a large army in the country. Honecker's political career began in the 1930s when he became an official of the Communist Party of Germany, a position for which he was imprisoned by the Nazi Germany, Nazis. Following World War II, he was freed by the Soviet army and relaunched h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
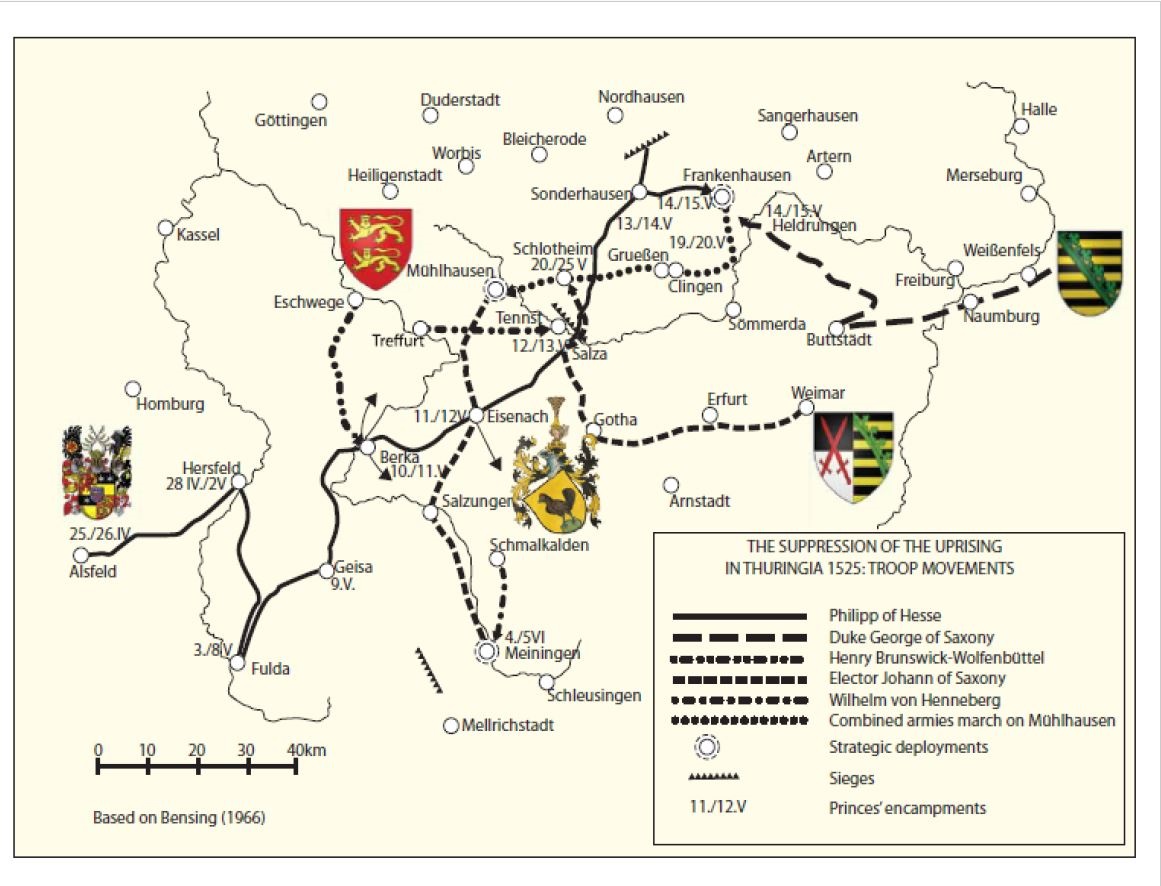
Battle Of Frankenhausen
The Battle of Frankenhausen was fought on 14 and 15 May 1525. It was an important battle in the German Peasants' War and the final act of the war in Thuringia: joint troops of Landgrave Philip I of Hesse and Duke George of Saxony defeated the peasants under their spiritual leader Thomas Müntzer near Frankenhausen in the County of Schwarzburg. Preparations On April 29, 1525, the struggles in and around Frankenhausen had culminated into an open revolt. Large parts of the citizenry joined the uprising, occupied the town hall, and stormed the castle of the Counts of Schwarzburg. In the following days, a rising number of insurgents gathered around the town, and when Müntzer arrived with 300 fighters from Mühlhausen on May 11, several thousand peasants of the surrounding Thuringian and Saxon estates camped in the fields and pastures. Philip of Hesse and his father-in-law George of Saxony had originally targeted Mühlhausen as their strategic objective but, when news arri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triptych
A triptych ( ) is a work of art (usually a panel painting) that is divided into three sections, or three carved panels that are hinged together and can be folded shut or displayed open. It is therefore a type of polyptych, the term for all multi-panel works. The middle panel is typically the largest and it is flanked by two smaller related works, although there are triptychs of equal-sized panels. The form can also be used for pendant jewelry. Beyond its association with art, the term is sometimes used more generally to connote anything with three parts, particularly if integrated into a single unit. Etymology The word ''triptych'' was formed in English by compounding the prefix '' tri-'' with the word '' diptych''. ''Diptych'' is borrowed from the Latin , which itself is derived from the Late Greek () . is the neuter plural of () . In art The triptych form appears in early Christian art, and was a popular standard format for altar paintings from the Middle Ages onwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altarpiece
An altarpiece is a painting or sculpture, including relief, of religious subject matter made for placing at the back of or behind the altar of a Christian church. Though most commonly used for a single work of art such as a painting or sculpture, or a set of them, the word can also be used of the whole ensemble behind an altar, otherwise known as a reredos, including what is often an elaborate frame for the central image or images. Altarpieces were one of the most important products of Christian art especially from the late Middle Ages to the era of Baroque painting. The word altarpiece, used for paintings, usually means a framed work of panel painting on wood, or later on canvas. In the Middle Ages they were generally the largest genre for these formats. Murals in fresco tend to cover larger surfaces. The largest painted altarpieces developed complicated structures, especially winged altarpieces with hinged side wings that folded in to cover the main image, and were painted o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonn
Bonn () is a federal city in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located on the banks of the Rhine. With a population exceeding 300,000, it lies about south-southeast of Cologne, in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region. This metropolitan area, Germany's largest, is also the second largest in the European Union by GDP, with over 11 million residents. Bonn served as the capital of West Germany from 1949 until 1990 and was the seat of government for reunified Germany until 1999, when the government relocated to Berlin. The city holds historical significance as the birthplace of Germany's current constitution, the Basic Law. Founded in the 1st century BC as a settlement of the Ubii and later part of the Roman province Germania Inferior, Bonn is among Germany's oldest cities. It was the capital city of the Electorate of Cologne from 1597 to 1794 and served as the residence of the Archbishops and Prince-electors of Cologne. The period during which Bonn was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Der Freischütz
' (Friedrich Wilhelm Jähns, J. 277, Opus number, Op. 77 ''The Marksman'' or ''The Freeshooter'') is a German List of operas by Carl Maria von Weber, opera with spoken dialogue in three acts by Carl Maria von Weber with a libretto by Johann Friedrich Kind, Friedrich Kind, based on a story by Johann August Apel and Friedrich Laun from their 1810 collection ''Gespensterbuch''. It premiered on 18 June 1821 at the Schauspielhaus Berlin. It is considered the first German Romantische Oper, Romantic opera. The opera's plot is mainly based on Johann August Apel, August Apel's tale "Der Freischütz" from the ''Gespensterbuch'' though the hermit, Kaspar and Ännchen are new to Kind's libretto. That Weber's tunes were just German folk music is a common misconception. Its unearthly portrayal of the supernatural in the famous Wolf's Glen scene has been described as "the most expressive rendering of the gruesome that is to be found in a musical score". Performance history The reception of ''De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Maria Von Weber Museum
The Carl Maria von Weber Museum is a cultural site in Dresden, in Saxony, Germany. The composer Carl Maria von Weber (1786–1826) lived here during part of his career; the house is now a museum about his life and work. History Weber in Hosterwitz The building is the only home of the composer still in existence. It is in , at that time a village, now part of Dresden, and was originally a vine-grower's house. It was rented by Weber from Gottfried Felsner; during the summer months from 1818 to 1819, and 1822 to 1824, the composer and his family lived here."Carl Maria von Weber Museum Dresden" Music Museums in Germany. Retrieved 30 May 2023. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astoria Hotel (Leipzig)
Hotel Astoria may refer to: * Hotel Astoria, Brussels, later Corinthia Grand Hotel Astoria, Belgium * Hotel Astoria (Copenhagen), Denmark * Danubius Hotel Astoria, Budapest, Hungary * Hotel Astoria (Saint Petersburg), Russia * Hotel Astoria (Belgrade), later Queen's Astoria Design Hotel, Serbia * Hotel Astoria (Oregon), later John Jacob Astor Hotel, in Astoria, Oregon, United States * Hotel Astoria at the Waldorf-Astoria (1893–1929), in Manhattan, New York, United States * Astoria Hotels and Resorts, Philippine hotel chain * Astoria Hotel (Vancouver) * Astoria Palace Hotel, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil * Waldorf-Astoria (other) See also * * Astoria Palace Hotel, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil * Waldorf-Astoria (other) Waldorf Astoria New York is a historic Manhattan hotel built in 1931. Waldorf-Astoria may also refer to: * Waldorf-Astoria (1893–1929), the predecessor of the current Waldorf Astoria New York * Waldorf Astoria Hotels & Resorts, a hospitality hot ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath who formulated a mathematical model, model of Celestial spheres#Renaissance, the universe that placed heliocentrism, the Sun rather than Earth at its center. Copernicus likely developed his model independently of Aristarchus of Samos, an List of ancient Greek astronomers, ancient Greek astronomer who had formulated such a model some eighteen centuries earlier. The publication of Copernicus' model in his book ' (''On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres''), just before his death in 1543, was a major event in the history of science, triggering the Copernican Revolution and making a pioneering contribution to the Scientific Revolution. Copernicus was born and died in Royal Prussia, a semiautonomous and multilingual region created within the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland from lands regained from the Teutonic Order after the Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466), Thirteen Years' War. A Poly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Luther
Martin Luther ( ; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, Theology, theologian, author, hymnwriter, professor, and former Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. Luther was the seminal figure of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, and his theological beliefs form the basis of Lutheranism. He is widely regarded as one of the most influential figures in Western world, Western and History of Christianity, Christian history. Born in Eisleben, Luther was ordained to the Priesthood in the Catholic Church, priesthood in 1507. He came to reject several teachings and practices of the contemporary Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Church, in particular the view on indulgences and papal authority. Luther initiated an international debate on these in works like his ''Ninety-five Theses'', which he authored in 1517. In 1520, Pope Leo X demanded that Luther renounce all of his writings, and when Luther refused to do so, Excommunication in the Catholic Church, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Borodino
The Battle of Borodino ( ) or Battle of Moscow (), in popular literature also known as the Battle of the Generals, took place on the outskirts of Moscow near the village of Borodino on 7 September 1812 during Napoleon's invasion of Russia. The ' fought against the Imperial Russian Army. After the Russian retreat in the Battle of Smolensk the road to Moscow lay open. Napoleon fought against General Mikhail Kutuzov, whom the Emperor Alexander I had appointed to replace Barclay de Tolly on 29 August 1812 after Smolensk was razed and captured by the French army. After the Battle of Borodino, Napoleon remained on the battlefield with his army; the Imperial Russian forces retreated southwards. What followed was the French occupation of Moscow, while the retreating Russians resorted to scorched earth tactics to trap Napoleon and his men within their own largest city. The failure of the ' to completely destroy the Imperial Russian army, and in particular Napoleon's reluctance to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents within the city limits, over 19.1 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in Moscow metropolitan area, its metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's List of largest cities, largest cities, being the List of European cities by population within city limits, most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest List of urban areas in Europe, urban and List of metropolitan areas in Europe, metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow became the capital of the Grand Principality of Moscow, which led the unification of the Russian lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |