|
Wechsler Individual Achievement Test
The Wechsler Individual Achievement Test Second Edition (WIAT-II; Wechsler, 2005) assesses the academic achievement of children, adolescents, college students and adults, aged 4 through 85. The test enables the assessment of a broad range of academics skills or only a particular area of need. The WIAT-II is a revision of the original WIAT ( The Psychological Corporation), and additional measures. There are four basic scales: Reading, Math, Writing and Oral Language. Within these scales there is a total of 9 sub-test scores. History The first WIAT was published in 1992 and it was standardized in UK and published as the word, "WOND and WOLD". It was revised in 2001 and followed by the UK version in 2005. Each revision has brought with it several updates and changes. The WIAT-II contains the basic contacademically. There are a small number of differences made between the versions of the subtests in the UK and US. These include changes in the picture items, replacing of Americanisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Achievement
Academic achievement or academic performance is the extent to which a student, teacher or institution has attained their short or long-term educational goals. Completion of educational benchmarks such as secondary school diplomas and bachelor's degrees represent academic achievement. Academic achievement is commonly measured through Test (assessment), examinations or continuous assessments but there is no general agreement on how it is best evaluated or which aspects are most important—procedural knowledge such as skills or declarative knowledge such as facts. Furthermore, there are inconclusive results over which individual factors successfully predict academic performance, elements such as test anxiety, environment, motivation, and emotions require consideration when developing models of school achievement. In California, the achievement of schools is measured by the Academic Performance Index (California public schools), Academic Performance Index. Academic achievement is som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Psychological Corporation
Harcourt Assessment was a company that published and distributed educational and psychological assessment tools and therapy resources and provided educational assessment and data management services for national, state, district and local assessments. On January 30, 2008, Harcourt Assessment was merged into Pearson's Assessment & Information group after being acquired from Reed Elsevier for $950 million. History Harcourt Assessment's history dates to the early part of the 20th century. Although the company name derives from Harcourt Brace & Company, which was established in 1919, the corporate heritage goes back to 1905 and the founding of World Book Company. Many of the educational products produced by Harcourt Assessment originated at World Book. The psychological assessments originated at The Psychological Corporation, which was founded in 1921. Harcourt Brace & Company (1919) Alfred Harcourt and Donald Brace were friends at Columbia University in New York, and both wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silent Reading
Silent reading is reading done silently, or without speaking the words being read. Before the reintroduction of separated text (spaces between words) in the Late Middle Ages, the ability to read silently may have been considered rather remarkable, though some scholars object to this idea. In contrast, reading aloud activates many more parts of the brain due to the dual-route of feedback when pronouncing and reading. History Scholars assume that reading aloud (Latin ''clare legere'') was the more common practice in antiquity, and that reading silently (''legere tacite'' or ''legere sibi'') was unusual.Carruthers, Mary. 2008. ''The Book of Memory: A Study of Memory in Medieval Culture''. 2nd. ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 212 ff. In his ''Confessions'', Saint Augustine remarks on Saint Ambrose's unusual habit of reading silently in the 4th century AD: "When Ambrose read, his eyes ran over the columns of writing and his heart searched out the meaning, but hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoword
A pseudoword is a unit of speech or text that appears to be an actual word in a certain language, while in fact it has no meaning. It is a specific type of nonce word, or even more narrowly a nonsense word, composed of a combination of phonemes which nevertheless conform to the language's phonotactic rules. It is thus a kind of vocable: utterable but meaningless. Such words lacking a meaning in a certain language or absent in any text corpus or dictionary can be the result of (the interpretation of) a truly random signal, but there will often be an underlying deterministic source, as is the case for examples like ''jabberwocky'' and '' galumph'' (both coined in a nonsense poem by Lewis Carroll), '' dord'' (a ghost word published due to a mistake), ciphers, and typos. A string of nonsensical words may be described as gibberish. Word salad, in contrast, may contain legible and intelligible words but without semantic or syntactic correlation or coherence. Characteristics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Consistency
In statistics and research, internal consistency is typically a measure based on the correlations between different items on the same test (or the same subscale on a larger test). It measures whether several items that propose to measure the same general construct produce similar scores. For example, if a respondent expressed agreement with the statements "I like to ride bicycles" and "I've enjoyed riding bicycles in the past", and disagreement with the statement "I hate bicycles", this would be indicative of good internal consistency of the test. Cronbach's alpha Internal consistency is usually measured with Cronbach's alpha, a statistic calculated from the pairwise correlations between items. Internal consistency ranges between negative infinity and one. Coefficient alpha will be negative whenever there is greater within-subject variability than between-subject variability. A commonly accepted rule of thumb for describing internal consistency is as follows: Very high reliabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability (statistics)
In statistics and psychometrics, reliability is the overall consistency of a measure. A measure is said to have a high reliability if it produces similar results under consistent conditions:It is the characteristic of a set of test scores that relates to the amount of random error from the measurement process that might be embedded in the scores. Scores that are highly reliable are precise, reproducible, and consistent from one testing occasion to another. That is, if the testing process were repeated with a group of test takers, essentially the same results would be obtained. Various kinds of reliability coefficients, with values ranging between 0.00 (much error) and 1.00 (no error), are usually used to indicate the amount of error in the scores. For example, measurements of people's height and weight are often extremely reliable.The Marketing Accountability Standards Board (MASB) endorses this definition as part of its ongoinCommon Language: Marketing Activities and Metrics Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
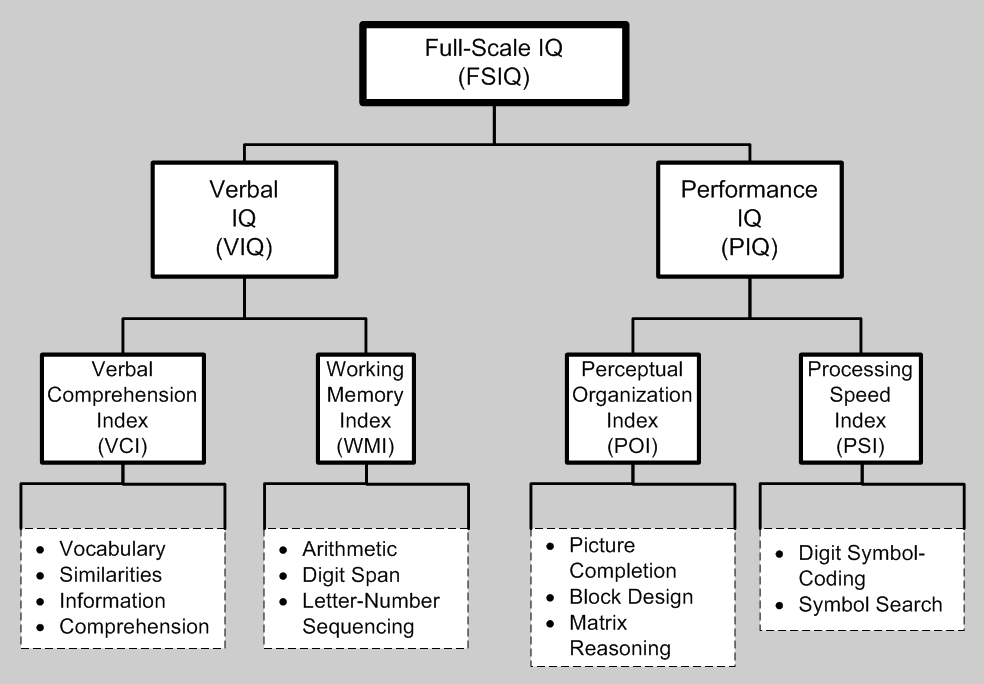
Wechsler Intelligence Scale For Children
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) is an individually administered intelligence test for children between the ages of 6 and 16. The Fifth Edition (WISC-V; Wechsler, 2014) is the most recent version. The WISC-V takes 45 to 65 minutes to administer. It generates a Full Scale IQ (formerly known as an intelligence quotient or IQ score) that represents a child's general intellectual ability. It also provides five primary index scores, namely Verbal Comprehension Index, Visual Spatial Index, Fluid Reasoning Index, Working Memory Index, and Processing Speed Index. These indices represent a child's abilities in discrete cognitive domains. Five ancillary composite scores can be derived from various combinations of primary or primary and secondary subtests. Five complementary subtests yield three complementary composite scores to measure related cognitive abilities. Technical papers by the publishers support other indices such as VECI, EFI, and GAI (Raiford et al., 2015). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WPPSI
The Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (WPPSI) is an intelligence test designed for children ages 2 years 6 months to 7 years 7 months developed by David Wechsler in 1967. It is a descendant of the earlier Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale and the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children tests. Since its original publication the WPPSI has been revised three times in 1989, 2002, (followed by the UK version in 2003) and 2012. The latest version, WPPSI–IV, published by Pearson Education, is a revision of the WPPSI-R (Wechsler, 1989) and the WPPSI-III (Wechsler, 2002). It provides subtest and composite scores that represent intellectual functioning in verbal and performance cognitive domains, as well as providing a composite score that represents a child's general intellectual ability (i.e., Full Scale IQ). History The original WPPSI (Wechsler, 1967) was developed as an intelligence measure for 4-6:6yr olds in response to an increasing need for the assessment of pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is an IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability in adults and older adolescents. For children between the ages of 6 and 16, Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) is commonly used. The original WAIS (Form I) was published in February 1955 by David Wechsler, Chief Psychologist at Bellevue Hospital (1932–1967) in NYC, as a revision of the Wechsler–Bellevue Intelligence Scale released in 1939. It is currently in its fifth edition (''WAIS-5''), released in 2024 by Pearson. It is the most widely used IQ test, for both adults and older adolescents, in the world. History The WAIS was founded to get to know Wechsler's patients at Bellevue Hospital and on his definition of intelligence, which he defined as "... the global capacity of a person to act purposefully, to think rationally, and to deal effectively with his environment." He believed that intelligence was made up of specific elements that could b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City University London
City, University of London was a public university from 1966 to 2024 in London, England. It merged with St George's, University of London to form City St George's, University of London in August 2024. The names "City, University of London" and "St George’s, University of London" continued as trading names until March 2025. Originally founded in 1894 as the Northampton Institute, it officially became a university when The City University was created by royal charter in 1966. The Inns of Court School of Law, which merged with City in 2001, was established in 1852, making it the university's oldest constituent part. City joined the federal University of London on 1 September 2016, becoming part of the eighteen colleges and ten research institutes that then made up that university. City has strong links with the City of London, and the Lord Mayor of London serves as the university's rector. The university has its main campus in Central London in the London Borough of Islington, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and developmentally inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction. Impairments resulting from deficits in self-regulation such as time management, inhibition, task initiation, and sustained attention can include poor professional performance, relationship difficulties, and numerous health risks, collectively predisposing to a diminished quality of life and a reduction in life expectancy. As a consequence, the disorder costs society hundreds of billions of US dollars each year, worldwide. It is associated with other mental disorders as well as non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment. While ADHD involves a lack of sustained attention to tasks, inhibitory deficits also can lead to diffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Test
Cognitive tests are assessments of the cognitive capabilities of humans and other animals. Tests administered to humans include various forms of IQ tests; those administered to animals include the mirror test (a test of visual self-awareness) and the T maze test (which tests learning ability). Such testing is used in psychology and psychometrics, as well as other fields studying human and animal intelligence. Modern cognitive tests originated through the work of James McKeen Cattell who coined the term "mental tests". They followed Francis Galton's development of physical and physiological tests. For example, Galton measured strength of grip and height and weight. He established an "Anthropometric Laboratory" in the 1880s where patrons paid to have physical and physiological attributes measured. Galton's measurements had an enormous influence on psychology. Cattell continued the measurement approach with simple measurements of perception. Cattell's tests were eventually abandoned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |