|
Watanabe Shōzaburō
Watanabe ( and other variantsSee #Miscellaneous) is a Japanese surname derived from the noble and samurai Watanabe clan, a branch of the Minamoto clan, descending from the Emperor Saga (786-842), the 52nd Emperor of Japan, and refers to a location called 'Watanabe no tsu' which was settled by the Watanabe clan, who took the name of the place. It was located in the medieval period near the mouth of the Yodogawa River in Settsu Province, in present-day city of Osaka. History Origin The surname Watanabe comes from the Watanabe clan founded by Watanabe no Tsuna (953-1025), of the Saga Genji branch of the Minamoto clan, and his official name was Minamoto no Tsuna. He established the Watanabe branch of the Minamoto clan, taking the name from his stronghold at Watanabe no tsu, a port on the Yodogawa River in Settsu Province, and in 1020 he was appointed Tango no Kami (Governor of Tango Province). He was the son of Minamoto no Atsuru (933-953), married to a daughter of the '' Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minamoto No Tōru
was a Japanese poet and statesman. He was born the son of Emperor Saga and a member of the Saga Genji clan. He is sometimes mentioned as the model for Hikaru Genji in important Japanese literary classic ''The Tale of Genji''. Under his title , he is the author of poem 14 in the ''Hyakunin Isshu'' poetry anthology: Here is another translation: : ''The dye with hare’s-foot-fern, of Michinoku—who else would have made me feel as disturbed?'' The poet is also famous for making a replica of the '' uta-makura'' Shiogama, a poetic place name, in his garden. His tomb resides at the Seiryō-ji, a Buddhist temple situated on what was once Saga Moor in Kyoto. We also see two of his poems included in the ''Gosen Wakashū The , often abbreviated as ''Gosenshū'' ("Later Collection"), is the second imperial anthology of Japanese poetry, Japanese Waka (poetry), waka compiled in 951 in poetry, 951 at the behest of Emperor Murakami by the Five Men of the Pear Chamber ...''. Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
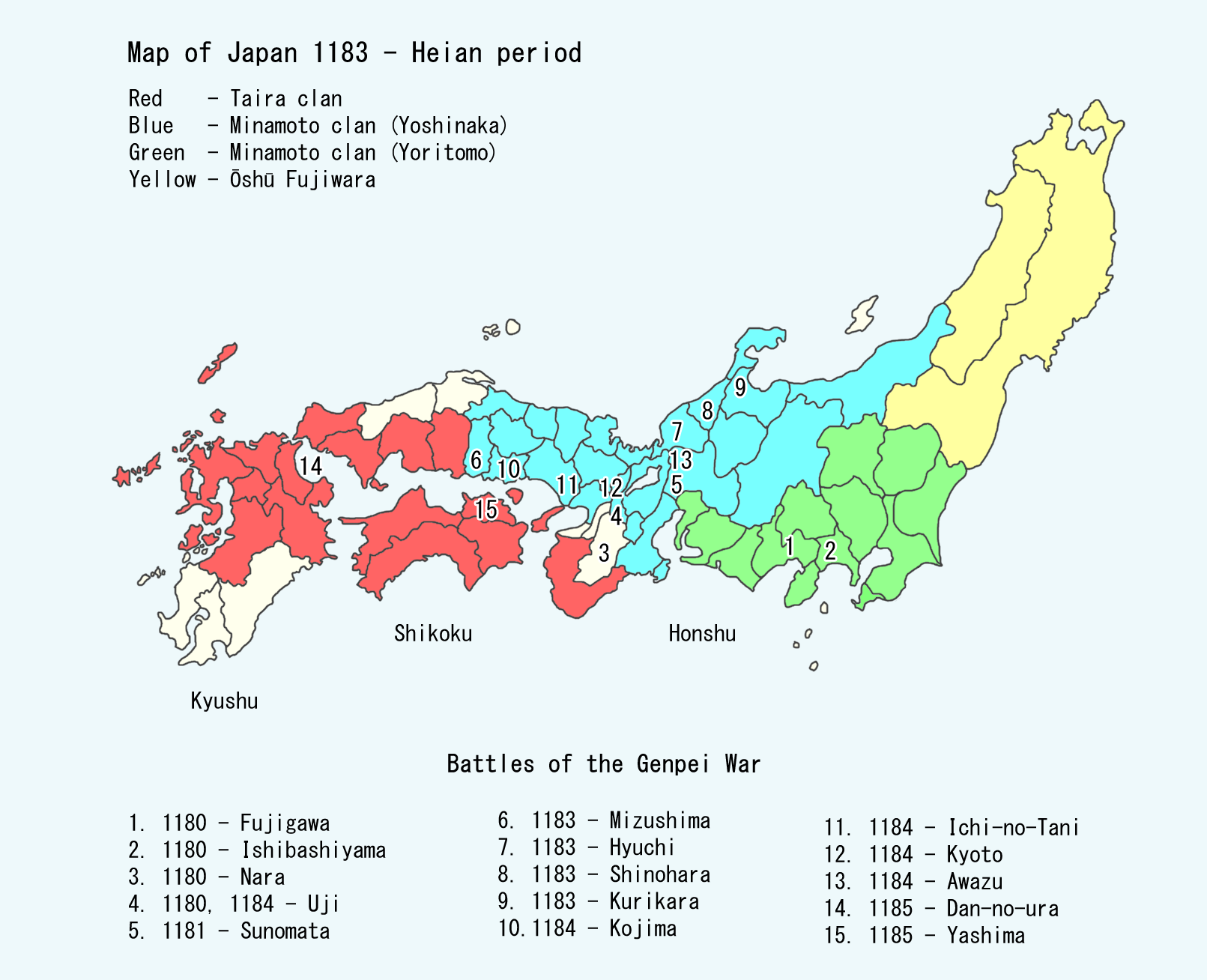
Genpei War
The was a national civil war between the Taira clan, Taira and Minamoto clan, Minamoto clans during the late Heian period of Japan. It resulted in the downfall of the Taira and the establishment of the Kamakura shogunate under Minamoto no Yoritomo, who appointed himself as ''Shōgun'' in 1192, governing Japan as a military dictator from the eastern city of Kamakura. It followed a ''coup d'état'' by the Taira in 1179 with the removal of rivals from all government posts, and subsequently banishing them, and a call to arms against the Taira, led by the Minamoto in 1180. The ensuing Battle of Uji (1180), Battle of Uji took place just outside Kyoto, starting a five-year-long war, concluding with a decisive Minamoto victory in the naval Battle of Dan-no-ura. However, it has been pointed out that the Battle of Ōshū in 1189 was the last battle during this period of civil war, as it completed Yoritomo's nationwide domination through the annexation of Tōhoku region, Northeast Japan. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
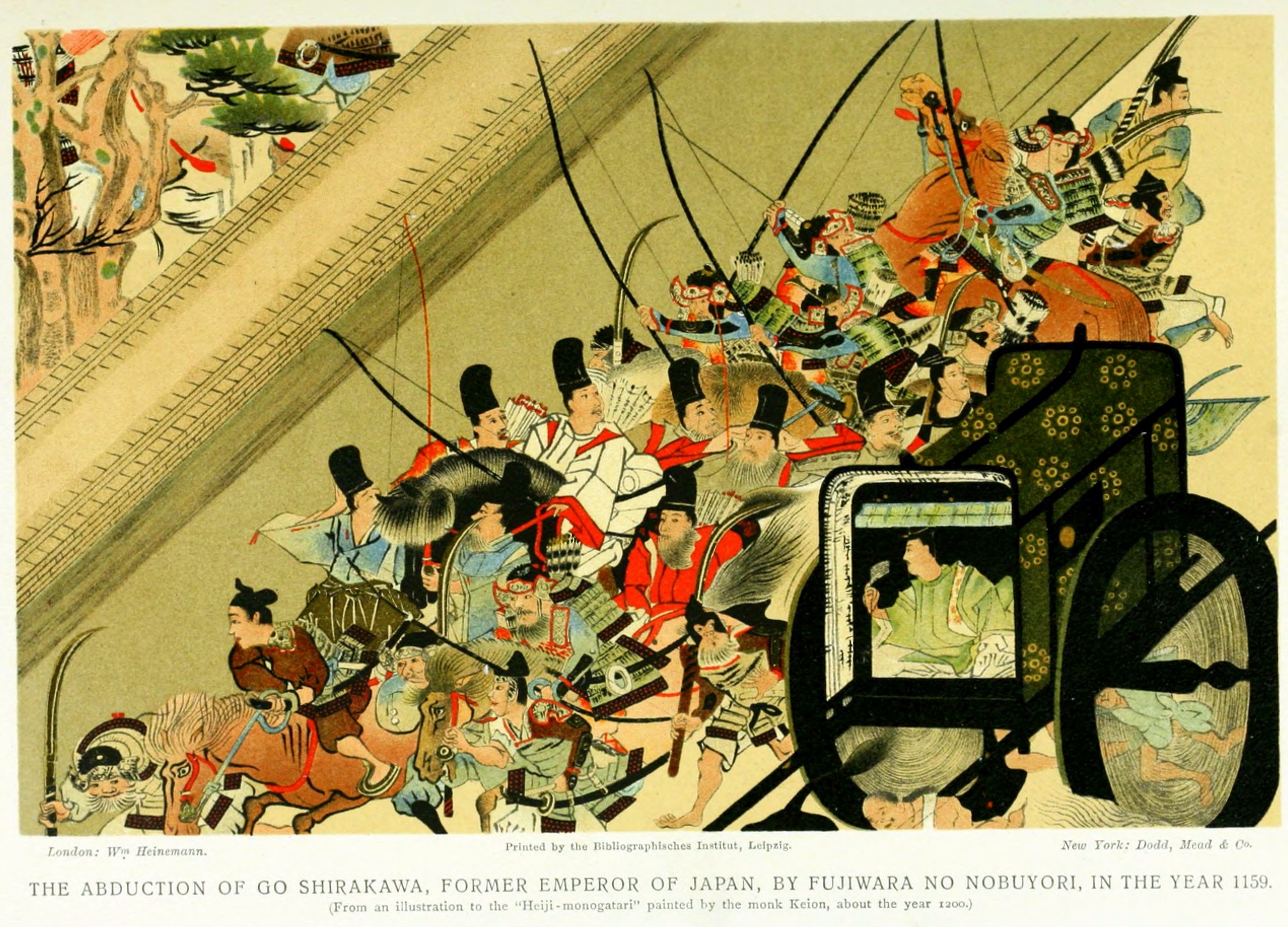
Hōgen Rebellion
The was a short civil war fought in order to resolve a dispute about Japanese Imperial succession. The dispute was also about the degree of control exercised by the Fujiwara clan who had become hereditary Imperial regents during the Heian period. ''Hōgen no ran'' produced a series of unanticipated consequences. It created a foundation from which the dominance of the samurai clans would come to be established. It is considered the beginning in a chain of events which would produce the first of three samurai-led governments in the history of Japan. Context A simmering power struggle in the Imperial court was focused on three figures in 1155. After the former Emperor Toba and the former Emperor Sutoku abdicated, each intended to continue to wield various kinds of power behind the throne during the reign of Emperor Konoe in cloistered rule. However, when young Konoe died, the dynamics of the contending factions changed. * August 23, 1155 ('' Kyūju 2, 24th day of the 7t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Go-Shirakawa
was the 77th emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. His de jure reign spanned the years from Heian period, 1155 through 1158, though arguably he effectively maintained imperial power for almost thirty-seven years through the Cloistered rule, ''insei'' system – scholars differ as to whether his rule can be truly considered part of the ''insei'' system, given that the Hōgen Rebellion undermined the imperial position. However, it is broadly acknowledged that by politically outmaneuvering his opponents, he attained greater influence and power than the diminished authority of the emperor's position during this period would otherwise allow. posthumous name, Posthumously, this 12th-century sovereign was named after the 11th-century Emperor Shirakawa. ''Go-'' (後), translates literally as "later"; and thus, he is sometimes called the "Later Emperor Shirakawa", or in some older sources, may be identified as "Shirakawa, the second" or as "Shirakawa II". Unu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira
The was one of the four most important clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period of Japanese history – the others being the Minamoto, the Fujiwara, and the Tachibana. The clan is divided into four major groups, named after the emperors they descended from: Kanmu Heishi, Ninmyō Heishi, Montoku Heishi, and Kōkō Heishi, the most influential of which was the Kanmu Heishi line. In the twilight of the Heian period, the Taira controlled the boy emperor Antoku (himself the grandson of the powerful ''Kugyō'' Taira no Kiyomori) and had effectively dominated the Imperial capital of Heian. However, they were opposed by their rivals the Minamoto clan (the Genji), which culminated in the Genpei War (1180–1185 AD). The five-year-long war concluded with a decisive Taira defeat in the naval Battle of Dan-no-Ura, which resulted in the deaths of Antoku and Taira leaders. Following the war, the victorious Minamoto established Japan's first shogunate in Kamaku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minamoto No Yoritomo
was the founder and the first shogun of the Kamakura shogunate, ruling from 1192 until 1199, also the first ruling shogun in the history of Japan.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Minamoto no Yoriie" in . He was the husband of Hōjō Masako who acted as regent (''shikken'') after his death. Yoritomo was the son of Minamoto no Yoshitomo and belonged to Seiwa Genji's prestigious Kawachi Genji family. After successfully maneuvering himself to the position of rightful heir of the Minamoto clan, he led his clan against the Taira clan, Taira from his capital in Kamakura, beginning the Genpei War in 1180. After five years of civil war, the Minamoto clan finally defeated the Taira in the Battle of Dan-no-ura in 1185. Yoritomo established the supremacy of the samurai caste and the first shogunate (''bakufu'') which was to be centered around Kamakura, thus beginning the History of Japan#Feudal Japan, feudal age in Japan, which lasted until the 17th century. Early life Yoritomo was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongaku
Mongaku (文覚) was a Japanese samurai and Shingon Buddhist priest of the late Heian and early Kamakura period. He was a close associate of shogun Minamoto no Yoritomo, having contributed to the declaration of the Genpei War. Myōe was the disciple of his disciple Jōkaku. His secular name, before ordination, was Endō Moritō. He is also known as Mongaku Shōnin. Life Mongaku was born the son of Endō Mochitō, a samurai in the Watanabe faction of the Settsu Genji clan (a branch of the Minamoto clan). He initially served in the Imperial Palace Guards of the North Side. He fell in love with Kesa, the wife of Minamoto no Wataru, but killed her by accident. Out of repentance, he then ordinated as a priest, visiting sacred places across the country. Mongaku moved to live at Jingo-ji temple in 1168, and participated in its restoration work motivated by his reverence towards Kūkai. In 1173, he requested a manorial temple estate for Jingo-ji from Cloistered Emperor Go-Shirakaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's Japanese archipelago, four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa Island, Okinawa and the other Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Ryukyu Islands, Islands). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands. Kyushu has a land area of and a population of 14,311,224 in 2018. In ancient times, there is a theory that Kyushu was home to its own independent dynasty, where a unique, southern-influenced culture and tradition distinct from that of Honshu flourished. In the 8th-century Taihō Code reforms, Dazaifu (government), Dazaifu was established as a special administrative term for the region. Geography The island is mountainous, and Japan's most active volcano, Mount Aso at , is on Kyūshū. There are many other signs of tectonic activity, including numerous areas of hot springs. The most famous of these are in Beppu, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Shirakawa
was the 72nd emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 白河天皇 (72)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession. Shirakawa's reign lasted from 1073 to 1087. Genealogy Before his ascension to the Chrysanthemum Throne, his personal name (''imina'') was Sadahito''-shinnō'' (貞仁親王). He was the eldest son of Emperor Go-Sanjō and Fujiwara Shigeko (藤原茂子). Shirakawa had one Empress and one Imperial Consort and nine Imperial sons and daughters. *Empress (chūgū): Fujiwara no Kenshi (藤原賢子)—Minamoto Akifusa‘s daughter, adopted by Fujiwara Morozane ** First Son: Imperial Prince Atsufumi (敦文親王; 1075–1077) ** First Daughter: Imperial Princess Yasuko (媞子内親王) later Ikuhomon’in (郁芳門院) ** Third Daughter: Imperial Princess Reishi (令子内親王) ''saigū'' ** Third Son: Imperial Prince Taruhito (善仁親王) later Emperor Horikawa ** Fourth Daughter: Imperial Princess Shinshi (禛子内親王; 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
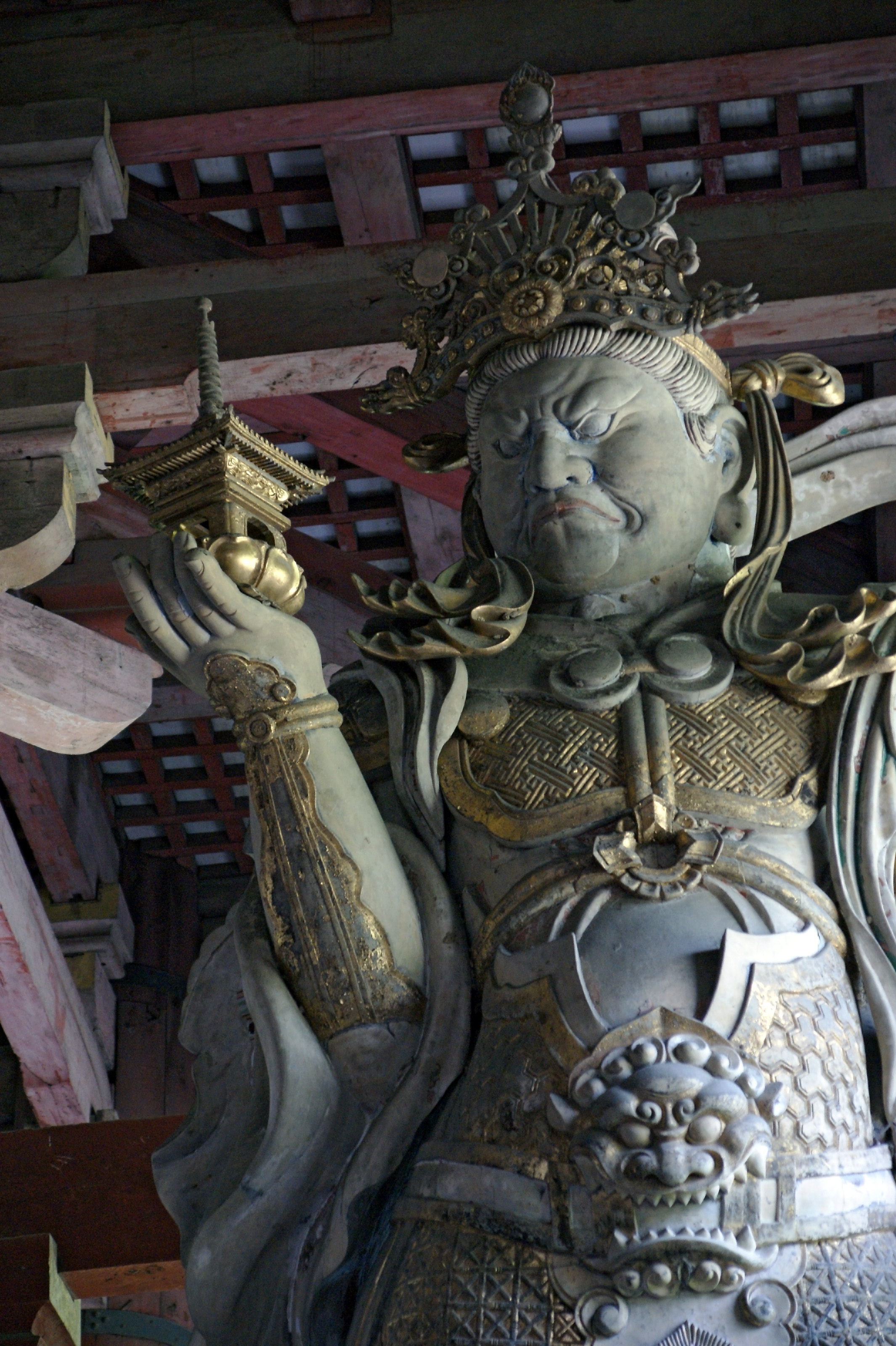
Four Heavenly Kings
The Four Heavenly Kings are four Buddhism, Buddhist gods or Deva (Buddhism), ''devas'', each of whom is believed to watch over one cardinal direction of the world. The Hall of Four Heavenly Kings is a standard component of Chinese Buddhism, Chinese Buddhist Buddhist temple, temples. Names The Kings are collectively named as follows: Individually, they have different names and features. File:Guardian of Phra Meru Mas of Bhumibol Adulyadej - Vessavana (right side).jpg, Vaiśravaṇa of the north direction, king of yakṣas. File:Guardian of Phra Meru Mas of Bhumibol Adulyadej - Virulhaka (right side).jpg, Virūḍhaka of the south direction, king of kumbhāṇḍas. File:Guardian of Phra Meru Mas of Bhumibol Adulyadej - Dhatarattha (left side).jpg, Dhṛtarāṣṭra of the east direction, king of gandharvas. File:Guardian of Phra Meru Mas of Bhumibol Adulyadej - Virupakkha (left side).jpg, Virūpākṣa of the west direction, king of nāgas. Mythology All four Kings ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Four Guardian Kings
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |