|
Washington County, Virginia
Washington County is a county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 53,935. Its county seat is Abingdon. Washington County is part of the Kingsport–Bristol–Bristol, TN-VA Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is a component of the Johnson City–Kingsport–Bristol, TN-VA Combined Statistical Area, commonly known as the " Tri-Cities" region, which includes Bristol TN-VA, Kingsport TN, and Johnson City TN. History For thousands of years, indigenous peoples of varying cultures lived in the area. At the time of European massacre, the Chiska had a chief village near what is now Saltville, destroyed by the Spaniards in 1568. The Cherokee annexed the region from the Xualae around 1671, and ceded it to the Virginia Colony in 1770 at the Treaty of Lochaber. The county was formed by Virginians in 1776 from Fincastle County. It was named for George Washington, who was then commander-in-chief of the Continental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot forces to victory in the American Revolutionary War against the British Empire. He is commonly known as the Father of the Nation for his role in bringing about American independence. Born in the Colony of Virginia, Washington became the commander of the Virginia Regiment during the French and Indian War (1754–1763). He was later elected to the Virginia House of Burgesses, and opposed the perceived oppression of the American colonists by the British Crown. When the American Revolutionary War against the British began in 1775, Washington was appointed Commanding General of the United States Army, commander-in-chief of the Continental Army. He directed a poorly organized and equipped force against disciplined British troops. Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saltville, Virginia
Saltville is a town in Smyth and Washington counties in the U.S. state of Virginia. The population was 1,824 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Kingsport– Bristol (TN)– Bristol (VA) Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is a component of the Johnson City–Kingsport–Bristol, TN-VA Combined Statistical Area – commonly known as the " Tri-Cities" region. History Saltville was named for the salt marshes in the area. Prior to European settlement, these marshes attracted local wildlife. Excavations at the SV-2 archaeological site in the area have recovered several well preserved skeletons of now extinct species dating back to the last ice age. Indigenous peoples of varying cultures hunted at the marshes. The historic Native American people in the area were the Chisca. Archaeologists in 1992 proposed the existence of a prehistoric "Saltville Complex Petty Chiefdom", with a paramount village located at the Northwood High School site, 44SM8. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lee County, Virginia
Lee County is the westernmost county in the U.S. Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 22,173. Its county seat is Jonesville. History The area of far western Virginia and eastern Kentucky supported large Archaic Native American populations. The first known Europeans to enter what is present-day Lee County were a party of Spanish explorers, Juan de Villalobos and Francisco de Silvera, sent by Hernando de Soto in 1540, in search of gold. The county was formed after the American Revolutionary War in 1792 from Russell County. It was named for Light Horse Harry Lee, the Governor of Virginia from 1791 to 1794, who was famous for his exploits as a leader of light cavalry during the war. He was the father of Robert E. Lee, later a West Point graduate and career U.S. Army officer who became the General in Chief of the Armies of the Confederate States during the American Civil War. Lee County was the final front on the Kentucky Trace, now known as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russell County, Virginia
Russell County () is a county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 25,781. Its county seat is Lebanon. History On January 2, 1786, Russell County was established from a section of Washington County. L.P. Summers, a Washington County historian later wrote, "Washington County lost a great extent of country and many valuable citizens when Russell County was formed." The county was named for Culpeper County native Colonel William Russell. The first court met in May 1786 in the Castle's Woods settlement (present-day Castlewood) in the house of William Robinson. Later, a new place was built to house the County Seat. The structure used as a courthouse still stands, and is referred to as " The Old Courthouse." The present Courthouse, located in Lebanon, has been in use since 1874. Once vast, Russell County was split several times, giving rise to Tazewell County, Lee County, Scott County, Wise County, Buchanan County and Dickenso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bob Benge
Robert "Bob" Benge (c. 1762–1794), also known as Captain Benge (or "The Bench" to frontiersmen), was a Cherokee leader in the Upper Towns, in present-day far Southwest Virginia during the Cherokee–American wars (1783–1794). Early life He was born as Bob Benge about 1762 in the Overhill Cherokee town of Toqua, to a Cherokee woman and a Scots-Irish trader named John Benge, who lived full-time among the Cherokee and had taken a "country wife." They also had a daughter Lucy. Benge stood out physically because of his red hair. Under the Cherokee matrilineal kinship and clan system, children were considered born into their mother's family and clan. Their mother's eldest brother was considered the most important male figure in their growing up, especially for boys. The children were reared largely in Cherokee culture and identified as Cherokee. The available sources strongly imply, but do not prove, that young Benge and his sister Lucy were half-siblings of Sequoyah, also known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragging Canoe
Dragging Canoe (ᏥᏳ ᎦᏅᏏᏂ, pronounced ''Tsiyu Gansini'', – February 29, 1792) was a Cherokee red (or war) chief who led a band of Cherokee warriors who resisted colonists and United States settlers in the Upper South. During the American Revolution and afterward, Dragging Canoe's forces were sometimes joined by Upper Muskogee, Chickasaw, Shawnee, and Indians from other tribes, along with British Loyalists, and agents of France and Spain. The Cherokee American Wars lasted more than a decade after the end of the American Revolutionary War. During that time, Dragging Canoe became the preeminent war leader among the Indians of the southeast. He served as war chief, or '' skiagusta'', of the group known as the Chickamauga Cherokee (or "Lower Cherokee"), from 1777 until his death in 1792. Biography Tsiyu Gansini was born about 1738. Dragging Canoe was the son of Attakullakulla (''Tsalagi'', or "Little Carpenter")—a Nipissing head-man—and ''Nionne Ollie'' ("Tam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee–American Wars
The Cherokee–American wars, also known as the Chickamauga Wars, were a series of raids, campaigns, ambushes, minor skirmishes, and several full-scale frontier battles in the Old Southwest from 1776 to 1794 between the Cherokee and American settlers on the frontier. Most of the events took place in the Upper South region. While the fighting stretched across the entire period, there were extended periods with little or no action. The Cherokee leader Dragging Canoe, whom some earlier historians called "the Savage Napoleon", and his warriors, and other Cherokee fought alongside warriors from several other tribes, most often the Muscogee in the Old Southwest and the Shawnee in the Old Northwest. During the Revolutionary War, they also fought alongside British troops, Loyalist militia, and the King's Carolina Rangers against the rebel colonists, hoping to expel them from their territory. Open warfare broke out in the summer of 1776 in the Overmountain settlements of the Washing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
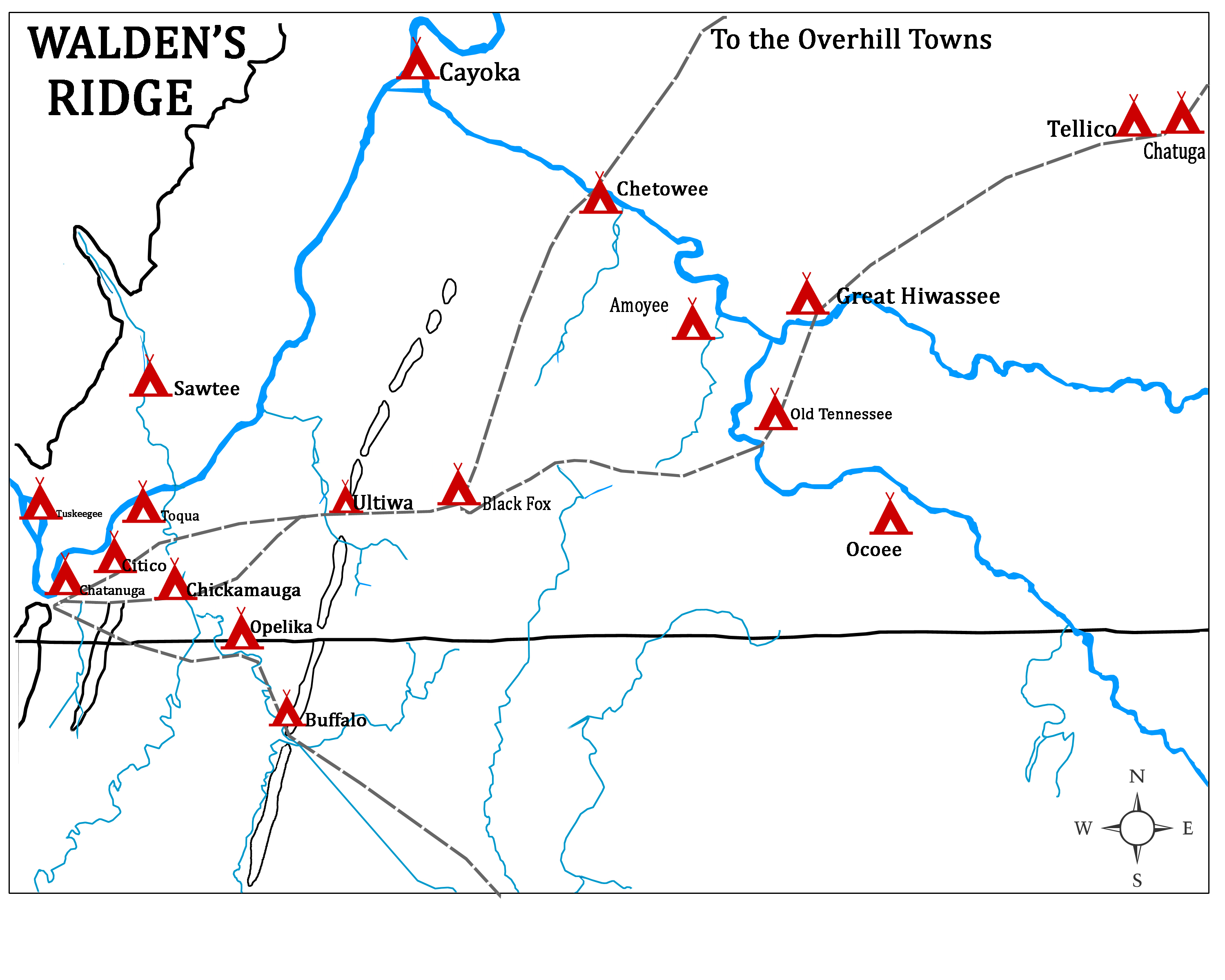
Chickamauga Cherokee
The Chickamauga Cherokee is a Native American group who separated from the Cherokee from the American Revolutionary War to the early 1800s. Most of the Cherokee people signed peace treaties with the Americans in 1776-1777, after the Second Cherokee War. Followers of the skiagusta (war chief) Dragging Canoe moved with him down the Tennessee River, away from their historic Overhill Cherokee towns. Relocated to a more isolated area, they established 11 new towns to distance themselves from encroaching colonists. Frontier Americans associated Dragging Canoe and his band with their new town on Chickamauga Creek, and began to refer to the band as the Chickamaugas. The Chickamauga moved further west and southwest into present-day Alabama five years later, establishing five larger settlements. They were then more commonly known as the Lower Cherokee, a term closely associated with the people of the five lower towns. Dragging Canoe, the first Chicamauga chief, separated from the Upp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies representing the Thirteen Colonies and later the United States during the American Revolutionary War. It was formed on June 14, 1775, by a resolution passed by the Second Continental Congress, meeting in Philadelphia after the war's outbreak at the Battles of Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775. Therefore, June 14th is celebrated as the U.S. Army Birthday. The Continental Army was created to coordinate military efforts of the colonies in the war against the British Army during the American Revolutionary War, British, who sought to maintain control over the American colonies. General George Washington was appointed commander-in-chief of the Continental Army and maintained this position throughout the war. The Continental Army was supplemented by local Militia (United States), militias and volunteer troops that were either loyal to individual states or otherwise independent. Most of the Continental Army was disbanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fincastle County, Virginia
Fincastle County, Virginia, was created by act of the Virginia General Assembly April 8, 1772 from Botetourt County.Pendleton, William C. (1920)''History of Tazewell County and Southwest Virginia: 1748-1920'' pp. 255-57. W. C. Hill Printing Company. As the colonial government considered Virginia's western extent to be the Mississippi River, that became Fincastle's western limit. Its eastern boundary was essentially the New River (Wood's River at the time, including what is today the Kanawha River), thus dividing Botetourt County from north to south. The new county encompassed all of present-day Kentucky, plus southwestern West Virginia and a slice of Virginia's western "tail". Although no county seat was designated by the act creating the county, the colonial governor ordered it to be placed at the "Lead Mines" of present-day Wythe County; the community of Austinville later developed there. The governor of Virginia Colony, John Murray, Earl of Dunmore and Viscount of Finca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Lochaber
The Treaty of Lochaber was signed in South Carolina on 18 October 1770 by British representative John Stuart and the Cherokee people, fixing the boundary for the western limit of the colonial frontier settlements of Virginia and North Carolina. Lord Shelburne in London was determined to settle disputes along the western frontier in order to avoid more conflict between colonists and various Native American nations. Although he lost his office as Southern Secretary in October 1768, negotiations progressed with tribal chiefs (usually representing towns in their decentralized society) regarding the North American colonial frontier. The Treaty of Fort Stanwix in November 1768 fixed the boundary lines between tribes and colonists to the north of Virginia. The border variances from the Treaty of Hard Labour led to negotiations where 1000 Cherokee leaders were hosted by Alexander Cameron (d. 1781) at Lochabar Plantation in Ninety-Six District, South Carolina. Based on the terms of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |