|
Wanaku (Potosí)
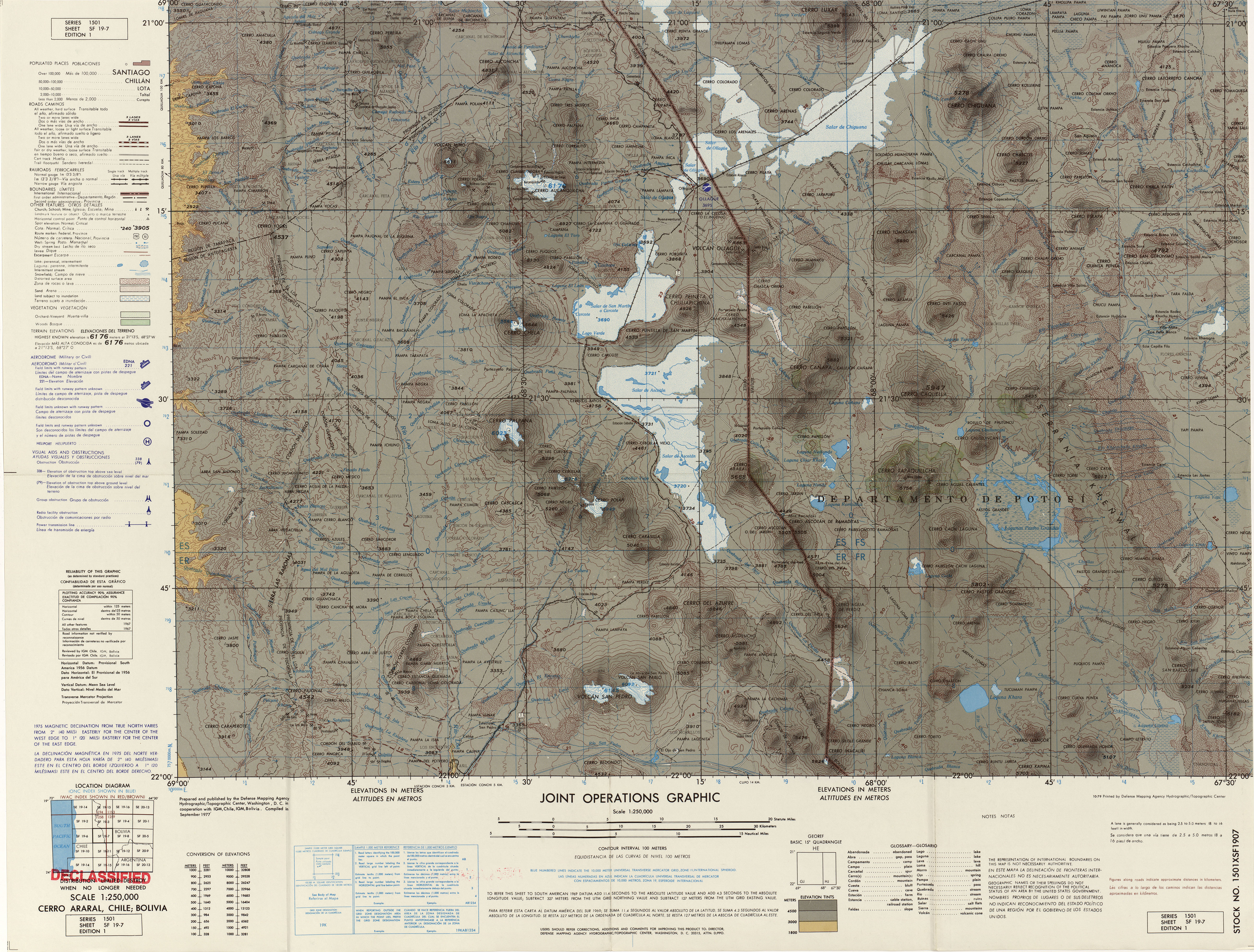
Wanaku ( Quechua for guanaco, Hispanicized spelling ''Huanaco, Huanacu'') is a mountain in the Andes of Bolivia, about high. It is situated in the Potosí Department, Nor Lípez Province, Quemes Municipality, Pelcoya Canton. Wanaku lies southeast of the Ollagüe Ollagüe () or Ullawi () is a massive andesite stratovolcano in the Andes on the Bolivia–Chile border, within the Antofagasta Region of Chile and the Potosí Department, Potosi Department of Bolivia. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the A ... (Ullawi) volcano and northeast of Ch'aska Urqu. References Mountains of Potosí Department Four-thousanders of the Andes {{Potosí-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, warm valleys, high-altitude Andean plateaus, and snow-capped peaks, encompassing a wide range of climates and biomes across its regions and cities. It includes part of the Pantanal, the largest tropical wetland in the world, along its eastern border. It is bordered by Brazil to the Bolivia-Brazil border, north and east, Paraguay to the southeast, Argentina to the Argentina-Bolivia border, south, Chile to the Bolivia–Chile border, southwest, and Peru to the west. The seat of government is La Paz, which contains the executive, legislative, and electoral branches of government, while the constitutional capital is Sucre, the seat of the judiciary. The largest city and principal industrial center is Santa Cruz de la Sierra, located on the Geog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potosí Department
Potosí (; Southern Quechua, Quechua: ''P'utuqsi''; Aymara language, Aymara: ''Putusi'') is a Departments of Bolivia, department in southwestern Bolivia. Its area is 118,218 km2 and its population is 856,419 (2024 census). The capital is the city of Potosí. It is a mostly barren, mountainous region with one large plateau to the west, where the largest Salt pan (geology), salt flat in the world, Salar de Uyuni, is located. Cerro Rico, Cerro Potosí was the richest province in the Spanish Empire, providing a great percentage of the silver that was Spanish treasure fleet, shipped to Europe. Potosi is also the location of the San Cristóbal mine (Bolivia), San Cristóbal silver, zinc and lead mines, developed by the US company Apex Silver Mines Limited of Colorado and sold in November 2008 to the Japanese Sumitomo Corporation. History In March 2023, social organisations in four regions of Potosí, with the support of regional MAS-IPSP lawmakers, called for a strike spannin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nor Lípez Province
Nor Lípez is a province in the Bolivian department of Potosí. Its seat is Colcha "K", also called Villa Martín. The majority of the area of the province was titled as the Nor Lípez Native Community Land on 19 April 2011. One of the largest mines of Bolivia, the San Cristóbal Mine, is located near San Cristóbal in Colcha "K" municipality. Geography Some of the highest mountains of the province are listed below: Location The province is one of sixteen provinces in the Potosí Department. It is located between 20° 27' and 22° 01' South and between 66° 18' and 68° 35' West. It is bordered by the Daniel Campos Province to the north, the Republic of Chile to the west, the Enrique Baldivieso Province and Sur Lípez Province to the south, Sud Chichas Province to the east, and the Antonio Quijarro Province to the northeast. The province extends over 270 km from east to west and 210 km from north to south. Division The province comprises tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18th parallel south, 18°S and 20th parallel south, 20°S latitude) and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from south to north through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depression (geology), depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, Mérida, Mérida, El Alto, and La Paz. The Altiplano, Altiplano Plateau is the world's second highest after the Tibetan Plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechua Language
Quechua (, ), also called (, 'people's language') in Southern Quechua, is an Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous language family that originated in central Peru and thereafter spread to other countries of the Andes. Derived from a common ancestral "Proto-Quechuan language, Proto-Quechua" language, it is today the most widely spoken Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with the number of speakers estimated at 8–10 million speakers in 2004,Adelaar 2004, pp. 167–168, 255. and just under 7 million from the most recent census data available up to 2011. Approximately 13.9% (3.7 million) of Peruvians speak a Quechua language. Although Quechua began expanding many centuries before the Inca Empire, Incas, that previous expansion also meant that it was the primary language family within the Inca Empire. The Spanish also tolerated its use until the Peruvian War of Independence, Peruvian struggle for independence in the 1780s. As a result, var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
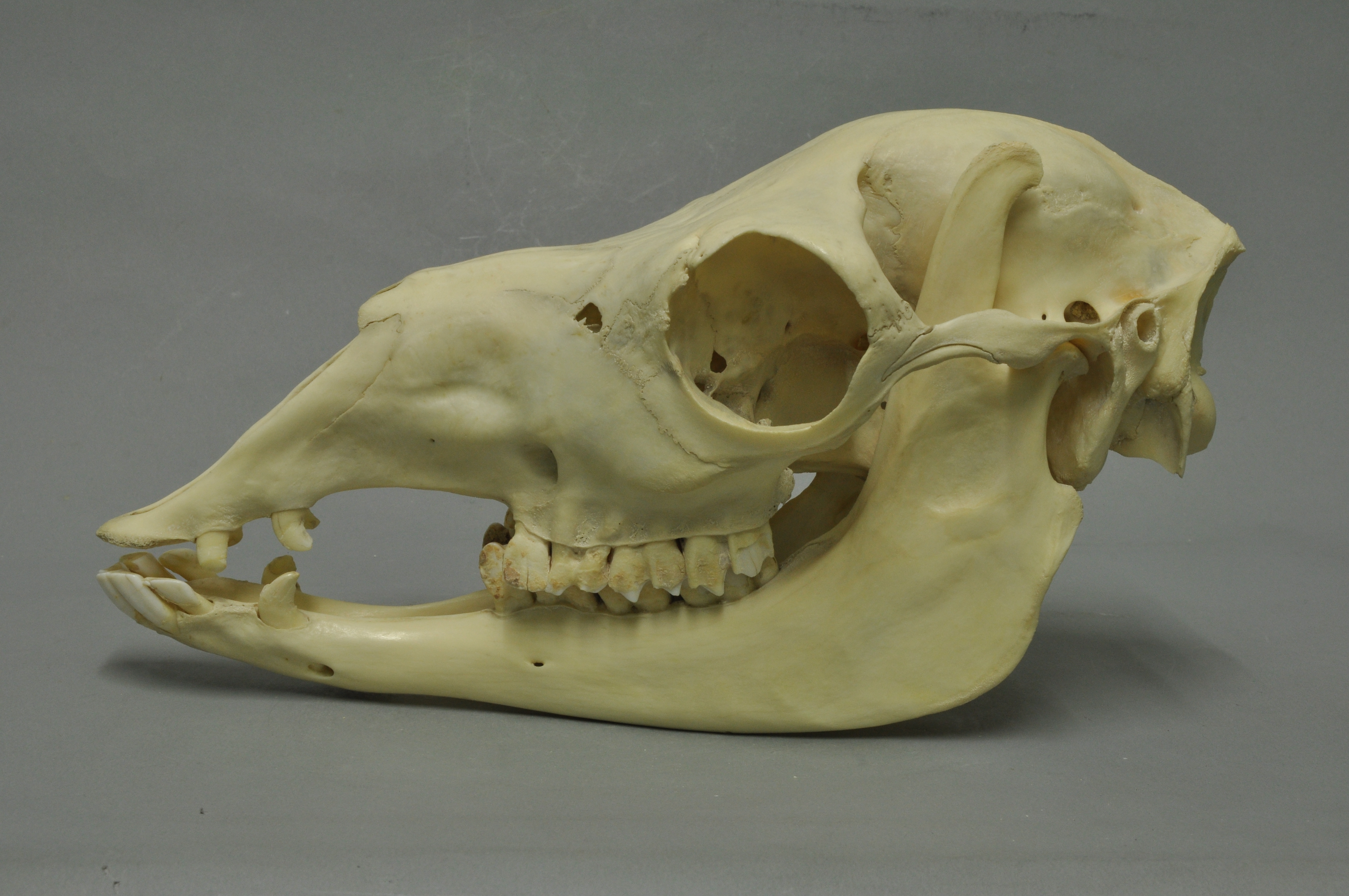
Guanaco
The guanaco ( ; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids; the other species is the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations. Etymology The guanaco gets its name from the Quechua word ''wanaku''. Young guanacos are called ''chulengos'' or "guanaquitos". Characteristics Guanacos stand between at the shoulder, body length of , and weigh . Their color varies very little (unlike the domestic llama), ranging from a light brown to dark cinnamon and shading to white underneath. Guanacos have grey faces and small, straight ears. The lifespan of a guanaco can be as long as 28 years. Guanacos are one of the largest terrestrial mammals native to South America today.San Diego Zoo's Animal Bytes Other terrestrial mammalian [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Pedro De Quemes Municipality
San Pedro de Quemes () is the second Municipalities of Bolivia, municipal section of the Nor Lípez Province in the Potosí Department in Bolivia. Its seat is San Pedro de Quemes. Geography The municipality lies at the Salar de Uyuni, Uyuni salt flat. Some of the highest mountains of the municipality are listed below: Many of the mountains and volcanoes are a natural border to Chile. Subdivision The municipality consists of the following cantons: * Cana - 44 inhabitants (''2001'') * Chiguana - 10 inhabitants * Pajancha - 52 inhabitants * Pelcoya Canton, Pelcoya - 135 inhabitants * San Pedro de Quemes Canton, San Pedro de Quemes- 574 inhabitants The people The people are mainly not Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous and 45,0% are citizens of Quechua people, Quechua descent.obd.descentralizacion.gov.bo/municipal/fichas/ (inactive) See also * Ch'iyar Quta, Nor Lípez, Ch'iyar Quta References External links San Pedro de Quemes Municipality: populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ollagüe
Ollagüe () or Ullawi () is a massive andesite stratovolcano in the Andes on the Bolivia–Chile border, within the Antofagasta Region of Chile and the Potosí Department, Potosi Department of Bolivia. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its highest summit is above sea level and features a summit crater that opens to the south. The western rim of the summit crater is formed by a compound of lava domes, the youngest of which features a vigorous fumarole that is visible from afar. Ollagüe is mostly of Pleistocene age. It started developing more than one million years ago, forming the so-called Vinta Loma and Santa Rosa series mostly of Andesite, andesitic lava flows. A fault (geology), fault bisects the edifice and two large landslides occurred in relation to it. Later two groups of Dacite, dacitic lava domes formed, Ch'aska Urqu (Nor Lípez), Ch'aska Urqu on the southeastern slope and La Celosa on the northwestern. Another centre named La Poruñita formed at that ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ch'aska Urqu (Nor Lípez)
Ch'aska Urqu (Quechua ''ch'aska'' star; tousled, ''urqu'' mountain, "star mountain" or "tousled mountain", also spelled ''Chasca Orkho'') is a mountain in the Andes of Bolivia, about high. It is located in the Potosí Department, Nor Lípez Province, Quemes Municipality, Pelcoya Canton. Ch'aska Urqu lies near the border with Chile, southeast of the Ollagüe Ollagüe () or Ullawi () is a massive andesite stratovolcano in the Andes on the Bolivia–Chile border, within the Antofagasta Region of Chile and the Potosí Department, Potosi Department of Bolivia. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the A ... (Ullawi) volcano and southwest of Wanaku. References Mountains of Potosí Department Four-thousanders of the Andes {{Potosí-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Potosí Department
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |