|
Völsunga Saga
The ''Völsunga saga'' (often referred to in English as the ''Volsunga Saga'' or ''Saga of the Völsungs'') is a legendary saga, a late 13th-century poetic rendition in Old Norse of the origin and decline of the Völsung clan (including the story of Sigurd and Brynhild and the destruction of the Burgundians). It is one of the most famous legendary sagas and an example of a "heroic saga" that deals with Germanic heroic legend. The saga covers topics including the quarrel between Sigi and Skaði, a huge family tree of great kings and powerful conquerors, the quest led by Sigmund and Sinfjǫtli to save princess Signý from the evil king Siggeir, and, most famously, Sigurd killing the serpent/dragon Fáfnir and obtaining the cursed ring Andvaranaut that Fáfnir guarded. Context and overview The saga is largely based on the epic poetry of the historic ''Elder Edda''. The earliest known pictorial representation of this tradition is the Ramsund carving in Sweden, which was created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigurd
Sigurd ( non, Sigurðr ) or Siegfried (Middle High German: ''Sîvrit'') is a legendary hero of Germanic heroic legend, who killed a dragon and was later murdered. It is possible he was inspired by one or more figures from the Frankish Merovingian dynasty, with Sigebert I being the most popular contender. Older scholarship sometimes connected him with Arminius, victor of the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. He may also have a purely mythological origin. Sigurd's story is first attested on a series of carvings, including runestones from Sweden and stone crosses from the British Isles, dating from the eleventh century. In both the Norse and continental Germanic tradition, Sigurd is portrayed as dying as the result of a quarrel between his wife ( Gudrun/Kriemhild) and another woman, Brunhild, whom he has tricked into marrying the Burgundian king Gunnar/Gunther. His slaying of a dragon and possession of the hoard of the Nibelungen is also common to both traditions. In other respect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elder Edda
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems, which is distinct from the ''Prose Edda'' written by Snorri Sturluson. Several versions exist, all primarily of text from the Icelandic medieval manuscript known as the ''Codex Regius'', which contains 31 poems. The ''Codex Regius'' is arguably the most important extant source on Norse mythology and Germanic heroic legends. Since the early 19th century, it has had a powerful influence on Scandinavian literature, not only through its stories, but also through the visionary force and the dramatic quality of many of the poems. It has also been an inspiration for later innovations in poetic meter, particularly in Nordic languages, with its use of terse, stress-based metrical schemes that lack final rhymes, instead focusing on alliterative devices and strongly concentrated imagery. Poets who have acknowledged their debt to the ''Codex Regius'' include Vilhelm Ekelund, August Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rerir
In ''Völsunga saga'', Rerir, the son of Sigi, succeeds his murdered father and avenges his death. He rules in Hunaland and becomes a powerful ruler. Rerir's son is Völsung. Rerir and his wife were unable to have children until the goddess Frigg, the wife of Odin sent them a giantess named Hljod in the shape of a crow to deliver an apple of fertility to the couple.Byock (1990:36) Shortly after, Rerir’s wife becomes pregnant. However Rerir dies from an illness after the conception. His wife remained pregnant for six years, until she realized that she was dying and commanded that the child be delivered by Caesarian section, an operation that in those days cost the life of the mother. When the child called Völsung was delivered, he was already well grown and he “kissed his mother before she died.” Byock (1990:37) Mount Rerir is a location in the fictional world of Middle-earth. Notes References * Byock, Jesse L. (Trans.) (1990). ''The Saga of the Volsungs: The Norse Epic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunaland
Hunaland and its people are mentioned several times in the Poetic Edda, and in the Fornaldarsagas. Its origins are partly the old Frankish kingdom (the Franks were once called ''Hugones'', in Latin, and ''Hūgas'' in Old English) and partly in the Huns. The Frankish hero Sigurd is called the ''Hunnish king'' in epic poetry. Also the '' Hervarar saga'' and the '' Vilkina saga'' mention Hunaland, its kings and its hosts. In Old Norse sources, Hunaland often has a mythological character and can shift between different parts of Europe, depending on what kind of skills the hero is to show. It is separated from other countries by the forest Myrkviðr, but one source may locate it up in the north at Bjarmaland, another source says that it borders on Reidgotaland, a third source places it in parts of Germany and other sources place it on either side of the Gulf of Bothnia down to Gästrikland, in Sweden. See also * Norsemen * Frankish Empire Francia, also called the Kingdom of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
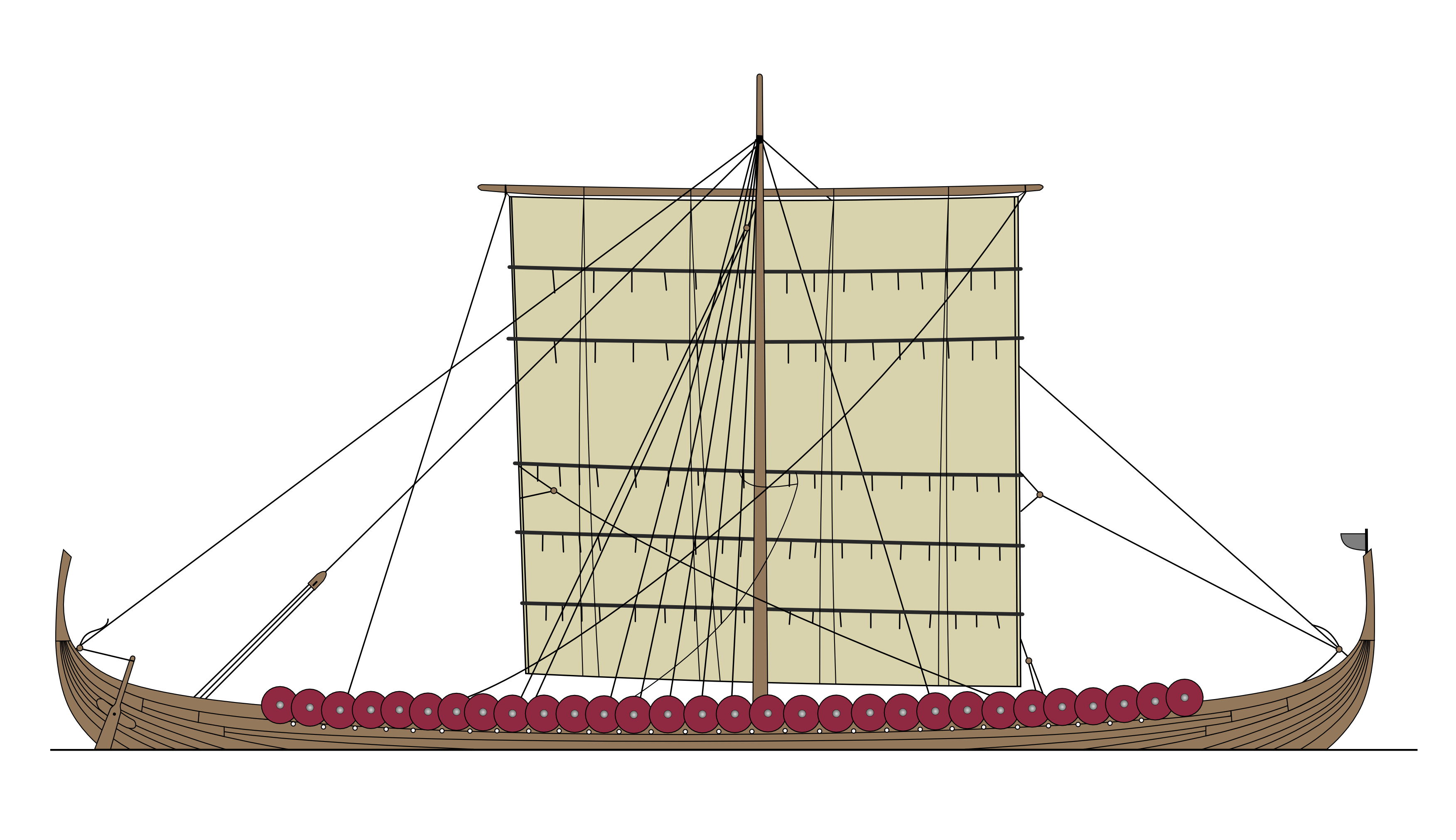
Longship
Longships were a type of specialised Scandinavian warships that have a long history in Scandinavia, with their existence being archaeologically proven and documented from at least the fourth century BC. Originally invented and used by the Norsemen (commonly known as the Vikings) for commerce, exploration, and warfare during the Viking Age, many of the longship's characteristics were adopted by other cultures, like Anglo-Saxons, and continued to influence shipbuilding for centuries. The longship's design evolved over many centuries, and continuing up until the sixth century with clinker-built ships like Nydam. The longship appeared in its complete form between the ninth and 13th centuries. The character and appearance of these ships have been reflected in Scandinavian boatbuilding traditions to the present day. The particular skills and methods employed in making longships are still used worldwide, often with modern adaptations. They were all made out of wood, with cloth sails ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowdrift
A snowdrift is a deposit of snow sculpted by wind into a mound during a snowstorm. Snowdrifts resemble sand dunes and are formed in a similar manner, namely, by wind moving light snow and depositing it when the wind has virtually stopped, usually against a stationary object. Snow normally crests and slopes off toward the surface on the windward side of a large object. On the leeward side, areas near the object are a bit lower than surrounding areas, but are generally flatter. The impact of snowdrifts on transportation can be more significant than the snowfall itself, such as in the USA during the Great Blizzard of 1978. Snowdrifts are many times found at or on roads, as the crest of the roadbed or the furrows along the road create the disruption to the wind needed to shed its carried snow. Snow fences may be employed on the windward side of the road to intentionally create a drift before the snow-laden wind reaches the road. Photo gallery File:Long Mynd snowdrift.jpeg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrall
A thrall ( non, þræll, is, þræll, fo, trælur, no, trell, træl, da, træl, sv, träl) was a slave or serf in Scandinavian lands during the Viking Age. The corresponding term in Old English was . The status of slave (, ) contrasts with that of the freeman (, ) and the nobleman (, ). The Middle Latin rendition of the term in early Germanic law is . Etymology Thrall is from the Old Norse , meaning a person who is in bondage or serfdom. The Old Norse term was lent into late Old English, as . The term is from a Common Germanic ("runner", from a root "to run"). Old High German had a cognate, , meaning "servant, runner". The English derivation ''thraldom'' is of High Medieval date. The verb "to enthrall" is of Early Modern origin (metaphorical use from the 1570s, literal use from 1610). The corresponding native term in Anglo-Saxon society was (from Germanic , perhaps from a PIE root , "to run") A related Old English term is "labourer, hireling" (from Germanic , cogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odin
Odin (; from non, Óðinn, ) is a widely revered Æsir, god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, victory, sorcery, poetry, frenzy, and the Runes, runic alphabet, and depicts him as the husband of the goddess Frigg. In wider Germanic mythology and paganism, the god was also known in Old English as ', in Old Saxon as , in Old Dutch as ''Wuodan'', in Old Frisian as ''Wêda'', and in Old High German as , all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic theonym *''Wōðanaz'', meaning 'lord of frenzy', or 'leader of the possessed'. Odin appears as a prominent god throughout the recorded history of Northern Europe, from the Roman occupation of regions of Germania (from BCE) through movement of peoples during the Migration Period (4th to 6th centuries CE) and the Viking Age (8th to 11th centuries CE). In the modern pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ragnar Lodbrok
according to legends, was a Viking hero and a Danish and Swedish king.Gutenberg Project version published 13 December 2017. He is known from of the , Icelandic s, and near-contemporary chronicles. According to traditional literature, Ragnar distinguished himself by conducting many raids against the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Library, Denmark
The Royal Library ( da, Det Kongelige Bibliotek) in Copenhagen is the national library of Denmark and the university library of the University of Copenhagen. It is among the largest libraries in the world and the largest in the Nordic countries. In 2017, it merged with the State and University Library in Aarhus to form a combined national library. The combined library organisation (the separate library locations in Copenhagen and Aarhus are maintained) is known as the Royal Danish Library ( da, Det Kgl. Bibliotek). It contains numerous historical treasures, and a copy of all works printed in Denmark since the 17th century are deposited there. Thanks to extensive donations in the past, the library holds nearly all known Danish printed works back to and including the first Danish books, printed in 1482 by Johann Snell. History The library was founded in 1648 by King Frederik III, who contributed a comprehensive collection of European works. It was opened to the public in 1793. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time; the Huns' arrival is associated with the migration westward of an Iranian people, the Alans. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, and by 430, they had established a vast, if short-lived, dominion in Europe, conquering the Goths and many other Germanic peoples living outside of Roman borders and causing many others to flee into Roman territory. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they invaded Italy. After the death of Attila in 453, the Huns ceased to be a major thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of The Burgundians
The Kingdom of the Burgundians or First Kingdom of Burgundy was established by Germanic Burgundians in the Rhineland and then in eastern Gaul in the 5th century. History Background The Burgundians, a Germanic tribe, may have migrated from the Scandinavian island of Bornholm to the Vistula basin in the 3rd century AD. However, the first documented King of the Burgundians, Gjúki (Gebicca), lived in the late 4th century east of the Rhine. In 406 the Alans, Vandals, Suevi, and possibly the Burgundians, crossed the Rhine and invaded Roman Gaul. The Burgundians settled as ''foederati'' in the Roman province of Germania Secunda along the Middle Rhine. Kingdom In 411 AD, the Burgundian king Gunther (or Gundahar or Gundicar) in cooperation with Goar, king of the Alans, set up Jovinus as a puppet emperor. Under the pretext of Jovinus' imperial authority, Gunther settled on the western (i.e., Roman) bank of the Rhine, between the river Lauter and the Nahe, seizing the settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



