|
Kingdom Of The Burgundians
The Kingdom of the Burgundians or First Kingdom of Burgundy was established by Germanic Burgundians in the Rhineland and then in eastern Gaul in the 5th century. History Background The Burgundians, a Germanic tribe, may have migrated from the Scandinavian island of Bornholm to the Vistula basin in the 3rd century AD. However, the first documented King of the Burgundians, Gjúki (Gebicca), lived in the late 4th century east of the Rhine. In 406 the Alans, Vandals, Suevi, and possibly the Burgundians, crossed the Rhine and invaded Roman Gaul. The Burgundians settled as ''foederati'' in the Roman province of Germania Secunda along the Middle Rhine. Kingdom In 411 AD, the Burgundian king Gunther (or Gundahar or Gundicar) in cooperation with Goar, king of the Alans, set up Jovinus as a puppet emperor. Under the pretext of Jovinus' imperial authority, Gunther settled on the western (i.e., Roman) bank of the Rhine, between the river Lauter and the Nahe, seizing the settlement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunther
Gundaharius or Gundahar (died 437), better known by his legendary names Gunther ( gmh, Gunther) or Gunnar ( non, Gunnarr), was a historical king of Burgundy in the early 5th century. Gundahar is attested as ruling his people shortly after they crossed the Rhine into Roman Gaul. He was involved in the campaigns of the failed Roman usurper Jovinus before the latter's defeat, after which he was settled on the left bank of the Rhine as a Roman ally. In 436, Gundahar launched an attack from his kingdom on the Roman province of Belgica Prima. He was defeated by the Roman general Flavius Aetius, who destroyed Gundahar's kingdom with the help of Hunnish mercenaries the following year, resulting in Gundahar's death. The historical Gundahar's death became the basis for a tradition in Germanic heroic legend in which the legendary Gunther met his death at the court of Attila the Hun (Etzel/Atli). The character also became attached to other legends: most notably he is associated with Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossing Of The Rhine
The crossing of the Rhine River by a mixed group of barbarians which included Vandals, Alans and Suebi is traditionally considered to have occurred on the last day of the year 406 (December 31, 406). The crossing transgressed one of the Late Roman Empire's most secure '' limites'' or boundaries and so it was a climactic moment in the decline of the Empire. It initiated a wave of destruction of Roman cities and the collapse of Roman civic order in northern Gaul. That, in turn, occasioned the rise of three usurpers in succession in the province of Britannia. Therefore, the crossing of the Rhine is a marker date in the Migration Period during which various Germanic tribes moved westward and southward from southern Scandinavia and northern Germania. Ancient sources Several written accounts document the crossing, supplemented by the time line of Prosper of Aquitaine, which gives a firm date of 31 December 406 in his year-by-year chronicle: "In the sixth consulship of Arca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suevi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names such as the Marcomanni, Quadi, Hermunduri, Semnones, and Lombards. New groupings formed later, such as the Alamanni and Bavarians, and two kingdoms in the Migration Period were simply referred to as Suebian. Although Tacitus specified that the Suebian group was not an old tribal group itself, the Suebian peoples are associated by Pliny the Elder with the Irminones, a grouping of Germanic peoples who claimed ancestral connections. Tacitus mentions Suebian languages, and a geographical "Suevia". The Suevians were first mentioned by Julius Caesar in connection with the invasion of Gaul by the Germanic king Ariovistus during the Gallic Wars. Unlike Tacitus he described them as a single people, distinct from the Marcomanni, within the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal Kingdom, Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century. The Vandals migrated to the area between the lower Oder and Vistula rivers in the second century BC and settled in Silesia from around 120 BC. They are associated with the Przeworsk culture and were possibly the same people as the Lugii. Expanding into Roman Dacia, Dacia during the Marcomannic Wars and to Pannonia during the Crisis of the Third Century, the Vandals were confined to Pannonia by the Goths around 330 AD, where they received permission to settle from Constantine the Great. Around 400, raids by the Huns from the east forced many Germanic tribes to migrate west into the territory of the Roman Empire and, fearing that they might be targeted next, the Vandals were also pushed westwards, Crossing of the Rhine, crossing the Rhine in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
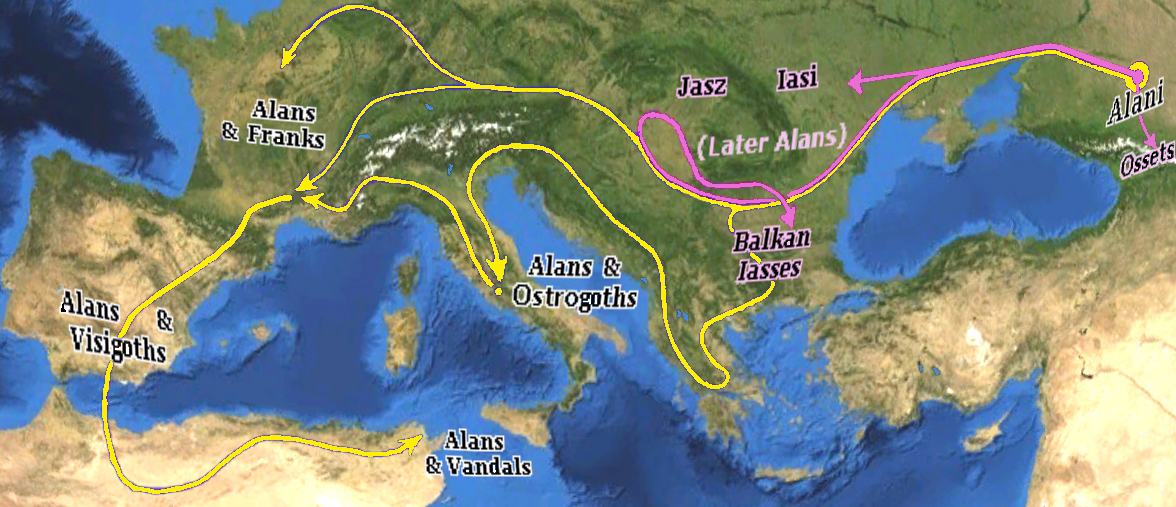
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjúki
Gibica (also ''Gebicca'', ''Gifica'', ''Gjúki'', ''Gebicar'', ''Gibicho'' or ''Gippich'') was the King of the Burgundians in the late 4th century until his death in or around 407. He was the father of Gundomar I, Giselher and Gunther. He is mentioned in Widsith as ''Gifica'' and as ''Gjúki'' in the eddic poem '' Atlakviða'', where he was the father of Gunnar (see Gunther). As one of the earliest kings of the Nibelungs, the clan is called the Gjúkungar. In the ''Prose Edda,'' Snorri Sturluson says that Gjúki was the father of sons Gunnar and Hogni and a daughter Gudrun. Gotthorm (slayer of Sigurd) is his stepson from his wife Grimhild's previous marriage. The ''Prose Edda'' mentions Gudny, a second daughter of Gjúki and Grimhild. In the Gudrunarkvida, this second daughter is named Gullrond. See also *Völsunga saga *Tribes of Widsith "Widsith" ( ang, Wīdsīþ, "far-traveller", lit. "wide-journey"), also known as "The Traveller's Song", is an Old English poem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland. The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in the south of Poland, above sea level in the Silesian Beskids (western part of Carpathian Mountains), where it begins with the Little White Vistula (''Biała Wisełka'') and the Black Little Vistula (''Czarna Wisełka''). It flows through Poland's largest cities, including Kraków, Sandomierz, Warsaw, Płock, Włocławek, Toruń, Bydgoszcz, Świecie, Grudziądz, Tczew and Gdańsk. It empties into the Vistula Lagoon (''Zalew Wiślany'') or directly into the Gdańsk Bay of the Baltic Sea with a delta of six main branches (Leniwka, Przekop, Śmiała Wisła, Martwa Wisła, Nogat and Szkarpawa). The river is often associated with Polish culture, history and national identity. It is the country's most important waterway and natural sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bornholm
Bornholm () is a Danish island in the Baltic Sea, to the east of the rest of Denmark, south of Sweden, northeast of Germany and north of Poland. Strategically located, Bornholm has been fought over for centuries. It has usually been ruled by Denmark, but also by Sweden and by Lübeck. The ruin of Hammershus, at the northwestern tip of the island, is the largest medieval fortress in northern Europe, testament to the importance of its location. Bornholm and Ertholmene comprise the last remaining Danish territory in Skåneland east of Øresund, having been surrendered to Sweden in 1658, but regained by Denmark in 1660 after a local revolt. The island is known as ("sunshine island") because of its weather and ("rock island") because of its geology, which consists of granite, except along the southern coast. The heat from the summer is stored in the rock formations and the weather is quite warm until October. As a result of the climate, a local variety of the common fig, k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer more narrowly to the Scandinavian Peninsula (which excludes Denmark but includes part of Finland), or more broadly to include all of Finland, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands. The geography of the region is varied, from the Norwegian fjords in the west and Scandinavian mountains covering parts of Norway and Sweden, to the low and flat areas of Denmark in the south, as well as archipelagos and lakes in the east. Most of the population in the region live in the more temperate southern regions, with the northern parts having long, cold, winters. The region became notable during the Viking Age, when Scandinavian peoples participated in large scale raiding, conquest, colonization and trading mostly throughou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Republican era, Cisalpina was annexed in 42 BC to Roman Italy), and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Gallia Belgica, Belgica, and Gallia Aquitania, Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section. Term Historically, the Rhinelands refers (physically speaking) to a loosely defined region embracing the land on the banks of the Rhine in Central Europe, which were settled by Ripuarian and Salian Franks and became part of Frankish Austrasia. In the High Middle Ages, numerous Imperial States along the river emerged from the former stem duchy of Lotharingia, without developing any common political or cultural identity. A "Rhineland" conceptualization can be traced to the period of the Holy Roman Empire from the sixteenth until the eighteenth centuries when the Empire's Imperial Estates (territories) were grouped into regional districts in charge of defence and judicial execution, known as Imperial Circles. Three of the ten circles through which the Rhine flowed r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |