|
Villa Gordiani
Villa Gordiani is a Roman gardens, park along the Via Prenestina, in Rome, Italy. It is home to several ancient Roman remains, traditionally identified with the villa of the Gordian imperial family, which included three Roman emperors of the 3rd century, Gordian I, Gordian II and Gordian III. History The complex, which is mentioned in ancient sources such as the ''Historia Augusta'', had a portico with some 200 columns, in different stones. It also included basilicas and baths. During the 13th century, the ''Tor de' Schiavi'' (literally "Tower of the Slaves", although the name derives from the dello Schiavo family, who acquired it in 1571) was built over the remains. In 1422 the area was acquired by the House of Colonna, Colonna family. The monumental entrance of the villa is an octagonal structure dating perhaps to the late 3rd-early 4th century, when the villa was enlarged and restored. The complex and the garden were restored in the 1960s, and has now the status of an archaeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Gardens
Roman gardens and ornamental horticulture became highly developed under Roman civilization, and thrived from 150 BC to 350 AD. The Gardens of Lucullus (''Horti Lucullani''), on the Pincian Hill in Rome, introduced the Persian gardens, Persian garden to Europe around 60 BC. It was seen as a place of peace and tranquillity, a refuge from urban life, and a place filled with religious and symbolic meaning. As Roman culture developed and became increasingly influenced by foreign civilizations, the use of gardens expanded. The Roman garden's history, function, and style is investigated through archaeological and Archaeobotany, archaeobotanical research, famously conducted at Pompeii, literary sources, and Fresco, wall paintings and mosaics in homes. Influences Roman gardening was influenced by Egyptian and Persian gardens, Persian gardening techniques, through acquaintance with Greek gardening. The gardens of Ancient Persia were organized around rills, known from Pasargadae and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Ancient Roman Architecture ...
{{Category pair, Ancient Greek architecture, Byzantine architecture Archit Architectural history Roman Classical architecture Roman Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Villas In Italy
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television * Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *Ῥωμ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Roman Buildings And Structures In Rome
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parks In Rome
A park is an area of natural, semi-natural or planted space set aside for human enjoyment and recreation or for the protection of wildlife or natural habitats. Urban parks are urban green space, green spaces set aside for recreation inside towns and cities. National parks and country parks are green spaces used for recreation in the countryside. State parks and provincial parks are administered by sub-national government states and agencies. Parks may consist of grassy areas, rocks, soil and trees, but may also contain buildings and other artifacts such as monuments, fountains or playground structures. Many parks have fields for playing sports such as baseball and football, and paved areas for games such as basketball. Many parks have trails for walking, biking and other activities. Some parks are built adjacent to bodies of water or watercourses and may comprise a beach or boat dock area. Urban parks often have benches for sitting and may contain picnic tables and barbecue gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villa Of Livia
The Villa of Livia ( la, Ad Gallinas Albas) is an ancient Roman villa at Prima Porta, north of Rome, Italy, along the Via Flaminia. It may have been part of Livia Drusilla's dowry that she brought when she married Octavian (later called the emperor Augustus), her second husband, in 39 BC. However, it may also have been a gift given to her by Octavian upon their betrothal. The ancient sources (e.g. Suetonius) tell us that Livia returned to this villa following the marriage. It was her sumptuous country residence complementing her house on the Palatine Hill in Rome. Remarkable frescoes of garden views were found which have since been removed to the Palazzo Massimo museum in Rome. Location The villa occupied the height dominating the view down the Tiber Valley to Rome. Some of the walling that retained the villa's terraces can still be seen. The location was strategically important due to the iron-rich cliffs of red tuff that approach the river Tiber at this point, the confluence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
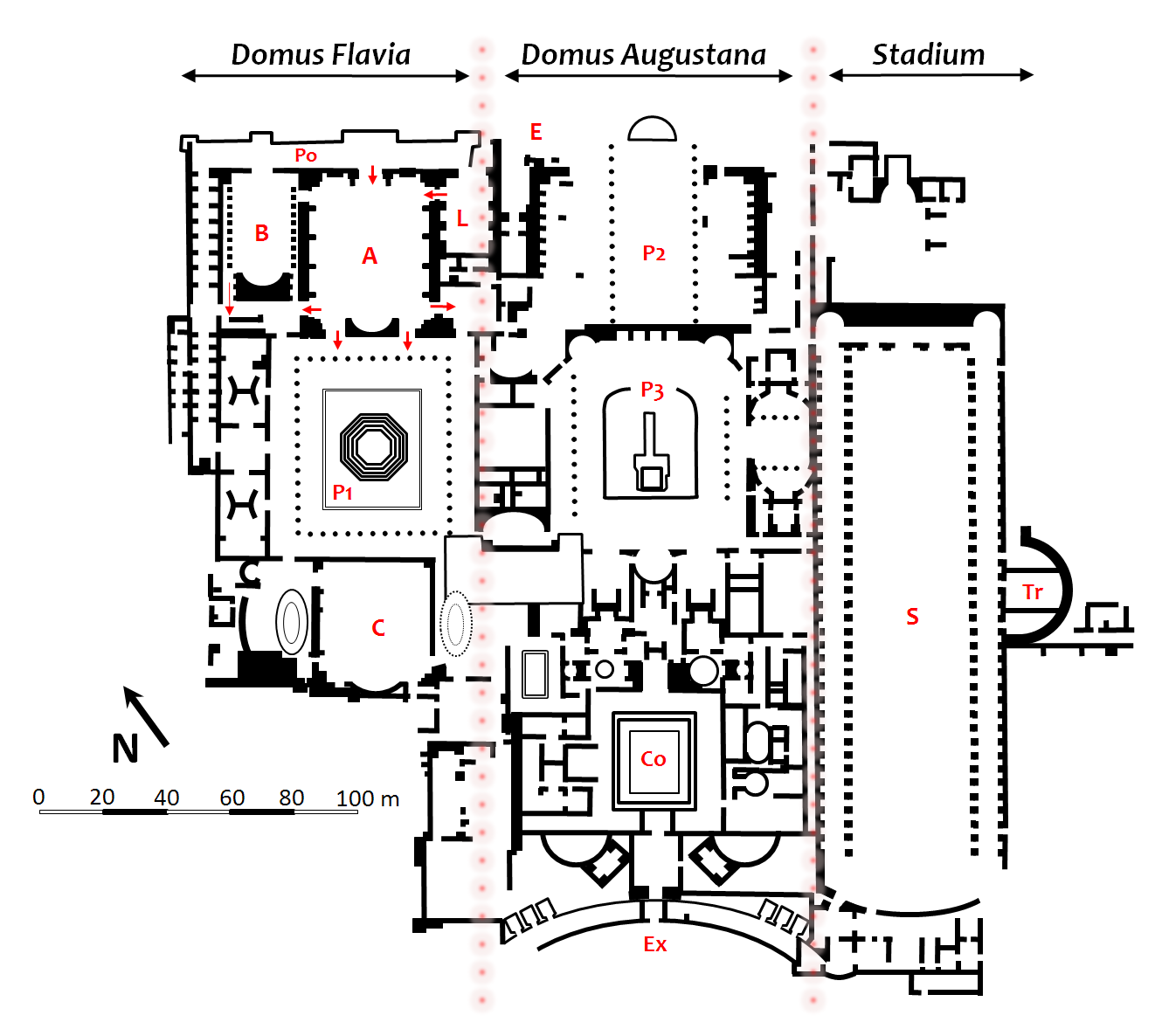
Palace Of Domitian
The Palace of Domitian was built as Roman emperor Domitian's official residence in 81–92 AD and was used as such by subsequent emperors. Its remains sit atop and dominate the Palatine Hill in Rome, alongside other palaces. The Palace is a massive structure separated today into three areas, in part following the way business matters and private life were separated so they could be conducted in parallel. The modern names used for these parts are: * the Domus Flavia * the Domus Augustana * the garden or "stadium". It has not been fully exposed as parts lie under more recent buildings. The palace was one of Domitian's many architectural projects, renovation of the Circus Maximus, renovation of the Pantheon, and three temples deifying his family members: the temple of Vespasian and Titus, the '' Porticus Diuorum'', and the Temple of the gens Flavia. History It was designed by the architect Rabirius. The palace was built on top of earlier buildings, notably Nero's Domus Transito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Roman And Byzantine Domes
Domes were a characteristic element of the architecture of Ancient Rome and of its medieval continuation, the Byzantine Empire. They had widespread influence on contemporary and later styles, from Russian and Ottoman architecture to the Italian Renaissance and modern revivals. The domes were customarily hemispherical, although octagonal and segmented shapes are also known, and they developed in form, use, and structure over the centuries. Early examples rested directly on the rotunda walls of round rooms and featured a central oculus for ventilation and light. Pendentives became common in the Byzantine period, provided support for domes over square spaces. Early wooden domes are known only from a literary source, but the use of wooden formwork, concrete, and unskilled labor enabled domes of monumental size in the late Republic and early Imperial period, such as the so-called "Temple of Mercury" bath hall at Baiae. Nero introduced the dome into Roman palace architecture in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Colonna
The House of Colonna, also known as ''Sciarrillo'' or ''Sciarra'', is an Italian noble family, forming part of the papal nobility. It was powerful in medieval and Renaissance Rome, supplying one pope (Martin V) and many other church and political leaders. The family is notable for its bitter feud with the Orsini family over influence in Rome, until it was stopped by papal bull in 1511. In 1571, the heads of both families married nieces of Pope Sixtus V. Thereafter, historians recorded that "no peace had been concluded between the princes of Christendom, in which they had not been included by name". History Origins According to tradition, the Colonna family is a branch of the Counts of Tusculum — by Peter (1099–1151) son of Gregory III, called Peter "de Columna" from his property the Columna Castle in Colonna, in the Alban Hills. Further back, they trace their lineage past the Counts of Tusculum via Lombard and Italo-Roman nobles, merchants, and clergy through the Early Mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Prenestina
The Via Praenestina (modern Italian: Via Prenestina) was an ancient Roman road in central Italy. Initially called Via Gabiana, from Gabii, the ancient city of Old Latium to which it ran, it received a new name having been extended as far as Praeneste (modern Palestrina). Once past Praeneste the road continued towards the Apennines and the source of the Anio River. At the ninth mile the road crosses a ravine by the well-preserved and lofty Ponte di Nona, with seven arches, the finest ancient bridge in the neighbourhood of Rome. The line of the road is, considering the difficulty of the country beyond Gabii, very straight. Half-way between Gabii and Praeneste is a well-preserved single-arched bridge, Ponte Amato Ponte, a word meaning ''bridge'' in Italian, Portuguese, and Galician languages, may refer to: Places England *Pontefract, a town in the Metropolitan City of Wakefield France * Ponte Leccia, a civil parish (hameau) in the department of Haute-Co .... Ashby cites h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historia Augusta
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, designated heirs and usurpers from 117 to 284. Supposedly modeled on the similar work of Suetonius, ''The Twelve Caesars'', it presents itself as a compilation of works by six different authors (collectively known as the ''Scriptores Historiae Augustae''), written during the reigns of Diocletian and Constantine I and addressed to those emperors or other important personages in Ancient Rome. The collection, as extant, comprises thirty biographies, most of which contain the life of a single emperor, but some include a group of two or more, grouped together merely because these emperors were either similar or contemporaneous. The true authorship of the work, its actual date, its reliability and its purpose have long been matters for controversy by historians and scholars ever since Hermann Dessau, in 1889, rejected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordian III
Gordian III ( la, Marcus Antonius Gordianus; 20 January 225 – February 244) was Roman emperor from 238 to 244. At the age of 13, he became the youngest sole emperor up to that point (until Valentinian II in 375). Gordian was the son of Antonia Gordiana and Junius Balbus, who died before 238. Antonia Gordiana was the daughter of Emperor Gordian I and younger sister of Emperor Gordian II. Very little is known of his early life before his acclamation. Gordian had assumed the name of his maternal grandfather in 238. Rise to power In 235, following the murder of Emperor Alexander Severus in Moguntiacum (modern Mainz), the capital of the Roman province Germania Superior, Maximinus Thrax was acclaimed emperor. In the following years, there was a growing opposition against Maximinus in the Roman Senate and amongst the majority of the population of Rome. In 238, a rebellion broke out in the Africa Province, where Gordian's grandfather and uncle, Gordian I and II, were proclaimed jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |