|
Viking Axe
The Dane axe is an early type of battle axe, primarily used during the transition between the European Viking Age and early Middle Ages. Other names for the weapon include English long axe, Danish axe, and hafted axe. Construction Most axes, both in period illustrations and extant artifact, that fall under the description of Danish axe possess type L or type M heads according to the Petersen axe typology. Both types consist of a wide, thin blade, with pronounced "horns" at both the toe and heel of the bit. Cutting surfaces vary, but is generally between . Type L blades tend to be smaller, with the toe of the bit swept forward for superior shearing capability. Later type M blades are typically larger overall, with a more symmetrical toe and heel. The blade itself was reasonably light and forged very thin, making it superb for cutting. The thickness of the body on top the edge is as thin as 2 mm. Many of these axes were constructed with a reinforced bit, typically of a highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dane Axe
The Dane axe is an early type of battle axe, primarily used during the transition between the European Viking Age and early Middle Ages. Other names for the weapon include English long axe, Danish axe, and hafted axe. Construction Most axes, both in period illustrations and extant artifact, that fall under the description of Danish axe possess type L or type M heads according to the Petersen axe typology. Both types consist of a wide, thin blade, with pronounced "horns" at both the toe and heel of the bit. Cutting surfaces vary, but is generally between . Type L blades tend to be smaller, with the toe of the bit swept forward for superior shearing capability. Later type M blades are typically larger overall, with a more symmetrical toe and heel. The blade itself was reasonably light and forged very thin, making it superb for cutting. The thickness of the body on top the edge is as thin as 2 mm. Many of these axes were constructed with a reinforced bit, typically of a highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
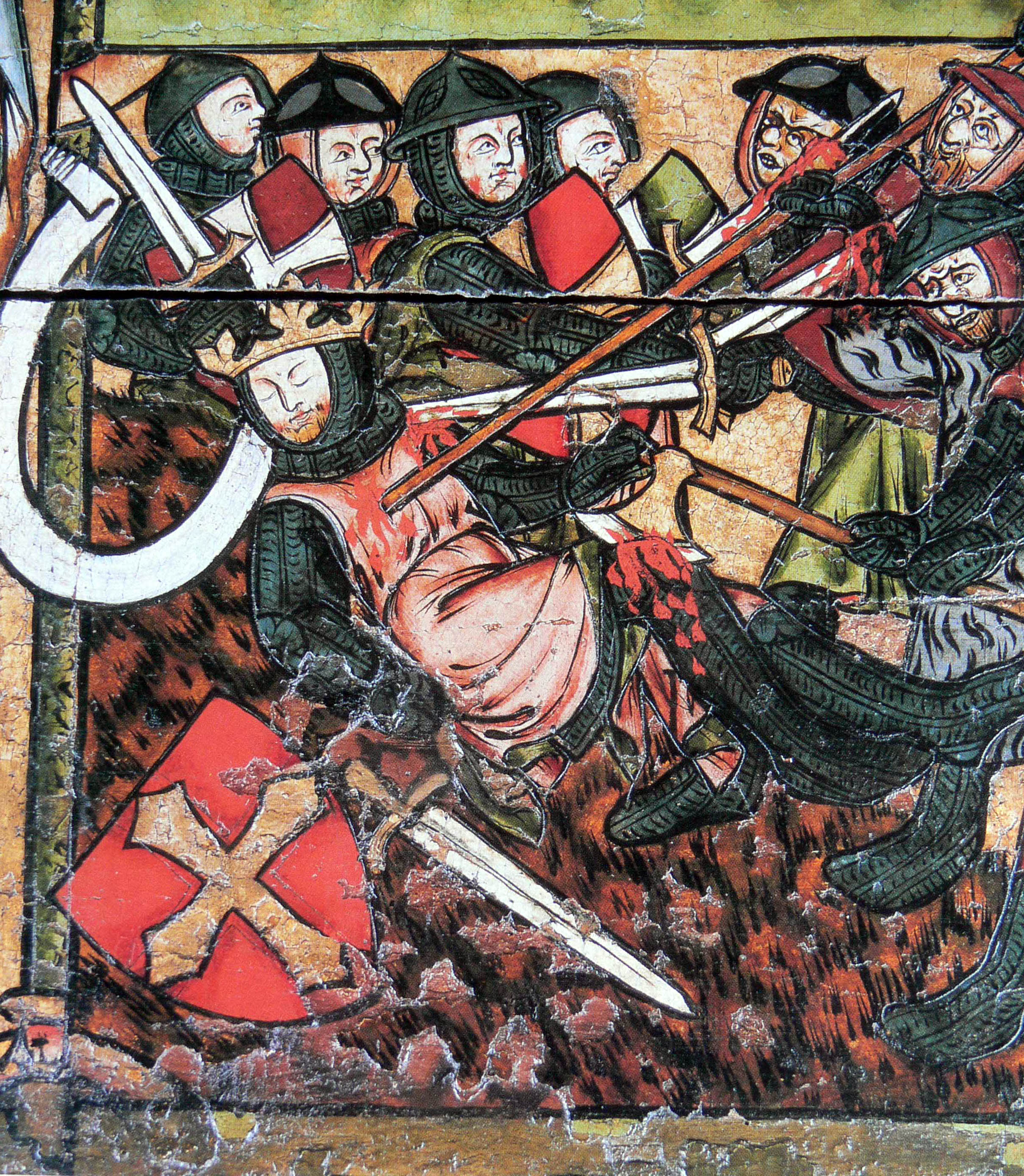
Maciejowski Bible
The Morgan Bible (mostly Morgan Library & Museum, New York, Ms M. 638), also called the Morgan Picture Bible, Crusader Bible, Shah Abbas Bible or Maciejowski Bible, is a unique medieval illuminated manuscript. It is a picture book Bible consisting of 46 surviving folios. The book consists of miniature paintings of events from the Hebrew Bible, set in the scenery and costumes of thirteenth-century France, and depicted from a Christian perspective. It is not a complete Bible, as it consists largely of illustrations of stories of kings, especially King David. The illustrations are now surrounded by text in three scripts and five languages: Latin, Persian, Arabic, Judeo-Persian, and Hebrew. The level of detail in the images and the remarkable state of preservation of the work make it particularly valuable to scholars. Forty-three folios are in the Morgan Library & Museum in New York City, with two folios in the Bibliothèque nationale de France (MS nouv. acq. lat. 2294). A singl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Knight's Tale
"The Knight's Tale" ( enm, The Knightes Tale) is the first tale from Geoffrey Chaucer's '' The Canterbury Tales''. The Knight is described by Chaucer in the "General Prologue" as the person of highest social standing amongst the pilgrims, though his manners and clothes are unpretentious. We are told that he has taken part in some fifteen crusades in many countries and also fought for one pagan leader against another. Though the list of campaigns is real, his characterization is idealized. Most readers have taken Chaucer's description of him as "a verray, parfit gentil knyght" to be sincere but Terry Jones suggested that this description was ironic, and that Chaucer's readers would have deduced that the Knight was a mercenary. He is accompanied on his pilgrimage by the Squire, his 20-year-old son. The story introduces themes and arguments typically encountered in the literature of knighthood, including courtly love and ethical dilemmas. Sources and composition The epic poem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Child's History Of England
''A Child's History of England'' is a book by Charles Dickens. It first appeared in serial form in '' Household Words'', running from 25 January 1851 to 10 December 1853. Dickens also published the work in book form in three volumes: the first volume on 20 December 1851, the second on 25 December 1852 and the third on 24 December 1853. Although the volumes were published in December, each was postdated the following year. They bore the titles: * Volume I. – England from the Ancient Times, to the Death of King John (1852) * Volume II. – England from the Reign of Henry the Third, to the Reign of Richard the Third (1853) * Volume III. – England from the Reign of Henry the Seventh to the Revolution of 1688 (1854) Dickens dedicated the book to "My own dear children, whom I hope it may help, bye and bye, to read with interest larger and better books on the same subject". The history covered the period between 50 BC and 1689, ending with a chapter summarising events from then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian era.. His works enjoyed unprecedented popularity during his lifetime and, by the 20th century, critics and scholars had recognised him as a literary genius. His novels and short stories are widely read today. Born in Portsmouth, Dickens left school at the age of 12 to work in a boot-blacking factory when his father was incarcerated in a debtors' prison. After three years he returned to school, before he began his literary career as a journalist. Dickens edited a weekly journal for 20 years, wrote 15 novels, five novellas, hundreds of short stories and non-fiction articles, lectured and performed readings extensively, was an indefatigable letter writer, and campaigned vigorously for children's rights, for education, and for other social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard The Lionheart
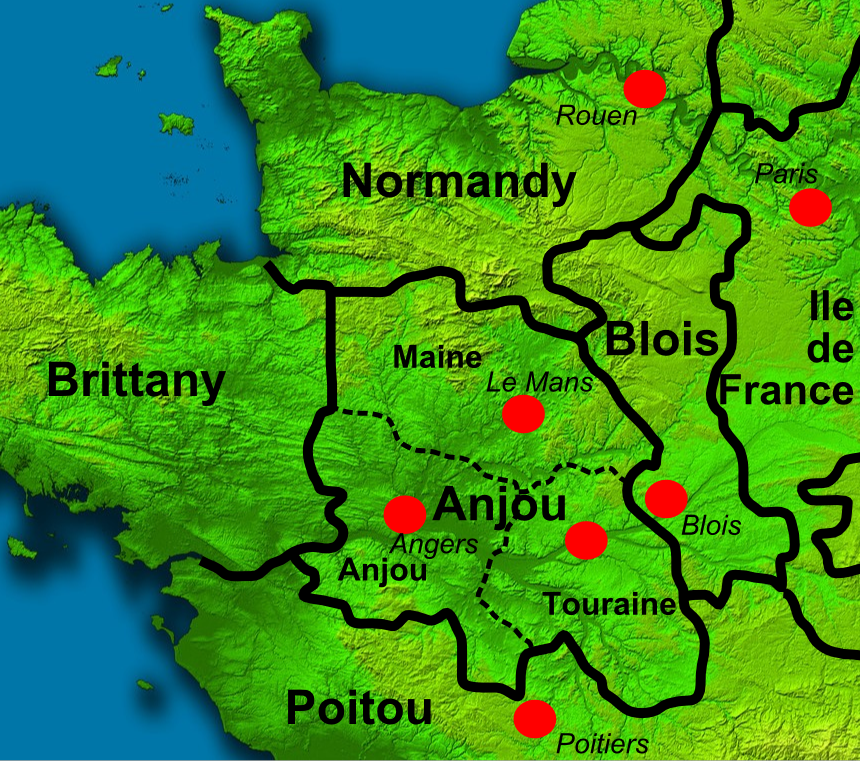
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199) was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Aquitaine and Gascony, Lord of Cyprus, and Count of Poitiers, Anjou, Maine, and Nantes, and was overlord of Brittany at various times during the same period. He was the third of five sons of King Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine and seemed unlikely to become king, but all his brothers except the youngest, John, predeceased their father. Richard is known as Richard Cœur de Lion (Norman French: ''Le quor de lion'') or Richard the Lionheart because of his reputation as a great military leader and warrior. The troubadour Bertran de Born also called him Richard Oc-e-Non ( Occitan for ''Yes and No''), possibly from a reputation for terseness. By the age of 16, Richard had taken command of his own army, putting down rebellions in Poitou against his father. Richard was an important Christian commander during the Third Crusade, leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lincoln (1141)
The Battle of Lincoln, or the First Battle of Lincoln, occurred on 2 February 1141 in Lincoln, England between King Stephen of England and forces loyal to Empress Matilda. Stephen was captured during the battle, imprisoned, and effectively deposed while Matilda ruled for a short time. Account The forces of King Stephen of England had been besieging Lincoln Castle but were themselves attacked by a relief force loyal to Empress Matilda and commanded by Robert, 1st Earl of Gloucester, Matilda's half-brother. The Angevin army consisted of the divisions of Robert's men, those of Ranulf, Earl of Chester and those disinherited by Stephen, while on the flank was a mass of Welsh troops led by Madog ap Maredudd, Lord of Powys, and Cadwaladr ap Gruffydd. Cadwaladr was the brother of Owain, King of Gwynedd, but Owain did not support any side in the Anarchy. Stephen's force included William of Ypres; Simon of Senlis; Gilbert of Hertford; William of Aumale, Alan of Richmond and Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Of England
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne '' jure uxoris'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 1135 until 1144. His reign was marked by the Anarchy, a civil war with his cousin and rival, the Empress Matilda, whose son, Henry II, succeeded Stephen as the first of the Angevin kings of England. Stephen was born in the County of Blois in central France as the fourth son of Stephen-Henry, Count of Blois, and Adela, daughter of William the Conqueror. His father died while Stephen was still young, and he was brought up by his mother. Placed into the court of his uncle Henry I of England, Stephen rose in prominence and was granted extensive lands. He married Matilda of Boulogne, inheriting additional estates in Kent and Boulogne that made the couple one of the wealthiest in England. Stephen narrowly escaped drowning with Henry I's son, William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of Norway
The coat of arms of Norway is the arms of dominion of king Harald V of Norway, and as such represents both the monarch and the kingdom (nation and the state). It depicts a standing golden lion on a red background, bearing a golden crown and axe with silver blade (blazoned ''Gules, a lion rampant Or, crowned Or, holding an axe Or with a blade argent''). The coat of arms is used by the King (including the King's Council), the Parliament, and the Supreme Court, which are the three powers according to the Constitution. It is also used by several national, regional, and local authorities that are subordinate to the aforementioned, for example the County Governors and both the district courts and the courts of appeal. Since 1905, two parallel versions exist: the more elaborate version used by the King and the simpler one used by the State. The arms in banner form serve as basis for the monarch's flag, known as the Royal Standard. In addition, there are former and existing lands (e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olaf II Of Norway
Olaf II Haraldsson ( – 29 July 1030), later known as Saint Olaf (and traditionally as St. Olave), was King of Norway from 1015 to 1028. Son of Harald Grenske, a petty king in Vestfold, Norway, he was posthumously given the title ''Rex Perpetuus Norvegiae'' ( en, Eternal/Perpetual King of Norway) and canonised at Nidaros (Trondheim) by Bishop Grimkell, one year after his death in the Battle of Stiklestad on 29 July 1030. His remains were enshrined in Nidaros Cathedral, built over his burial site. His sainthood encouraged the widespread adoption of Christianity by Scandinavia's Vikings/Norsemen. Pope Alexander III confirmed Olaf's local canonisation in 1164, making him a recognised saint of the Catholic Church and started to be known as ''Rex Perpetuus Norvegiae'' – ''eternal king of Norway''. Following the Reformation he was a commemorated historical figure among some members of the Lutheran and Anglican Communions. The saga of Olav Haraldsson and the legend of Olaf the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Stiklestad
The Battle of Stiklestad ( no, Slaget på Stiklestad, non, Stiklarstaðir) in 1030 is one of the most famous battles in the history of Norway. In this battle, King Olaf II of Norway () was killed. During the pontificate of Pope Alexander III, the Roman Catholic Church declared Olaf a saint in 1164. His younger half-brother, Harald Hardrada (), was also present at the battle. Harald was only fifteen when the battle of Stiklestad took place. He became King of Norway in 1047, until his death in a failed invasion of England at the Battle of Stamford Bridge in 1066. The authenticity of the battle as a historical event is subject to question. Contemporary sources say the king was murdered. According to the '' Anglo Saxon Chronicle'' of 1030, Olaf was killed by his own people. Adam of Bremen wrote in 1070 that Olaf was killed in an ambush, and so did Florence of Worcester in 1100. Those are the only contemporary sources that mention the death of the king. After the king's canoniza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallowglass
The Gallowglass (also spelled galloglass, gallowglas or galloglas; from ga, gallóglaigh meaning foreign warriors) were a class of elite mercenary warriors who were principally members of the Norse-Gaelic clans of Ireland between the mid 13th century and late 16th century. Originally applied to Scots, who shared a common background and language with the Irish, but as they were descendants of 10th-century Norse settlers who had intermarried with the local population in western Scotland, the Irish called them ("foreign Gaels"). An early family of gallowglasses was the MacSweeneys, settled by the O'Donnells in north Donegal. These were followed by MacDonnells, MacCabes and several other groups settled by powerful Irish nobles in different areas. The gallowglasses were attractive as heavily armoured, trained infantry to be relied upon as a strong defence for holding a position, unlike most Irish foot soldiers, who were less well armoured than the typical Irish noble who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |