|
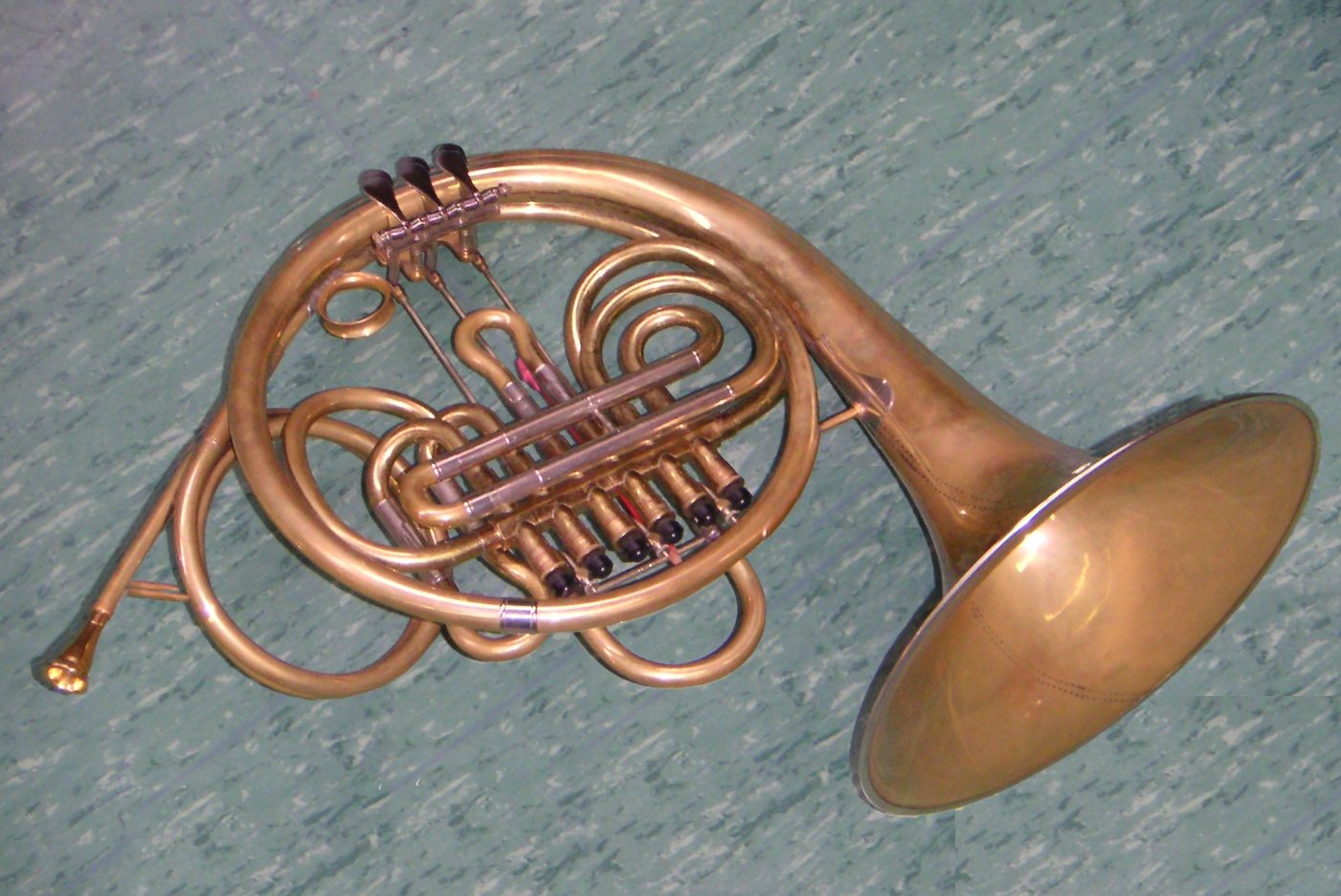
Vienna Horn
The Vienna horn (german: Wiener Horn) is a type of musical horn used primarily in Vienna, Austria, for playing orchestral or classical music. It is used throughout Vienna, including the Vienna Philharmonic The Vienna Philharmonic (VPO; german: Wiener Philharmoniker, links=no) is an orchestra that was founded in 1842 and is considered to be one of the finest in the world. The Vienna Philharmonic is based at the Musikverein in Vienna, Austria. It ... and ''Wiener Staatsoper''. History During the nineteenth century, a number of experiments were made in adding valves to the natural horn to enable it to play chromatically without the need for hand-stopping. These experiments included adding piston valves (as used in modern trumpets) to a French horn#Single horn, single F horn. The horn was still crook (music), crooked, by inserting other tubing, to re-tune the instrument for music written in base keys other than F. Description The Vienna horn uses a unique form of double-cylin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horn (instrument)
A horn is any of a family of musical instruments made of a tube, usually made of metal and often curved in various ways, with one narrow end into which the musician blows, and a wide end from which sound emerges. In horns, unlike some other brass instruments such as the trumpet, the bore gradually increases in width through most of its length—that is to say, it is conical rather than cylindrical. In jazz and popular-music contexts, the word may be used loosely to refer to any wind instrument, and a section of brass or woodwind instruments, or a mixture of the two, is called a horn section in these contexts. Types Variations include: *Lur (prehistoric) *Shofar *Roman horns: ** Cornu **Buccina * Dung chen *Dord * Sringa * Nyele *Wazza *Alphorn *Cornett *Serpent * Ophicleide *Natural horn **Bugle **Post horn *French horn *Vienna horn *Wagner tuba *Saxhorns, including: **Alto horn (UK: tenor horn), pitched in E ** Baritone horn, pitched in B * Valved bugles, including ** c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trumpet
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard B or C trumpet. Trumpet-like instruments have historically been used as signaling devices in battle or hunting, with examples dating back to at least 1500 BC. They began to be used as musical instruments only in the late 14th or early 15th century. Trumpets are used in art music styles, for instance in orchestras, concert bands, and jazz ensembles, as well as in popular music. They are played by blowing air through nearly-closed lips (called the player's embouchure), producing a "buzzing" sound that starts a standing wave vibration in the air column inside the instrument. Since the late 15th century, trumpets have primarily been constructed of brass tubing, usually bent twice into a rounded rectangular shape. There are many distinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornist
This list of horn players and pedagogues includes notable players of French horn, German horn, natural horn, Vienna horn, tenor (alto) horn, and alphorn. B * Radek Baborák, former Principal horn Berlin Philharmonic Orchestra, Munich Phil. Orch, Czech Phil. Orch. winner of the ARD, Geneva, Markneukirchen, Concertino Praga Hochschule für Musik Saar. * Andrew Bain, principal horn of the Los Angeles Philharmonic, LA studio player, horn professor at the Colburn School in Los Angeles, California * Georges Barboteu (1924–2006), Former professor at CNSM, member of the French French-horn school, horn instructor of many current French French hornists *Hermann Baumann (*1934), former principal horn Philharmonisches Orchester Dortmund and Stuttgart Radio Symphony Orchestra, winner of the ARD International Music Competition in 1964, soloist, performing on natural horn and valved horn * Richard Bissill, player, composer, arranger and professor * Aubrey Brain, player (1893–1955) * Den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary Valve
A rotary valve (also called rotary-motion valve) is a type of valve in which the rotation of a passage or passages in a transverse plug regulates the flow of liquid or gas through the attached pipes. The common stopcock is the simplest form of rotary valve. Rotary valves have been applied in numerous applications, including: * Changing the pitch of brass instruments. * Controlling the steam and exhaust ports of steam engines, most notably in the Corliss steam engine. * Periodically reversing the flow of air and fuel across the open hearth furnace. * Loading sample on chromatography columns. * Certain types of two-stroke and four-stroke engines. * Most hydraulic automotive power steering control valves. Use in brass instruments In the context of brass instruments, rotary valves are found on horns, trumpets, trombones, flugelhorns, and tubas. The cornet derived from the posthorn, by applying rotary valves to it in the 1820s in France. An alternative to a rotary valve trumpet wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legato
In music performance and notation, legato (; Italian for "tied together"; French ''lié''; German ''gebunden'') indicates that musical notes are played or sung smoothly and connected. That is, the player makes a transition from note to note with no intervening silence. Legato technique is required for slurred performance, but unlike slurring (as that term is interpreted for some instruments), legato does not forbid re- articulation. Standard notation indicates legato either with the word ''legato'', or by a slur (a curved line) under notes that form one legato group. Legato, like staccato, is a kind of articulation. There is an intermediate articulation called either ''mezzo staccato'' or ''non-legato'' (sometimes referred to as ''portato''). Classical string instruments In music for Classical string instruments, legato is an articulation that often refers to notes played with a full bow, and played with the shortest silence, often barely perceptible, between notes. The play ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
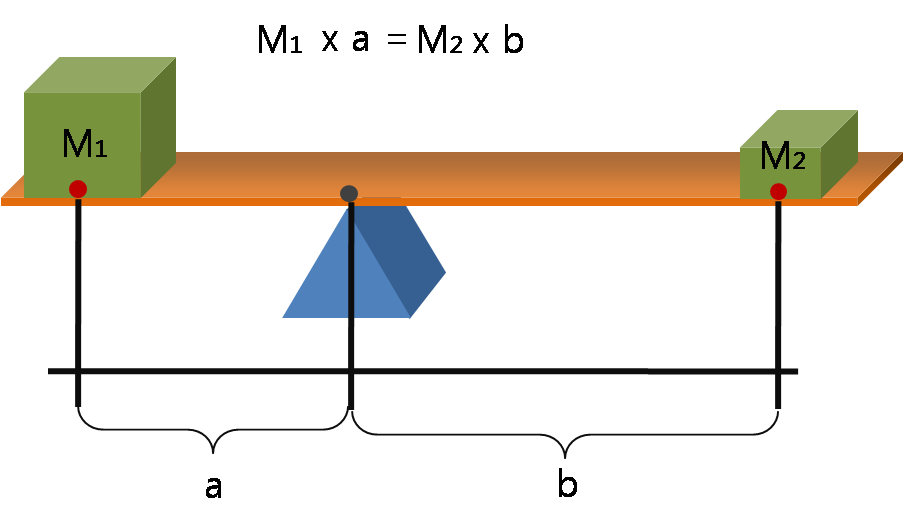
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or ''fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types. Also, leverage is mechanical advantage gained in a system. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage. The ratio of the output force to the input force is the mechanical advantage of the lever. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English around 1300 from Old French, in which the word was ''levier''. This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to the Latin ''levare'', itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push-rod
An overhead valve (OHV) engine, sometimes called a ''pushrod engine'', is a piston engine whose valves are located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier flathead engines, where the valves were located below the combustion chamber in the engine block. Although an overhead camshaft (OHC) engine also has overhead valves, the common usage of the term "overhead valve engine" is limited to engines where the camshaft is located in the engine block. In these traditional OHV engines, the motion of the camshaft is transferred using pushrods (hence the term "pushrod engine") and rocker arms to operate the valves at the top of the engine. Some early intake-over-exhaust engines used a hybrid design combining elements of both side-valves and overhead valves. History Predecessors The first internal combustion engines were based on steam engines and therefore used slide valves. This was the case for the first Otto engine, which was first succes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
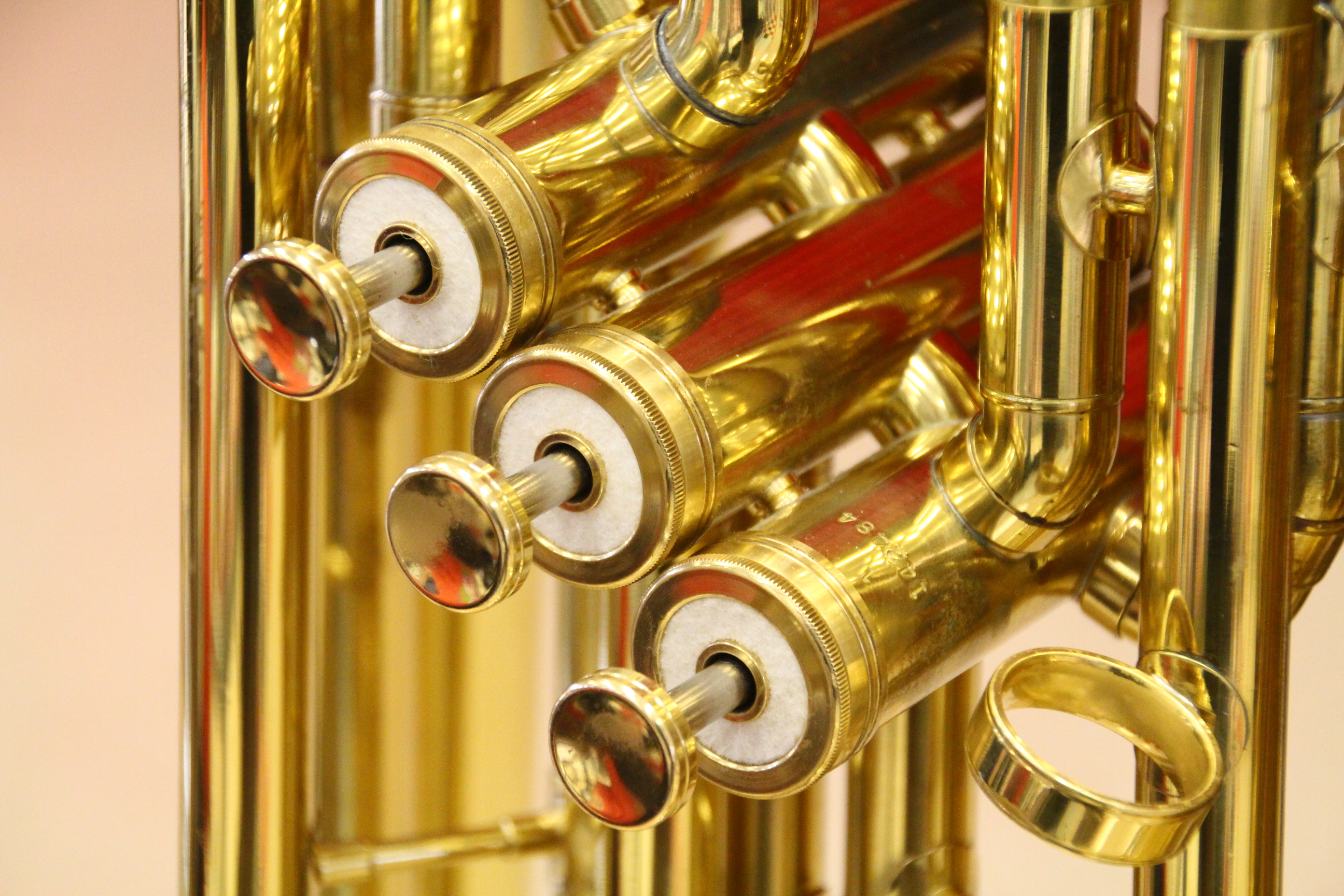
Pumpenvalve
Brass instrument valves are valves used to change the length of tubing of a brass instrument allowing the player to reach the notes of various harmonic series. Each valve pressed diverts the air stream through additional tubing, individually or in conjunction with other valves. This lengthens the vibrating air column thus lowering the fundamental tone and associated harmonic series produced by the instrument. Valves in brass instruments require regular maintenance and lubrication to ensure fast and reliable movement. Piston valve The first musical instruments with piston valves were developed just after the start of the 19th century. Stölzel valve The first of these types was the Stölzel valve, bearing the name of its inventor Heinrich Stölzel, who first applied these valves to the French horn in 1814. Until that point, there had been no successful valve design, and horn players had to stop off the bell of the instrument, greatly compromising tone quality to achieve a partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crook (music)
A crook, also sometimes called a shank, is an exchangeable segment of tubing in a natural horn (or other brass instrument, such as a natural trumpet) which is used to change the length of the pipe, altering the fundamental pitch and harmonic series which the instrument can sound, and thus the key in which it plays.Apel, pp. 392, 926. Master crook and coupler system Early horns had unalterable lengths and permanently attached mouthpieces. This presented problems in concert situations. A different horn was required for different keys, and the instrument could not be tuned. Around 1700 the Leichnamschneider brothers in Vienna developed a horn with a removable mouthpiece that could be connected to a short piece of tubing, called a master crook. Additional pieces, couplers, of different lengths were inserted between the master crook and the body of the horn to change the horn's length, and thus the pitch. Fine-tuning was done with even shorter segments called tuning bits. This simple a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Horn
The French horn (since the 1930s known simply as the horn in professional music circles) is a brass instrument made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell. The double horn in F/B (technically a variety of German horn) is the horn most often used by players in professional orchestras and bands, although the descant and triple horn have become increasingly popular. A musician who plays a horn is known as a list of horn players, horn player or hornist. Pitch is controlled through the combination of the following factors: speed of air through the instrument (controlled by the player's lungs and thoracic diaphragm); diameter and tension of lip aperture (by the player's lip muscles—the embouchure) in the mouthpiece; plus, in a modern horn, the operation of Brass instrument valve, valves by the left hand, which route the air into extra sections of tubing. Most horns have lever-operated rotary valves, but some, especially older horns, use piston valves (similar to a trumpet's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston Valve
A "piston valve" is a device used to control the motion of a fluid along a tube or pipe by means of the linear motion of a piston within a chamber or cylinder. Examples of piston valves are: * The valves used in many brass instruments * The valves used in pneumatic cannons * The valves used in many stationary steam engines and steam locomotives Brass instruments Cylindrical piston valves called Périnet valves (after their inventor François Périnet) are used to change the length of tube in the playing of most brass instruments, particularly the trumpet-like members of the family (cornet, flugelhorn, saxhorn, etc.). Other brass instruments use rotary valves, notably the orchestral horns and many tuba models, but also a number of rotary-valved variants of those brass instruments which more commonly employ piston valves. The first piston-valved musical instruments were developed just after the start of the 19th century. The Stölzel valve (invented by Heinrich Stölzel in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna
en, Viennese , iso_code = AT-9 , registration_plate = W , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , blank_name = Vehicle registration , blank_info = W , blank1_name = GDP , blank1_info = € 96.5 billion (2020) , blank2_name = GDP per capita , blank2_info = € 50,400 (2020) , blank_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank_info_sec1 = 0.947 · 1st of 9 , blank3_name = Seats in the Federal Council , blank3_info = , blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .wien , website = , footnotes = , image_blank_emblem = Wien logo.svg , blank_emblem_size = Vienna ( ; german: Wien ; ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |