|
Varduli
The Varduli were a pre-Ancient Rome, Roman tribe settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today is the eastern region of the autonomous community of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country and western Navarre, in northern Spain. Their historical territory corresponds with current Basque language, Basque-speaking areas, however it is debated whether the Varduli were actually Aquitanians, related to the Vascones, or if they were Celts, related to tribes such as the Cantabri and Celtiberians and which later underwent Late Basquisation, Basquisation. Etymology Their ethnonym ''Varduli'' is connected with an area that is referred to in documents from the early Middle Ages as Bardulia, which is identified as the cradle of Old Castile. Julio Caro Baroja, a Spanish anthropologist and linguist declared on his works that the term ''Varduli'' does not have a Basque language, Basque origin. History The Varduli are mentioned for the first time during Anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caristii
The Caristii were a pre-Roman tribe settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today are known as the historical territories of Biscay and Álava, in the Basque Country, northern Spain. Origins Their historical territory today corresponds very well with the extension of the Biscayan dialect of the Basque language, however it is discussed whether the Caristii were actually Aquitanians, related to the Vascones, or if they were Celts, related to tribes such as the Cantabri and Celtiberians and that later suffered a Basquisation. History The Caristii are first mentioned by Roman sources; Pliny the Elder names them ''Carietes'' and places them in the Basque interior territories, what today is the southernmost regions of the Basque Country, while Ptolemy places them between the river Deba and Nervión, present-day provinces of Biscay and Gipuzkoa, with a territory triangle-shaped, reaching the city of Vitoria by the south. Their territory limited with the Varduli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascones
The Vascones were a pre-Roman tribe who, on the arrival of the Romans in the 1st century, inhabited a territory that spanned between the upper course of the Ebro river and the southern basin of the western Pyrenees, a region that coincides with present-day Navarre, western Aragon and northeastern La Rioja, in the Iberian Peninsula. The Vascones are often considered ancestors of the present-day Basques to whom they left their name. Territory Roman period The description of the territory which the Vascones inhabited during ancient times appears in texts of classical authors, between the 1st century BC and the 2nd century AD, such as Livy, Strabo, Pliny the Elder and Ptolemy. Although these texts have been studied as sources of reference, some authors have pointed out the apparent lack of uniformity and also the existence of contradictions within the texts, in particular with Strabo. The oldest document corresponds to Livy (59 BC - AD 17), who in a brief passage of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
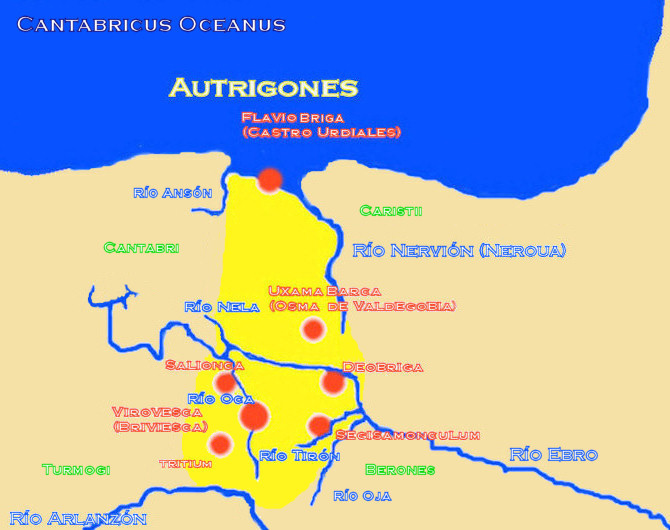
Autrigones
The Autrigones were a pre-Roman tribe that settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today is the western Basque Country (western regions of Biscay and Álava) and northern Burgos and the East of Cantabria, Spain. Their territory limited with the Cantabri territory at west, the Caristii at east, the Berones at the southeast and the Turmodigi at the south. It is discussed whether the Autrigones were Celts, theory supported by the existence of toponyms of Celtic origin, such as ''Uxama Barca'' and other with ''-briga'' endings and that eventually underwent a Basquisation along with other neighboring tribes such as the Caristii and Varduli. Location Roman historians as Pomponius Mela and Pliny the Elder located them in the northern region of present-day province of Burgos. Pliny the Elder writes about the "ten states of the Autrigones" and says the only ones worth mentioning are ''Tritium Autrigonum'' ( Monasterio de Rodilla, Burgos) and ''Virovesca'' (possibly the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bardulia
According to some sources, Bardulia is the ancient name of the territories that composed the primitive Castile in the north of what later became the province of Burgos. The name comes from ''Varduli'', the name of a tribe who, in pre-Roman and Roman times, populated the eastern part of the Cantabrian coast of the Iberian peninsula, primarily in present-day Guipúzcoa. Some assert that the Varduil also encompassed or assimilated the Caristii and Autrigones. It has been speculated that a possible expansion of the Basque territories—Late Basquisation, an expansion to the Basque Country in the 6th through 8th centuries—occasioned a westward migration of the Varduli to what the documents of the Low Middle Ages call ''Bardulia''. ''Bardulia'' and ''Castile'' The first written mention of ''Bardulia'' is a 10th-century chronicle that describes it as a former name for Castile. The '' Chronicle of Alfonso III'', written in Latin, uses the term four times, in various declensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
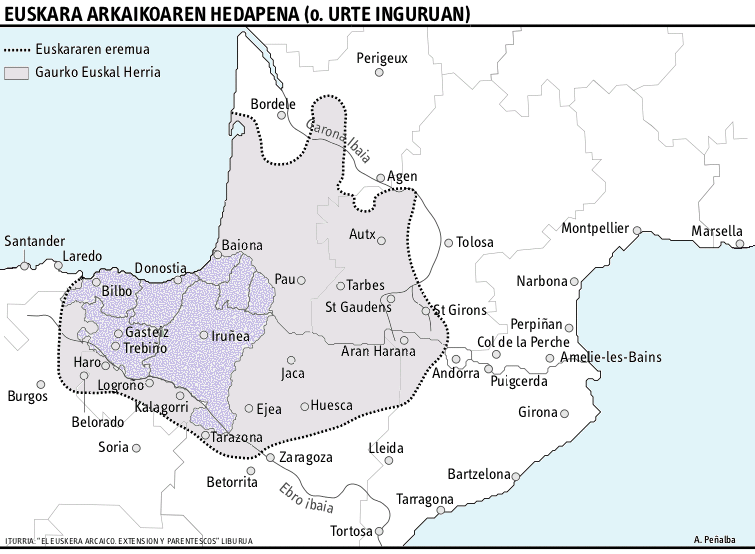
Late Basquisation
Late Basquisation is a minority hypothesis that dates the arrival of the first speakers of the Basque language in northeastern Iberia from Aquitaine to the 5th or 6th century AD – as opposed to the mainstream view of it being the last remaining descendant of one of the pre-Indo-European languages of Prehistoric Europe. History The Basque language is a language isolate that has survived the arrival of Indo-European languages in western Europe. Basque (and its ancestors or closely related languages such as Aquitanian) historally occupied a much larger territory, including parts of modern-day Béarn, Aragon, Rioja, Castile south of the Pyrenees, and large parts of modern-day Gascony to the north. Hypothesis The "Late Basquisation" hypothesis set the historical geographical spread of the Basque or the proto-Basque language later in history. It suggests that at the end of the Roman Republic and during the first centuries of the Empire, migration of Basque-speakers from Aquitai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Roads
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills, or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zadorra
The Zadorra is a river tributary of the Ebro in the Basque Country at the north of the Iberian Peninsula. The river flows across province Álava all along (with the exception of Burgos' exclave La Puebla de Arganzon) till it pours into the Ebro near Miranda de Ebro in Burgos' lands. The river's water volume is the largest in Álava, with its basin being the most extensive in the province. Nowadays it provides by means of the Zadorra Reservoir System (comprising reservoirs Uribarri-Ganboa, Urrunaga and Albina) water supply for Vitoria and half of the Basque Autonomous Community. The river rises in the slopes of the Entzia Plateau at the spring known as Los Corrales (municipality of San Millan/Donemiliaga), meandering thereafter across the Alavan Plains to the west (loops around Salvatierra/Agurain) past Vitoria by the north, where it takes a turn to the south heading to the Ebro through La Puebla de Arganzon. Landmarks * The village and iconic castle of Gebara sit by the river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum
The ''Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum'' (''CIL'') is a comprehensive collection of ancient Latin inscriptions. It forms an authoritative source for documenting the surviving epigraphy of classical antiquity. Public and personal inscriptions throw light on all aspects of Roman life and history. The ''Corpus'' continues to be updated in new editions and supplements. CIL also refers to the organization within the Berlin-Brandenburg Academy of Sciences and Humanities responsible for collecting data on and publishing the Latin inscriptions. It was founded in 1853 by Theodor Mommsen and is the first and major organization aiming at a comprehensive survey. Aim The ''CIL'' collects all Latin inscriptions from the whole territory of the Roman Empire, ordering them geographically and systematically. The earlier volumes collected and published authoritative versions of all inscriptions known at the time—most of these had been previously published in a wide range of publications. The descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Principate, which is the first phase of the Roman Empire, and Augustus is considered one of the greatest leaders in human history. The reign of Augustus initiated an imperial cult as well as an era associated with imperial peace, the '' Pax Romana'' or '' Pax Augusta''. The Roman world was largely free from large-scale conflict for more than two centuries despite continuous wars of imperial expansion on the empire's frontiers and the year-long civil war known as the "Year of the Four Emperors" over the imperial succession. Originally named Gaius Octavius, he was born into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian ''gens'' Octavia. His maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, and Octavius was named in Cae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantabrian Wars
The Cantabrian Wars (29–19 BC) (''Bellum Cantabricum''), sometimes also referred to as the Cantabrian and Asturian Wars (''Bellum Cantabricum et Asturicum''), were the final stage of the two-century long Roman conquest of Hispania, in what today are the provinces of Cantabria, Asturias and León in northwestern Spain. During the reign of Emperor Augustus, Rome waged a bloody conflict against the Cantabri and the Astures, the last independent Celtic nations of Hispania. These warlike peoples fiercely resisted Roman domination; ten years of war and eight legions with their auxiliary troops – more than 50,000 soldiers in total – were needed to subdue the region. Augustus moved to Segisama (modern Sasamon, Burgos) in 26 BC to supervise the campaign in person. The major fighting was completed in 19 BC, although there were minor rebellions until 16 BC and the Romans had to station two legions there for seventy more years. Antecedents The Cantabri first appear in history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadripart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |