|
Vanadyl
The vanadyl or oxovanadium(IV) cation, VO2+, is a functional group that is common in the coordination chemistry of vanadium. Complexes containing this functional group are characteristically blue and paramagnetic. A triple bond is proposed to exist between the V4+ and O2− centers. The description of the bonding in the vanadyl ion was central to the development of modern ligand-field theory. Natural occurrence Minerals Cavansite and pentagonite are vanadyl-containing minerals. Water VO2+, often in an ionic pairing with sodium (NaH2VO4), is the second most abundant transition metal in seawater, with its concentration only being exceeded by molybdenum. In the ocean the average concentration is 30 nM. Some mineral water springs also contain the ion in high concentrations. For example, springs near Mount Fuji often contain as much as 54 μg per liter. Vanadyl containing compounds Oxovanadium(IV) * vanadyl acetylacetonate, VO(acac)2 * vanadyl sulfate pentahydrate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadyl Sulfate
Vanadyl(IV) sulfate describes a collection of inorganic compounds of vanadium with the formula, VOSO4(H2O)x where 0 ≤ x ≤ 6. The pentahydrate is common. This hygroscopic blue solid is one of the most common sources of vanadium in the laboratory, reflecting its high stability. It features the vanadyl ion, VO2+, which has been called ''the'' "most stable diatomic ion". Vanadyl sulfate is an intermediate in the extraction of vanadium from petroleum residues, one commercial source of vanadium. Synthesis, structure, and reactions Vanadyl sulfate is most commonly obtained by reduction of vanadium pentoxide with sulfur dioxide: :V2O5 + 7 H2O + SO2 + H2SO4 → 2 (O)(H2O)4O4 From aqueous solution, the salt crystallizes as the pentahydrate, the fifth water is not bound to the metal in the solid. Viewed as a coordination complex, the ion is octahedral, with oxo, four equatorial water ligands, and a monodentate sulfate. The trihydrate has also been examined by crystallography. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadyl Nitrate
Vanadyl nitrate, also called vanadium oxytrinitrate or vanadium oxynitrate is an inorganic compound of vanadium in the +5 oxidation state with nitrate ligands and oxygen. The formula is VO(NO3)3. It is a pale yellow viscous liquid. Production It is made by soaking vanadium pentoxide in liquid dinitrogen pentoxide for durations around two days at room temperature. The yield for this method is about 85%. :V2O5 + 3 N2O5 → 2 VO(NO3)3. Purification can be achieved by vacuum distillation. Mononitratodioxovanadium (VO2NO3) is an intermediate in this synthesis. It is a brick red solid. Vanadyl nitrate can also be made from vanadyl trichloride VOCl3 and dinitrogen pentoxide. Structure VO(NO3)3 has a distorted pentagonal bipyramid shape with idealized Cs (mirror) symmetry. The vanadium oxygen bond (157.2 pm) is typical for vanadyl(V). Two nitrate groups in the pentagonal plane are bidentate (V-O distances range from 199 to 206 pm). The third nitrate spans the pentagonal plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
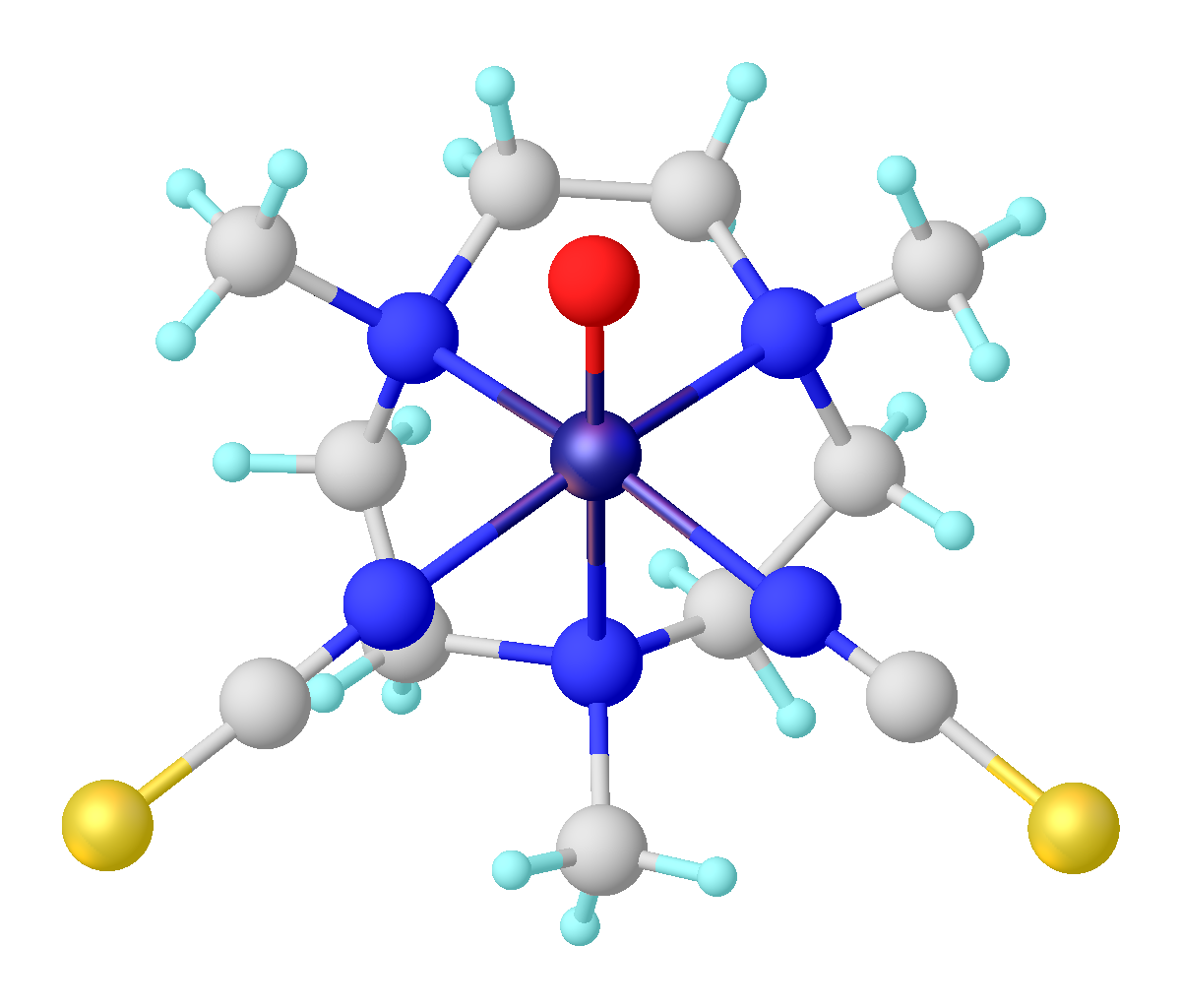
Vanadyl Acetylacetonate
Vanadyl acetylacetonate is the chemical compound with the formula VO(acac)2, where acac– is the conjugate base of acetylacetone. It is a blue-green solid that dissolves in polar organic solvents. The coordination complex consists of the vanadyl group, VO2+, bound to two acac– ligands via the two oxygen atoms on each. Like other charge-neutral acetylacetonate complexes, it is not soluble in water. Synthesis The complex is generally prepared from vanadium(IV), e.g. vanadyl sulfate: :VOSO4 + 2 Hacac → VO(acac)2 + H2SO4 It can also be prepared by a redox reaction starting with vanadium pentoxide. In this reaction, some acetylacetone is oxidized to acetic anhydride. Structure and properties The complex has a square pyramidal structure with a short V=O bond. This d1 compound is paramagnetic. Its optical spectrum exhibits two transitions. It is a weak Lewis acid, forming adducts with pyridine and methylamine. Applications It is used in organic chemistry as a catalyst for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadyl Perchlorate
Vanadyl perchlorate or vanadyl triperchlorate is a golden yellow coloured liquid or crystalline compound of vanadium, oxygen and perchlorate group. The substance consists of molecules covalently bound and is quite volatile. Formation Vanadyl perchlorate can be made by reacting vanadium pentoxide with dichlorine heptoxide at 5 °C. It is purified by distillation under a vacuum and recrystallisation at 21 °C. A solution of vanadium(V) perchlorate can be made by dissolving vanadium pentoxide in perchloric acid. The reaction of vanadium pentoxide and dichlorine hexoxide Dichlorine hexoxide is the chemical compound with the molecular formula , which is correct for its gaseous state. However, in liquid or solid form, this chlorine oxide ionizes into the dark red ionic compound chloryl perchlorate , which may be tho ... could produce VO(ClO4)3: : 2 V2O5 + 12 Cl2O6 → 4 VO(ClO4)3 + 12 ClO2 + 3 O2 Properties It can react with vanadium oxychloride to form another vanady ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pervanadyl
Pervanadyl () is a pale yellow oxycation of vanadium(V). It is the predominant vanadium(V) species in acidic solutions with pH between 0 and 2, and its salts are formed by protonation of vanadium(V) oxide in such solutions: : ('' K'' = ) The ion can form a complex with a single aminopolycarboxylate ligand, or with tridentate Schiff base ligands. The / redox couple is used at the cathode of the vanadium redox battery. The standard reduction potential of this couple is +1.00 V. See also * Vanadate In chemistry, a vanadate is an anionic coordination complex of vanadium. Often vanadate refers to oxoanions of vanadium, most of which exist in its highest oxidation state of +5. The complexes and are referred to as hexacyanovanadate(III) and no ..., vanadium(V) oxyanions References {{reflist Vanadyl compounds Vanadium(V) compounds Oxycations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer ( passivation) somewhat stabilizes the free metal against further oxidation. Spanish scientist Andrés Manuel del Río discovered compounds of vanadium in 1801 in Mexico by analyzing a new lead-bearing mineral he called "brown lead". Though he initially presumed its qualities were due to the presence of a new element, he was later erroneously convinced by French chemist Hippolyte Victor Collet-Descotils that the element was just chromium. Then in 1830, Nils Gabriel Sefström generated chlorides of vanadium, thus proving there was a new element, and named it "vanadium" after the Scandinavian goddess of beauty and fertility, Vanadís (Freyja). The name was based on the wide range of colors found in vanadium compounds. Del Rio's lead mineral was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadyl Isopropoxide
Vanadyl isopropoxide is the metal alkoxide with the formula VO(O-iPr)3 (iPr = CH(CH3)2). A yellow volatile liquid, it is a common alkoxide of vanadium. It is used as a reagent and as a precursor to vanadium oxides. The compound is diamagnetic. It is prepared by alcoholysis of vanadyl trichloride: :VOCl3 + 3 HOCH(CH3)2 → VO(OCH(CH3)2)3 + 3 HCl The related cyclopentanoxide VO(O-CH(CH2)4)3 is a dimer, one pair of alkoxide ligands bind weakly trans to the vanadyl The vanadyl or oxovanadium(IV) cation, VO2+, is a functional group that is common in the coordination chemistry of vanadium. Complexes containing this functional group are characteristically blue and paramagnetic. A triple bond is proposed to ex ... oxygens. References {{Vanadium compounds Vanadium(V) compounds Alkoxides Vanadyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavansite
Cavansite, whose name is derived from its chemical composition, ''calcium vanadium silicate'', is a deep blue hydrous calcium vanadium phyllosilicate mineral, occurring as a secondary mineral in basaltic and andesitic rocks along with a variety of zeolite minerals. Discovered in 1967 in Malheur County, Oregon, cavansite is a relatively rare mineral. It is polymorphic with the even rarer mineral, pentagonite. It is most frequently found in Pune, India and in the Deccan Traps, a large igneous province. Uses of cavansite Although cavansite contains vanadium, and could thus be a possible ore source for the element, it is not generally considered an ore mineral. However, because of its rich color and relative rarity, cavansite is a sought-after collector's mineral. Associated minerals * Members of the apophyllite group * Members of the zeolite group, particularly stilbite * babingtonite, Ca2 Fe2 Si5 O14 OH * quartz Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanyl
In inorganic chemistry, titanyl refers to the functional group TiIVO, sometimes written TiO2+. The term titanyl is used loosely to describe many titanium(IV) oxide compounds and complexes. For example, titanyl sulfate and potassium titanyl phosphate contain TiIVO centers with the connectivity O-Ti-O-Ti. In heterogeneous catalysis, titanyl refers to a terminal oxo ligand A transition metal oxo complex is a coordination complex containing an oxo ligand. Formally O2-, an oxo ligand can be bound to one or more metal centers, i.e. it can exist as a terminal or (most commonly) as bridging ligands (Fig. 1). Oxo ligan ... on a surface titanium(IV) center.{{cite journal, title=The Role of Synchrotron-Based Studies in the Elucidation and Design of Active Sites in Titanium−Silica Epoxidation Catalysts, authors=John Meurig Thomas, Gopinathan Sankar, journal=Accounts of Chemical Research, year=2001, volume=34, pages=571-581, doi=10.1021/ar010003w There are a few molecular titanyl comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2.png)