|
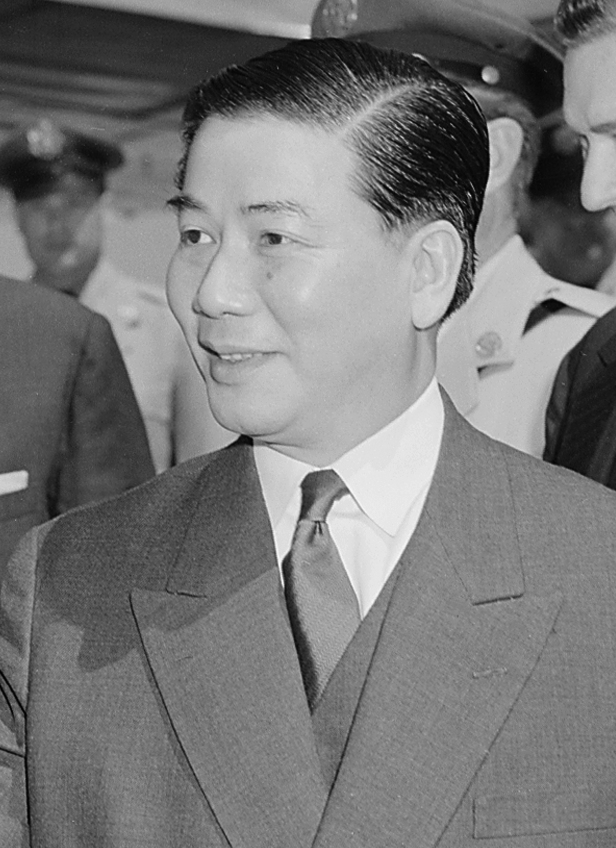
Vũ Văn Mẫu
Vũ Văn Mẫu (; 25 July 1914 – 20 August 1998) was a South Vietnamese diplomat and politician, who was the last Prime Minister of South Vietnam, serving under President Dương Văn Minh's leadership in 1975. He held the position for only two days before the collapse and surrender of South Vietnam on 30 April 1975. Early life and career He was born on 25 July 1914 in Hanoi, Tonkin, French Indochina. He earned a doctorate in law from the Faculté de droit de Paris and practiced law in Hanoi. After Vietnam’s partition in 1954, he moved to Saigon with his family and joined the Faculty of Law at the University of Saigon, where he became the Dean of the Faculty. He was recognized as an expert in civil and historical law. After several years as a professor he then became a local Saigon judge, rising through the ranks to become Judge of the Saigon Superior Court. During his legal career and even during retirement and exile, he authored a number of books, including one entitled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dương Văn Minh
Dương Văn Minh (; 16 February 19166 August 2001), popularly known as Big Minh, was a South Vietnamese politician and a senior general in the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) and a politician during the presidency of Ngô Đình Diệm. In 1963, he became chief of a military junta after 1963 South Vietnamese coup d'état, leading a coup in which Diệm Arrest and assassination of Ngo Dinh Diem, was assassinated. Minh lasted only three months before January 1964 South Vietnamese coup, being toppled by Nguyễn Khánh, but assumed power again as the fourth and last President of South Vietnam in April 1975, two days Fall of Saigon, before surrendering to People's Army of Vietnam, North Vietnamese forces. He earned his nickname "Big Minh", because he was approximately 1.83 m (6 ft) tall and weighed 90 kg (198 lb). Born in Tiền Giang province in the Mekong Delta region of southern Vietnam, Minh joined the French Army at the start of World War II, and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of Philosophy
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, DPhil; or ) is a terminal degree that usually denotes the highest level of academic achievement in a given discipline and is awarded following a course of Postgraduate education, graduate study and original research. The name of the degree is most often abbreviated PhD (or, at times, as Ph.D. in North American English, North America), pronounced as three separate letters ( ). The University of Oxford uses the alternative abbreviation "DPhil". PhDs are awarded for programs across the whole breadth of academic fields. Since it is an earned research degree, those studying for a PhD are required to produce original research that expands the boundaries of knowledge, normally in the form of a Thesis, dissertation, and, in some cases, defend their work before a panel of other experts in the field. In many fields, the completion of a PhD is typically required for employment as a university professor, researcher, or scientist. Definition In the context o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The UK includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and most of List of islands of the United Kingdom, the smaller islands within the British Isles, covering . Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. It maintains sovereignty over the British Overseas Territories, which are located across various oceans and seas globally. The UK had an estimated population of over 68.2 million people in 2023. The capital and largest city of both England and the UK is London. The cities o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Crisis
The Buddhist crisis () was a period of political and religious tension in South Vietnam between May and November 1963, characterized by a series of repressive acts by the South Vietnamese government and a campaign of civil resistance, led mainly by Buddhist monks. The crisis was precipitated by the shootings of nine unarmed civilians on May 8 in the central city of Huế who were protesting against a ban of the Buddhist flag. The crisis ended with a coup in November 1963 by the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN), and the arrest and assassination of President Ngô Đình Diệm on November 2, 1963. Background In South Vietnam, a country where the Buddhist majority was estimated to comprise between 70 and 90 percent of the population in 1963, president Ngô Đình Diệm's pro-Catholic policies antagonized many Buddhists. A member of the Catholic minority, Diệm headed a government biased towards Catholics in public service and military promotions, as well as in the allo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam (RVN; , VNCH), was a country in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975. It first garnered international recognition in 1949 as the State of Vietnam within the French Union, with its capital at Saigon, before becoming a republic in 1955, when the southern half of Vietnam was a member of the Western Bloc during part of the Cold War after the 1954 division of Vietnam. South Vietnam was bordered by North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and Thailand across the Gulf of Thailand to the southwest. Its sovereignty was recognized by the United States and 87 other nations, though it failed to gain admission into the United Nations as a result of a Soviet veto in 1957. It was succeeded by the Republic of South Vietnam in 1975. In 1976, the Republic of South Vietnam and North Vietnam merged to form the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. The end of the Secon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Vietnam
The State of Vietnam (; chữ Hán: 國家越南; ) was a state in Southeast Asia that existed from 1949 until 1955, first as an associated state of the French Union and later as an independent state (from 20 July 1954 to 26 October 1955). The state claimed authority over all of Vietnam during the First Indochina War, although large parts of its territory were controlled by the Democratic Republic of Vietnam. Established in 1949, the State of Vietnam was formed within the framework of the French Union as a compromise between Vietnamese nationalists and the French, in opposition to the communists. It gained international recognition in 1950 and aligned politically with the Western Bloc. Former emperor Bảo Đại became Chief of State. Following the 1954 Geneva Accords between the communist Viet Minh and the French, the State of Vietnam lost its remaining foothold in the northern half of the country, where most rural areas were already controlled by the Viet Minh. Ngô Đình ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bảo Đại
Bảo Đại (, vi-hantu, , , 22 October 191331 July 1997), born Nguyễn Phúc (Phước) Vĩnh Thụy (), was the 13th and final emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty, the last ruling dynasty of Vietnam. From 1926 to 1945, he was ''de jure'' emperor of Annam and Tonkin, which were then protectorates in French Indochina, covering the present-day central and northern Vietnam. Bảo Đại ascended the throne in 1932. The Japanese ousted the Vichy French administration in March 1945 and ruled through Bảo Đại, who proclaimed the Empire of Vietnam. Following the surrender of Japan and the subsequent August Revolution, he abdicated in August 1945 in favor of Hồ Chí Minh-led Democratic Republic of Vietnam and briefly served as an advisor in its government. Between 1946 and 1949, Bảo Đại left Vietnam to travel across China, Hong Kong and Europe. During this time, he switched his support from Hồ's Việt Minh to other anti-communist nationalist groups before signin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1955 State Of Vietnam Referendum
A referendum was held in the State of Vietnam (South Vietnam) to determine whether the country was a republic or monarchy. It was primarily a contest between Prime Minister Ngo Dinh Diem, who proposed a republic, and former emperor Bảo Đại, who had abdicated in 1945 and at the time of the referendum held the title of head of state. The referendum was the last phase in the power struggle between Bảo Đại and his prime minister. Bảo Đại disliked Diem and had frequently attempted to undermine him, having appointed him only because he was a conduit to American aid. At the time, the country was going through a period of insecurity, as Vietnam had been temporarily partitioned as a result of the 1954 Geneva Accords that ended the First Indochina War. The State of Vietnam controlled the southern half of the country, pending national elections that were intended to reunify the country under a common government. Still, the Vietnamese National Army was not in full control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saigon
Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC) ('','' TP.HCM; ), commonly known as Saigon (; ), is the most populous city in Vietnam with a population of around 14 million in 2025. The city's geography is defined by rivers and canals, of which the largest is Saigon River. As a Municipalities of Vietnam, municipality, Ho Chi Minh City consists of 16 List of urban districts of Vietnam, urban districts, five Huyện, rural districts, and one Municipal city (Vietnam), municipal city (sub-city). As the largest financial centre in Vietnam, Ho Chi Minh City has the largest gross regional domestic product out of all Vietnam provinces and municipalities, contributing around a quarter of the Economy of Vietnam, country's total GDP. Ho Chi Minh City metropolitan area, Ho Chi Minh City's metropolitan area is List of ASEAN country subdivisions by GDP, ASEAN's 5th largest economy, also the biggest outside an ASEAN country capital. The area was initially part of Cambodian states until it became part of the Vietna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |