|
Void Coefficient
In nuclear engineering, the void coefficient (more properly called void coefficient of reactivity) is a number that can be used to estimate how much the reactivity of a nuclear reactor changes as voids (typically steam bubbles) form in the reactor moderator or coolant. Net reactivity in a reactor depends on several factors, one of which is the void coefficient. Reactors in which either the moderator or the coolant is a liquid will typically have a void coefficient which is either negative (if the reactor is under-moderated) or positive (if the reactor is over-moderated). Reactors in which neither the moderator nor the coolant is a liquid (e.g., a graphite-moderated, gas-cooled reactor) will have a zero void coefficient. It is unclear how the definition of "void" coefficient applies to reactors in which the moderator/coolant is neither liquid nor gas ( supercritical water reactor). Explanation Nuclear fission reactors run on nuclear chain reactions, in which each nucleus that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Engineering
Nuclear engineering is the engineering discipline concerned with designing and applying systems that utilize the energy released by nuclear processes. The most prominent application of nuclear engineering is the generation of electricity. Worldwide, some 440 nuclear reactors in 32 countries generate 10 percent of the world's energy through nuclear fission. In the future, it is expected that nuclear fusion will add another nuclear means of generating energy. Both reactions make use of the nuclear binding energy released when atomic nucleons are either separated (fission) or brought together (fusion). The energy available is given by the binding energy curve, and the amount generated is much greater than that generated through chemical reactions. Fission of 1 gram of uranium yields as much energy as burning 3 tons of coal or 600 gallons of fuel oil, without adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. History Nuclear engineering was born in 1938, with the discovery of nuclear fission. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its Amphoterism, amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Lead compounds, Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criticality Accident
A criticality accident is an accidental uncontrolled nuclear fission chain reaction. It is sometimes referred to as a critical excursion, critical power excursion, divergent chain reaction, or simply critical. Any such event involves the unintended accumulation or arrangement of a critical mass of fissile material, for example enriched uranium or plutonium. Criticality accidents can release potentially fatal radiation doses if they occur in an unprotected environment. Under normal circumstances, a critical or supercritical fission reaction (one that is self-sustaining in power or increasing in power) should only occur inside a safely shielded location, such as a reactor core or a suitable test environment. A criticality accident occurs if the same reaction is achieved unintentionally, for example in an unsafe environment or during reactor maintenance. Though dangerous and frequently lethal to humans within the immediate area, the critical mass formed would not be capable of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Water Reactor
The light-water reactor (LWR) is a type of thermal-neutron reactor that uses normal water, as opposed to heavy water, as both its coolant and neutron moderator; furthermore a solid form of fissile elements is used as fuel. Thermal-neutron reactors are the most common type of nuclear reactor, and light-water reactors are the most common type of thermal-neutron reactor. There are three varieties of light-water reactors: the pressurized water reactor (PWR), the boiling water reactor (BWR), and (most designs of) the supercritical water reactor (SCWR). History Early concepts and experiments After the discoveries of fission, moderation and of the theoretical possibility of a nuclear chain reaction, early experimental results rapidly showed that natural uranium could only undergo a sustained chain reaction using graphite or heavy water as a moderator. While the world's first reactors ( CP-1, X10 etc.) were successfully reaching criticality, uranium enrichment began to devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scram
A scram or SCRAM is an emergency shutdown of a nuclear reactor effected by immediately terminating the fission reaction. It is also the name that is given to the manually operated kill switch that initiates the shutdown. In commercial reactor operations, this type of shutdown is often referred to as a "scram" at boiling water reactors, a "reactor ''trip''" at pressurized water reactors and "EPIS" at a CANDU reactor. In many cases, a scram is part of the routine shutdown procedure which serves to test the emergency shutdown system. Etymology There is no definitive origin for the term. United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission historian Tom Wellock notes that '' scram'' is English-language slang for leaving quickly and urgently (as in scrambling to get away), and he cites this as the original and most likely accurate basis for the use of ''scram'' in the technical context. Scram is sometimes cited as being an acronym for safety control rod axe man or safety cut rope axe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss Of Coolant Accident
A loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) is a mode of failure for a nuclear reactor; if not managed effectively, the results of a LOCA could result in reactor core damage. Each nuclear plant's emergency core cooling system (ECCS) exists specifically to deal with a LOCA. Nuclear reactors generate heat internally; to remove this heat and convert it into useful electrical power, a coolant system is used. If this coolant flow is reduced, or lost altogether, the nuclear reactor's emergency shutdown system is designed to stop the fission chain reaction. However, due to radioactive decay, the nuclear fuel will continue to generate a significant amount of heat. The decay heat produced by a reactor shutdown from full power is initially equivalent to about 5 to 6% of the thermal rating of the reactor. If all of the independent cooling trains of the ECCS fail to operate as designed, this heat can increase the fuel temperature to the point of damaging the reactor. *If water is present, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CANDU
The CANDU (CANada Deuterium Uranium) is a Canadian pressurized heavy-water reactor design used to generate electric power. The acronym refers to its deuterium oxide (heavy water) neutron moderator, moderator and its use of (originally, natural uranium, natural) uranium fuel. CANDU reactors were first developed in the late 1950s and 1960s by a partnership between Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (AECL), the Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario, Canadian General Electric, and other companies. There have been two major types of CANDU reactors, the original design of around 500 Watt#MWe, MWe that was intended to be used in multi-reactor installations in large plants, and the optimized CANDU 6 in the 600 MWe class that is designed to be used in single stand-alone units or in small multi-unit plants. CANDU 6 units were built in Quebec and New Brunswick, as well as Pakistan, Argentina, South Korea, Romania, and China. A single example of a non-CANDU 6 design was sold to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressurized Water Reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan, India and Canada). In a PWR, water is used both as a neutron moderator and as coolant fluid for the reactor core. In the core, water is heated by the energy released by the fission of atoms contained in the fuel. Using very high pressure (around 155 bar: 2250 psi) ensures that the water stays in a liquid state. The heated water then flows to a steam generator, where it transfers its thermal energy to the water of a secondary cycle kept at a lower pressure which allows it to vaporize. The resulting steam then drives steam turbines linked to an electric generator. A boiling water reactor (BWR) by contrast does not maintain such a high pressure in the primary cycle and the water thus vaporizes inside of the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) before being sent to the turbine. Most PWR designs ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiling Water Reactor
A boiling water reactor (BWR) is a type of nuclear reactor used for the generation of electrical power. It is the second most common type of electricity-generating nuclear reactor after the pressurized water reactor (PWR). BWR are thermal neutron reactors, where water is thus used both as a coolant and as a moderator, slowing down neutrons. As opposed to PWR, there is no separation between the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) and the steam turbine in BWR. Water is allowed to vaporize directly inside of the reactor core (at a pressure of approximately 70 bars) before being directed to the turbine which drives the electric generator. Immediately after the turbine, a heat exchanger called a condenser brings the outgoing fluid back into liquid form before it is sent back into the reactor. The cold side of the condenser is made up of the plant's secondary coolant cycle which is fed by the power plant's cold source (generally the sea or a river, more rarely air). The BWR was developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chernobyl Disaster
On 26 April 1986, the no. 4 reactor of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, located near Pripyat, Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union (now Ukraine), exploded. With dozens of direct casualties, it is one of only two nuclear energy accidents rated at the maximum severity on the International Nuclear Event Scale, the other being the 2011 Fukushima nuclear accident. The response involved more than Chernobyl liquidators, 500,000 personnel and cost an estimated 18billion Soviet ruble, rubles (about $84.5billion USD in 2025). It remains the worst nuclear disaster and the List of disasters by cost, most expensive disaster in history, with an estimated cost of US$700 billion. The disaster occurred while running a test to simulate cooling the reactor during an accident in blackout conditions. The operators carried out the test despite an accidental drop in reactor power, and due to a design issue, attempting to shut down the reactor in those conditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RBMK
The RBMK (, РБМК; ''reaktor bolshoy moshchnosti kanalnyy'', "high-power channel-type reactor") is a class of graphite moderated reactor, graphite-moderated nuclear reactor, nuclear power reactor designed and built by the Soviet Union. It is somewhat like a boiling water reactor as water boils in the pressure tubes. It is one of two power reactor types to enter serial production in the Soviet Union during the 1970s, the other being the VVER reactor. The name refers to its design where instead of a large steel Reactor pressure vessel, pressure vessel surrounding the entire core, the core is surrounded by a cylindrical annular steel tank inside a concrete vault and each fuel assembly is enclosed in an individual 8 cm (inner) diameter pipe (called a "technological channel"). The channels also contain the coolant, and are surrounded by graphite. The RBMK is an early Generation II reactor and the oldest commercial reactor design still in wide operation. Certain aspects of the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
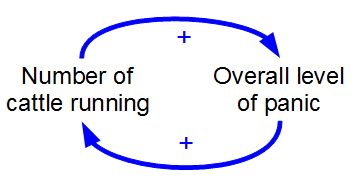
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, ''A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A''.Keesing, R.M. (1981). Cultural anthropology: A contemporary perspective (2nd ed.) p.149. Sydney: Holt, Rinehard & Winston, Inc. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics. Mathematically, positive feedback is defined as a positive loop gain around a closed loop of cause and effect. That is, positive feedback is Phase (waves), in phase with the input, in the sense that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |