|
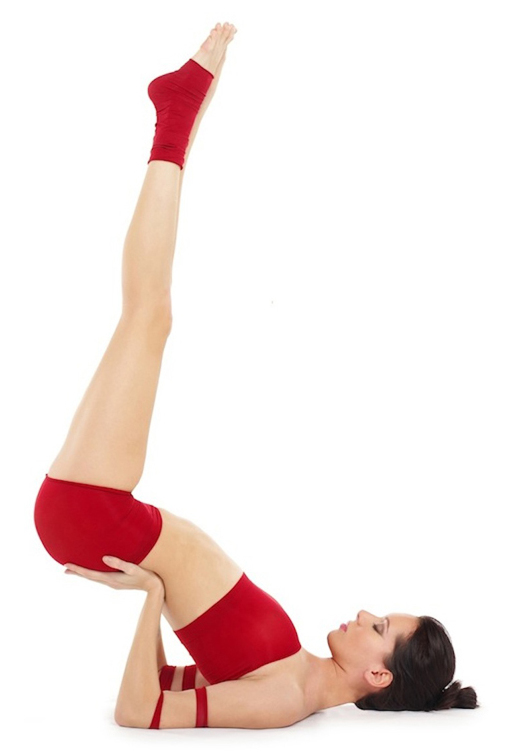
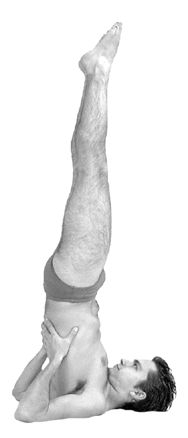
Viparīta Karaṇī
Viparita Karani (; ) or legs up the wall pose is both an asana and a mudra in hatha yoga. In modern yoga as exercise, it is commonly a fully supported pose using a wall and sometimes a pile of blankets, where it is considered a restful practice. As a mudra it was practised using any preferred inversion, such as a headstand or shoulderstand. The purpose of the mudra was to reverse the downward flow of vital fluid being lost from the head, using gravity. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit words , "inverted" or "reversed", and , "a particular type of practice". The practice is described in the 13th century ''Vivekamārtaṇḍa'' (verses 103–131) as a means of yogic withdrawal, pratyahara. The pose was practised from the 17th century onwards in hatha yoga under names such as Narakasana, Kapalasana and Viparitakaranasana; its purpose as a mudra was to reverse the downflow and loss of the life-giving substance (Bindu) through the use of gravity. In the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarvangasana
Sarvangasana (), Shoulder stand, or more fully Salamba Sarvangasana (Supported Shoulder stand), is an inverted asana in modern yoga as exercise; similar poses were used in medieval hatha yoga as a mudra. Many named variations exist, including with legs in lotus position and Supta Konasana with legs wide apart, toes on the ground. ''Sarvāṅgāsana'' has been nicknamed the "queen" or "mother" of all the asanas. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit , "supported", , "all limbs", i.e. "the whole body", and , "posture"," position", or "seat". The name Sarvangasana is modern, but similar inverted poses were in use in medieval hatha yoga as a mudra, Viparita Karani, which is documented in the 14th century '' Śiva Saṃhitā'' 4.45-47, the 15th century '' Haṭha Yoga Pradīpikā'' 3.78-81, the 17th century '' Gheraṇḍa Saṃhitā'' 3.33-35, and other early texts such as the '' Dattātreyayogaśāstra''. The purpose of Viparita Karani had been to reverse the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga Journal
''Yoga Journal'' is a website and digital journal, formerly a print magazine, on yoga as exercise founded in California in 1975 with the goal of combining the essence of traditional yoga with scientific understanding. It has produced live events and materials such as DVDs on yoga and related subjects. The magazine grew from the California Yoga Teachers Association's newsletter, which was called ''The Word''. ''Yoga Journal'' has repeatedly won Western Publications Association's Maggie Awards for "Best Health and Fitness Magazine". It has however been criticized for representing yoga as being intended for affluent white women; in 2019 it attempted to remedy this by choosing a wider variety of yoga models. The magazine was acquired by Outside in 2020. Beginnings ''Yoga Journal'' was started in May 1975 by the California Yoga Teachers Association (CYTA), with Rama Jyoti Vernon as President, William Staniger as the founding editor, and Judith Lasater on the board and serving as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iyengar Yoga
Iyengar Yoga, named after and developed by B. K. S. Iyengar, and described in his bestselling 1966 book '' Light on Yoga'', is a form of yoga as exercise that has an emphasis on detail, precision and alignment in the performance of yoga postures (asanas). The style often makes use of props, such as belts, blocks, and blankets, as aids in performing the asanas. The props enable beginning students, the elderly, or those with physical limitations to perform the asanas correctly, minimising the risk of injury or strain. History B. K. S. Iyengar learnt yoga from Tirumalai Krishnamacharya at the Mysore Palace, as did Pattabhi Jois; Iyengar Yoga and Jois's Ashtanga (vinyasa) yoga are thus branches of the same yoga lineage, sharing many of the same asanas and other practices. Iyengar began teaching yoga as exercise gradually, starting with individual pupils such as the violinist Yehudi Menuhin, whom he met in 1952; Menuhin's fame helped to propel Iyengar Yoga as a brand in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
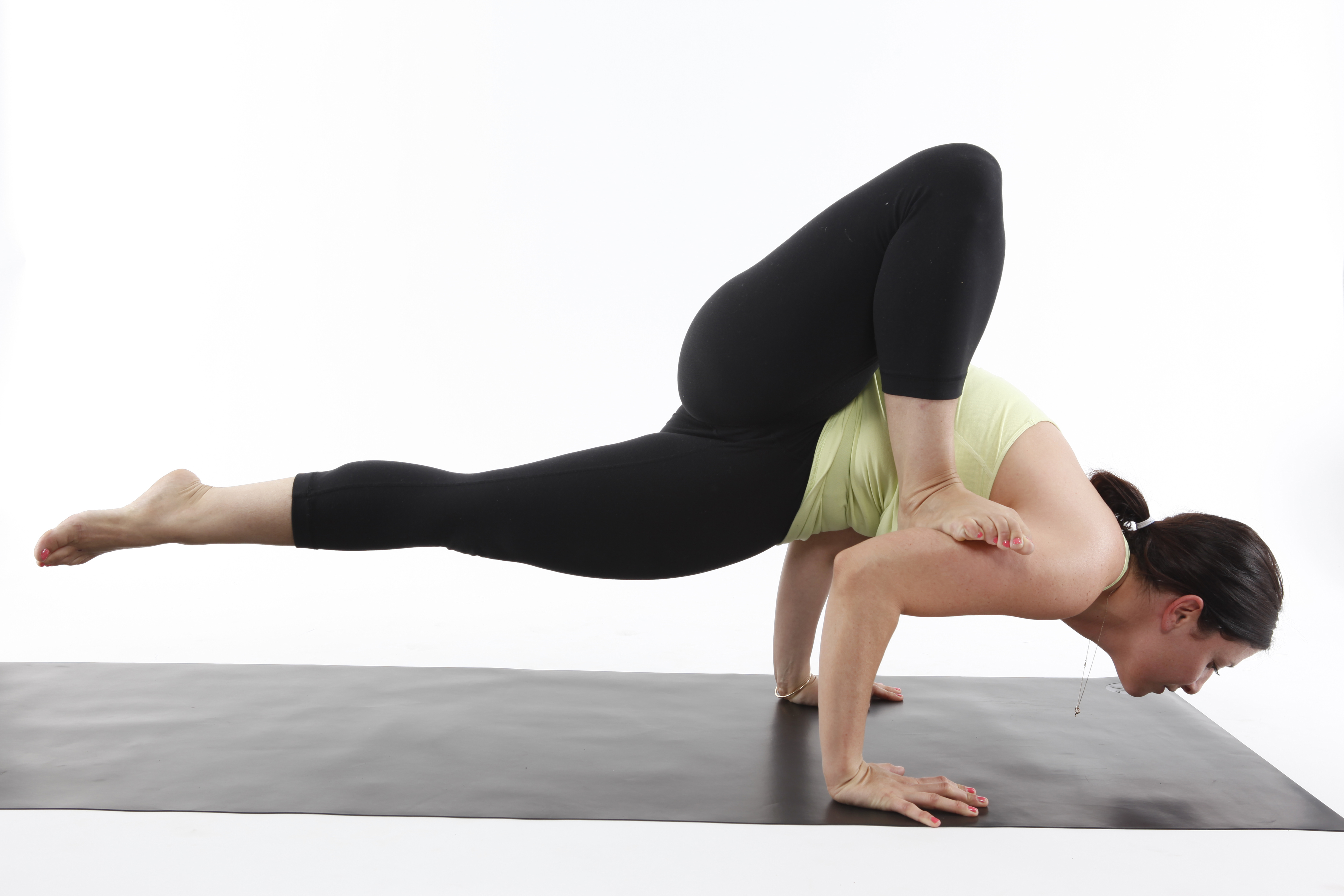
Balancing Bear-posture
Balancing may refer to: * Balancing (international relations) * Balancing and deranking, in grammar the use in subordinate clauses of verb forms identical to those in main clauses * Balancing (bridge), a term in contract bridge * Battery balancing, a technique that improves the available capacity of a battery pack with multiple cells * "Balancing" (''Brooklyn Nine-Nine''), an episode of the eighth season of ''Brooklyn Nine-Nine'' * "Balancing", an episode of the television series ''Teletubbies'' See also * Balance (other) Balance may refer to: Common meanings * Balance (ability) in biomechanics * Balance (accounting) * Balance or weighing scale * Balance, as in equality (mathematics) or equilibrium Arts and entertainment Film * ''Balance'' (1983 film), a Bulgar ... * Load balancing (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Spine
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a transverse foramen, an opening in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, verte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Spine
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae of intermediate size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae. They are distinguished by the presence of facets on the sides of the bodies for articulation with the heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region. General characteristics These are the general characteristics of the second through eighth thoracic vertebrae. The first and ninth through twelfth vertebrae contain certain peculiarities, and are detailed below. The vertebral bodies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extension (anatomy)
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamba Sarvāngāsana
Sarvangasana (), Shoulder stand, or more fully Salamba Sarvangasana (Supported Shoulder stand), is an inverted asana in modern yoga as exercise; similar poses were used in medieval hatha yoga as a mudra. Many named variations exist, including with legs in lotus position and Supta Konasana with legs wide apart, toes on the ground. ''Sarvāṅgāsana'' has been nicknamed the "queen" or "mother" of all the asanas. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit , "supported", , "all limbs", i.e. "the whole body", and , "posture"," position", or "seat". The name Sarvangasana is modern, but similar inverted poses were in use in medieval hatha yoga as a mudra, Viparita Karani, which is documented in the 14th century ''Śiva Saṃhitā'' 4.45-47, the 15th century '' Haṭha Yoga Pradīpikā'' 3.78-81, the 17th century '' Gheraṇḍa Saṃhitā'' 3.33-35, and other early texts such as the ''Dattātreyayogaśāstra''. The purpose of Viparita Karani had been to reverse the do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga As Exercise
Yoga as exercise is a physical activity consisting mainly of asana, postures, often connected by vinyasa, flowing sequences, sometimes accompanied by pranayama, breathing exercises, and frequently ending with savasana, relaxation lying down or meditation. Yoga in this form has become familiar across the world, especially Yoga in the United States, in the US and Europe. It is derived from medieval Haṭha yoga, which made use of similar postures, but it is generally simply called "yoga". Academic research has given yoga as exercise a variety of names, including modern postural yoga and transnational anglophone yoga. Postures were not central in any of the older traditions of yoga; posture practice was revived in the 1920s by yoga gurus including Yogendra and Kuvalayananda, who emphasised its health benefits. The flowing sequences of Surya Namaskar (Salute to the Sun) were pioneered by the Rajah of Aundh State, Aundh, Bhawanrao Shrinivasrao Pant Pratinidhi, in the 1920s. It and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haṭha Yoga
Hatha yoga (; Sanskrit हठयोग, International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ''haṭhayoga'') is a branch of yoga that uses physical techniques to try to preserve and channel vital force or energy. The Sanskrit word हठ ''haṭha'' literally means "force", alluding to a system of physical techniques. Some hatha yoga style techniques can be traced back at least to the 1st-century CE, in texts such as the Hindu Itihasa, Sanskrit epics and Buddhism's Pali canon. The oldest dated text so far found to describe hatha yoga, the 11th-century ''Amritasiddhi, Amṛtasiddhi'', comes from a Tantra, tantric Buddhist milieu. The oldest texts to use the terminology of ''hatha'' are also Vajrayana Buddhist. Hindu hatha yoga texts appear from the 11th century onward. Some of the early hatha yoga texts (11th-13th c.) describe methods to raise and conserve bindu (vital force, that is, semen, and in women ''rajas –'' menstrual fluid). This was seen as the physical esse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
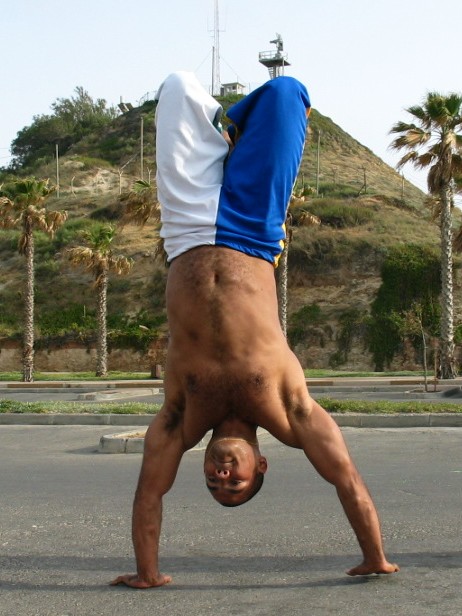
Adho Mukha Vrksasana
A handstand is the act of supporting the body in a stable, inverted vertical position by balancing on the hands. In a basic handstand, the body is held straight with arms and legs fully extended, with hands spaced approximately shoulder-width apart and the legs together. There are many variations of handstands, all of which require the performer to possess adequate balance and upper body strength. Kinematics Handstands use the wrist flexor muscles as well as the anterior deltoid, pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, biceps brachii, and trapezius descendens. It is considered demanding in terms of both the muscle and joint requirement. According to a 2017 study most handbalancers use wrist movement to maintain balance in a handstand. Another study found that handbalancers who were also expert gymnasts had better coordination than those at an intermediate level of gymnastics. More advanced practitioners also altered their center of pressure less to change the center of mass when ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |