|
Viipuri Province
Viipuri Province was a Historical provinces of Finland, historical province of Finland from 1812 to 1945. History The predecessor of the province was Vyborg Governorate, which was established in 1744 from territories ceded by the Swedish Empire to Russia in 1721 (Treaty of Nystad) and in 1743 (Treaty of Åbo). These territories originated as parts of the Viborg and Nyslott County and Kexholm County in 1721, and parts of the Savolax and Kymmenegård County in 1743. The governorate was also known as Old Finland. During the Napoleonic Wars, the Kingdom of Sweden (1721–1809), Kingdom of Sweden had allied itself with the Russian Empire, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and other parties against First French Empire, Napoleonic France. However, following the Treaties of Tilsit, Treaty of Tilsit in 1807, Russia made peace with France. In 1808, supported by France, Russia successfully challenged Swedish control over Finland in the Finnish War. In the Treaty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Finland
Between 1634 and 2009, Finland was administered as several provinces, or counties (, ). Finland had always been a unitary state: the provincial authorities were part of the central government's executive branch and apart from Åland, the provinces had little autonomy. There were never any elected provincial parliaments in continental Finland. The system was initially created by the Instrument of Government (1634), Instrument of Government of 1634 when Finland was a Finland as part of Sweden, part of Sweden. Its makeup was changed drastically on 1 September 1997, when the number of the provinces was reduced from twelve to six. This effectively made them purely administrative units, as linguistic and cultural boundaries no longer followed the borders of the provinces. The provinces were eventually abolished at the end of 2009. Consequently, different ministries may subdivide their areal organization differently. Besides the former provinces, the municipalities of Finland form the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First French Empire
The First French Empire or French Empire (; ), also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 6 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815, when Napoleon was exiled to Saint Helena. Although France had already established a French colonial empire, colonial empire overseas since the early 17th century, the French state had remained a France in the early modern period, kingdom under the Bourbons and a French First Republic, republic after the French Revolution. Historians refer to Napoleon's regime as the ''First Empire'' to distinguish it from the restorationist ''Second French Empire, Second Empire'' (1852–1870) ruled by his nephew Napoleon III. On 18 May 1804 (28 Floréal year XII on the French Republican calendar), Napoleon was granted the title Emperor of the French (, ) by the French and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic
The Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic (FSWR), more commonly referred to as Red Finland, was a self-proclaimed socialist state in Finland during the Finnish Civil War from January to May 1918. The FSWR was established by the Finnish People's Delegation, a government formed by members of the Social Democratic Party to rival the existing Government of Finland, with support of the Red Guards. The FSWR controlled the capital Helsinki and most of southern Finland until March. Kullervo Manner served as its sole leader as Chairman of the Central Committee of the Finnish People's Delegation. The FSWR collapsed when the Red Guards were defeated by the White Finns and Germany, with Manner and most of the Finnish People's Delegation fleeing to Soviet Russia. The name "Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic" () appeared only in the Treaty between Finnish People's Delegation and Russian Council of People's Commissars, signed on 1 March 1918. The People's Delegation had earlier used th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
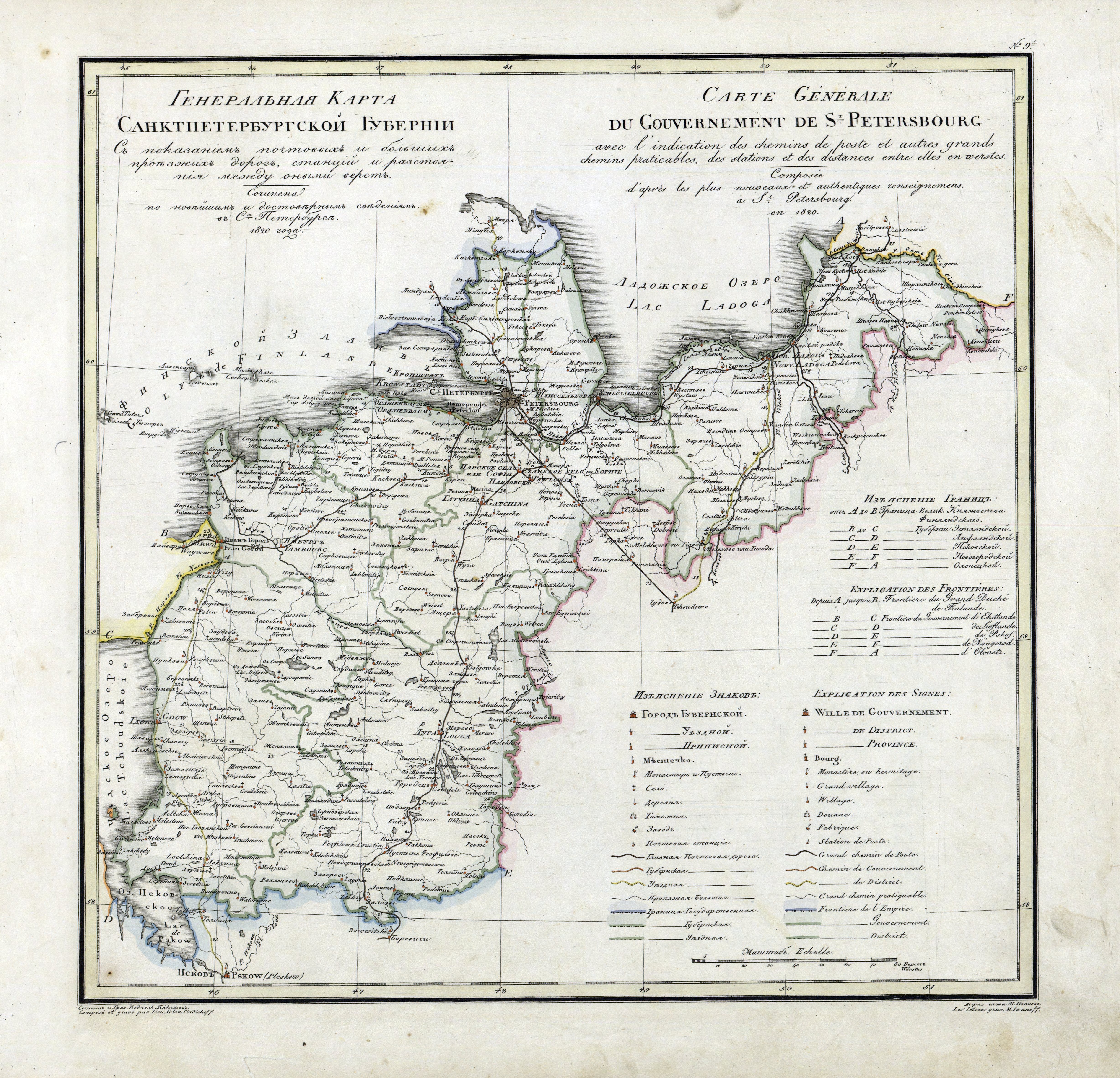
Saint Petersburg Governorate
Saint Petersburg Governorate was a province (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Saint Petersburg. The governorate was composed of of area and 2,112,033 inhabitants. It was bordered by Governorate of Estonia, Estonian and Governorate of Livonia, Livonian Governorates to the west, Pskov Governorate to the south, Novgorod Governorate to the east, Olonets Governorate to the northeast, and Viipuri Province, Vyborg Governorate of the Grand Duchy of Finland to the north. The governorate covered most of the areas of modern Leningrad Oblast and Ida-Viru County, Ida-Viru, Jõgeva County, Jõgeva, Tartu County, Tartu, Põlva County, Põlva, and Võru County, Võru counties of Estonia. Establishment Ingermanland Governorate (, ''Ingermanlandskaya guberniya'') was created from the territories reconquered from the Swedish Empire in the Great Northern War. In 1704 prince Alexander Menshikov was appointed as its first governor, and in 1706 it was first Russian region des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sestroretsk
Sestroretsk (; ; ) is a municipal town in Kurortny District of the federal city of St. Petersburg, Russia, located on the shores of the Gulf of Finland, the Sestra River and the Sestroretskiy Lake northwest of St. Petersburg. Population: 30,500 (1975). Munitions factory Sestroretsk was founded by Peter the Great in 1714 due to the construction of a munitions factory (today's ''Sestroretsk Toolmaking Factory''). Healthcare The town is known as a balneologic and climatic resort. A large hospital and rehabilitation center is situated within the boundaries of the town. It is the City hospital No. 40 of Saint Petersburg. Political history In 1812, the town was incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Finland, along with Old Finland. In 1864, the town was transferred to Russia in exchange for a promise of compensation, supposedly in the form of access to the Arctic Ocean at Petsamo. The representative body of local self-government - the municipal council - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Style
Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) indicate dating systems before and after a calendar change, respectively. Usually, they refer to the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar as enacted in various Europe, European countries between 1582 and 1923. In England, Wales, Ireland and British America, Britain's American colonies, there were two calendar changes, both in 1752. The first adjusted the start of a new year from 25 March (Lady Day, the Feast of the Annunciation) to 1 January, a change which Scotland had made in 1600. The second discarded the Julian calendar in favour of the Gregorian calendar, skipping 11 days in the month of September to do so.. "Before 1752, parish registers, in addition to a new year heading after 24th March showing, for example '1733', had another heading at the end of the following December indicating '1733/4'. This showed where the Historical Year 1734 started even though the Civil Year 1733 continued until 24th March. ... We as h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander I Of Russia
Alexander I (, ; – ), nicknamed "the Blessed", was Emperor of Russia from 1801, the first king of Congress Poland from 1815, and the grand duke of Finland from 1809 to his death in 1825. He ruled Russian Empire, Russia during the chaotic period of the Napoleonic Wars. The eldest son of Emperor Paul I and Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg, Alexander succeeded to the throne after his father was murdered. As prince and during the early years of his reign, he often used liberal rhetoric but continued Russian absolutism, Russia's absolutist policies in practice. In the first years of his reign, he initiated some minor social reforms and (in 1803–04) major liberal educational reforms, such as building more universities. Alexander appointed Mikhail Speransky, the son of a village priest, as one of his closest advisors. The over-centralized Collegium (ministry), Collegium ministries were abolished and replaced by the Committee of Ministers of the Russian Empire, Committee of Ministers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duke
Grand duke (feminine: grand duchess) is a European hereditary title, used either by certain monarchs or by members of certain monarchs' families. The title is used in some current and former independent monarchies in Europe, particularly: * in present-day Luxembourg, the last surviving Grand Duchy * historically by the sovereigns of former independent countries, such as Grand Duchy of Tuscany, Tuscany (from 1569 to 1860, now part of Italy) * in Grand Duchy of Baden, Baden, Grand Duchy of Hesse, Hesse, Grand Duchy of Oldenburg, Oldenburg, Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, Mecklenburg-Schwerin, Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Mecklenburg-Strelitz and Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (officially simply the Grand Duchy of Saxony) – grand duchies from 1815 to 1918, and all now part of Germany * formerly also in some countries in Northern Europe, such as the Grand Duchy of Finland or the Grand Duchy of Lithuania * currently by claimants to the Russian Imperial Throne (eg. Grand Duke Geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, цар, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official—but was usually considered by Western Europeans to be equivalent to "king". Tsar and its variants were the official titles in the First Bulgarian Empire (681–1018), Second Bulgarian Empire (1185–1396), the Kingdom of Bulgaria (1908–1946), the Serbian Empire (1346–1371), and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721). The first ruler to adopt the title ''tsar'' was Simeon I of Bulgaria. Simeon II, the last tsar of Bulgaria, is the last person to have held this title. Meaning in Slavic languages The title tsar is derived from the Latin title for the Roman emperors, ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Finland
The Grand Duchy of Finland was the predecessor state of modern Finland. It existed from 1809 to 1917 as an Autonomous region, autonomous state within the Russian Empire. Originating in the 16th century as a titular grand duchy held by the Monarchy of Sweden, King of Sweden, the country became autonomous after its annexation by Russia in the Finnish War of 1808–1809. The Grand Duke of Finland was the House of Romanov, Romanov Emperor of Russia, represented by the Governor-General of Finland, Governor-General. Due to the governmental structure of the Russian Empire and Finnish initiative, the Grand Duchy's autonomy expanded until the end of the 19th century. The Senate of Finland, founded in 1809, became the most important governmental organ and the precursor to the modern Government of Finland, the Supreme Court of Finland, and the Supreme Administrative Court of Finland. Economic, social and political changes in the Grand Duchy of Finland paralleled those in the Russian Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torne (Finnish And Swedish River)
The Torne, also known as the Tornio (, , , , ), is a river in northern Sweden and Finland. For approximately half of its length, it defines the border between these two countries. In the upper parts, the river is situated in Sweden before it meets the Muonio River where it adjoins the international border. It rises at the lake Torneträsk near the border with Norway and flows generally southeast for a distance of into the Gulf of Bothnia. It is the largest river in Norrbotten County both by length and by watershed area. At its source, the Torne is located close to the North Atlantic and Narvik on the other side of the watershed, with several thousands of kilometres between the locations via waterways. Geography The Torne basin has a total area of or (see sidebar). Of this, or is in Sweden, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |