|
Vidim (Mělník District)
Vidim is a municipality and village in Mělník District in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 100 inhabitants. The village is well preserved and is protected as a Cultural monument (Czech Republic)#Monument zones, village monument zone. Geography Vidim is located about north of Mělník and north of Prague. It lies in a hilly landscape of the Ralsko Uplands. The highest point is below the top of the hill Supí hora at above sea level. The entire municipal territory lies in the Kokořínsko – Máchův kraj Protected Landscape Area. History The first written mention of Vidim is from 1318. In the 14th century, it belonged to the Houska Castle, Houska estate owned by the Berka of Dubá family. In the 15th century, Vidim was owned by less important members of the families Lobkowicz family, Lobkowicz and Smiřický. In 1502, the village was purchased by Hrzáns of Hrzánov. Visim became the centre of a separate estate in 1572. From that year, the import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obec
(, ; plural ) is the Czech and Slovak word for a municipality (in the Czech Republic, in Slovakia and abroad). The literal meaning of the word is " commune" or " community". It is the smallest administrative unit that is governed by elected representatives. Cities and towns are also municipalities. Definition The legal definition (according to the Czech code of law with similar definition in the Slovak code of law) is: ''"The municipality is a basic territorial self-governing community of citizens; it forms a territorial unit, which is defined by the boundary of the municipality."'' Every municipality is composed of one or more cadastral areas. Every municipality is also composed of one or more municipal parts (), which are usually town quarters or villages. A municipality can have its own flag and coat of arms. Czech Republic Almost the entire area of the Czech Republic is divided into municipalities, with the only exception being military training areas. The smaller mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its Prague metropolitan area, metropolitan area is home to approximately 2.3 million people. Prague is a historical city with Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, Czech Gothic architecture, Gothic, Czech Renaissance architecture, Renaissance and Czech Baroque architecture, Baroque architecture. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Bohemia and residence of several Holy Roman Emperors, most notably Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV (r. 1346–1378) and Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, Rudolf II (r. 1575–1611). It was an important city to the Habsburg monarchy and Austria-Hungary. The city played major roles in the Bohemian Reformation, Bohemian and the Protestant Reformations, the Thirty Years' War and in 20th-century history a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vidim Zámek 3
Vidim may refer to: *Vidim (Mělník District) Vidim is a municipality and village in Mělník District in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 100 inhabitants. The village is well preserved and is protected as a Cultural monument (Czech Republic)#Monument zones, vill ..., a municipality and village in the Czech Republic * Vidim, Russia, an urban-type settlement in Irkutsk Oblast, Russia {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrecht Von Wallenstein
Albrecht Wenzel Eusebius von Wallenstein, Duke of Friedland (; 24 September 1583 – 25 February 1634), also von Waldstein (), was a Bohemian military leader and statesman who fought on the Catholic side during the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). His successful martial career made him one of the richest and most influential men in the Holy Roman Empire by the time of his death. Wallenstein became the supreme commander of the armies of Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand II and was a major figure of the Thirty Years' War. Wallenstein was born in the Kingdom of Bohemia into a poor Czech Protestant noble family, affiliated with the Utraquist Hussites, a group of notable anti-German sentiment in some of its circles, and following the teachings of the early reformer Jan Hus. He acquired a multilingual university education across Europe and converted to Catholicism in 1606. A marriage in 1609 to the wealthy widow of a Bohemian landowner gave him access to considerable estates and wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine, or disease, while parts of Germany reported population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War, the Torstenson War, the Dutch-Portuguese War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. The war had its origins in the 16th-century Reformation, which led to religious conflict within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Catholic and Lutheran states, but the settlement was destabilised by the subsequent expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries. Combined with differences over the limits of imperial authority, religion was thus an important factor in star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
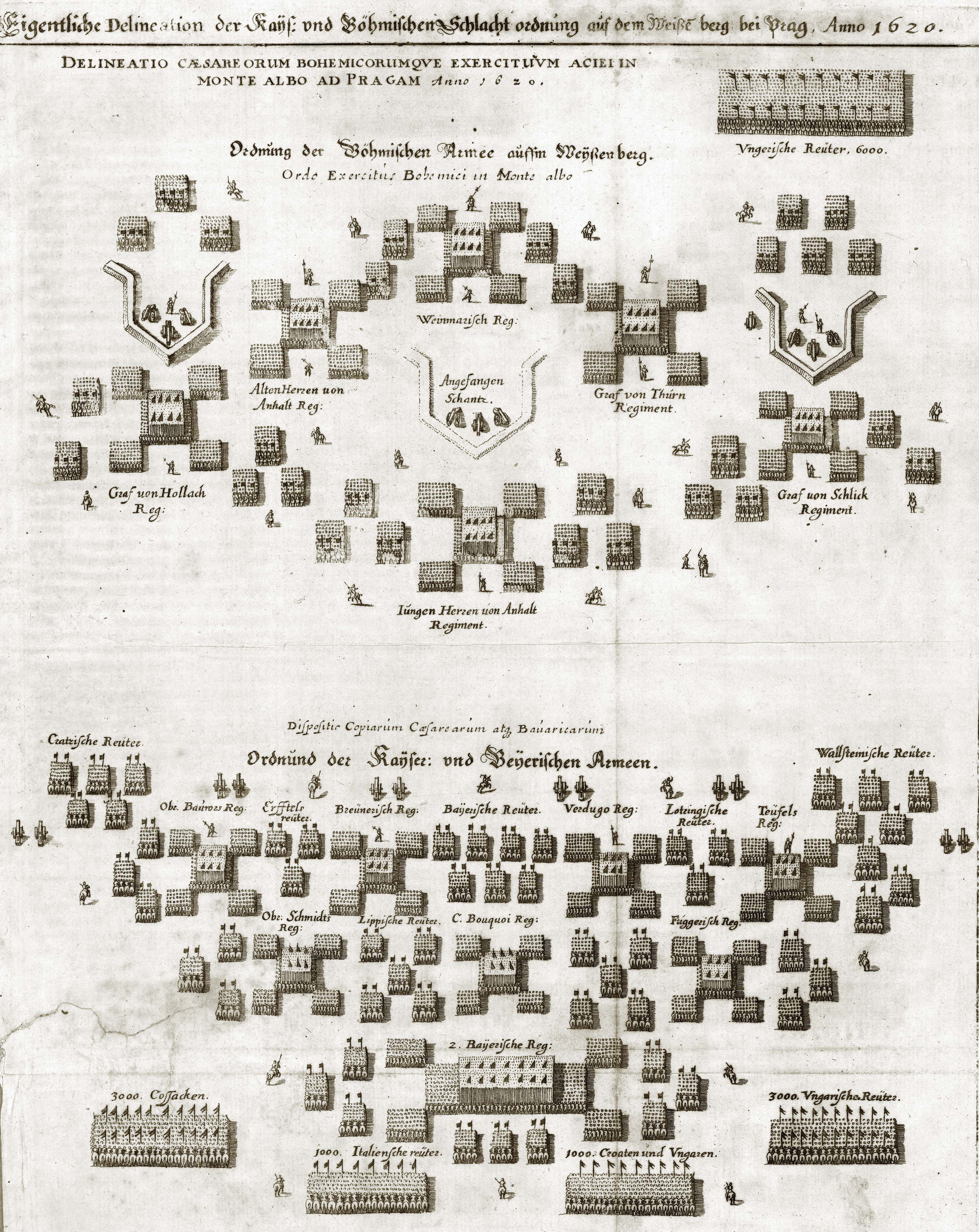
Battle Of White Mountain
The Battle of White Mountain (; ) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian Revolt and ensured Habsburg control for the next three hundred years. It was fought on 8 November 1620. An army of 21,000 Bohemians and mercenaries under Christian of Anhalt was defeated by 23,000 men of the combined armies of Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor, led by Charles Bonaventure de Longueval, Count of Bucquoy, and the German Catholic League led by Johann Tserclaes, later Count of Tilly, at Bílá Hora ("White Mountain") near Prague. Bohemian casualties were not severe but their morale collapsed and Imperial forces occupied Prague the next day. Prelude In the early 17th century most of the Bohemian estates, although under the dominion of the predominantly Catholic Holy Roman Empire, had large Protestant populations, and had been granted rights and protections allowing them varying degrees of religious and political freedom. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobkowicz Family
The House of Lobkowicz (''Lobkovicové'' in modern Czech, sg. ''z Lobkovic''; ''Lobkowitz'' in German) is an important Bohemian noble family that dates back to the 14th century and is one of the oldest noble families of the region. Over the centuries, the family expanded their possessions through marriage with the most powerful families of the region, which resulted in gaining vast territories all across central Europe. Due to that, the family was also incorporated into the German, Austrian and Belgian nobility. History The first Lobkowiczs were members of the gentry of north-eastern Bohemia in the late 14th century. On 3 August 1459 they were granted the title of Freiherr. In the 17th century, members of the family were awarded with the title of Prince, which was granted to them on 17 October 1623 by Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor. In 1786, Emperor Joseph II further ennobled the 7th Prince when he created him Duke of Roudnice (''Herzog von Raudnitz'' in German, ''vévoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berka Of Dubá
Berka of Dubá () was a cadet branch of a Bohemian noble family of Lords of Dubá established by Hynek Berka of Dubá (1249–1306). It held estates in what is today the Czech Republic and Saxony in Germany throughout the Middle Ages. Ancestors This old Czech family separated from the family of the lords of Dubé and are thus one of the lines of the :de:Ronow (Adelsgeschlecht), Ronows. The Ronows derive their origin from Smil from Tuháně from the end of the 12th century. His sons Jindřich and Častolov are mentioned in the first half of the 13th century as brothers from Tuhán and Žitava, who acquired the region in the north from the monarch. They and their sons founded other family branches, e.g. the lords of Klinštejn, the lords of Lipá, the Lichtenburks and the lords of Duba (Berkov, Adršpach, Škop). The majority of the Ronians supported the king militarily and also obtained property, titles, and important positions in the kingdom for this. As regards the Berka from D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houska Castle
Houska Castle () is an early Gothic architecture, Gothic castle in the municipality of Blatce in the Liberec Region of the Czech Republic. It lies about north of Prague. It is one of the best preserved castles of the period. Some notable features of the castle include a predominantly Gothic chapel, a green chamber with late-Gothic paintings, and a knight's drawing room. Folklore considers this castle to cover one of the gateways to Hell, built to prevent demons (trapped in lower levels) from reaching the rest of the world. History Houska Castle was built in the second half of the 13th century probably on the orders of Bohemian ruler Ottokar II of Bohemia during his reign (1253–78) to serve as an administration center from which the extensive royal estates could be managed. Later on, it passed to the hands of the aristocracy, frequently passing from the ownership of one to another. The castle was built in an area of forests, swamps and mountains with no external fortific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |