|
Vested
In law, vesting is the point in time when the rights and interests arising from legal ownership of a property are acquired by some Legal person, person. Vesting creates an immediately secured right of present or future deployment. One has a vested right to an asset that cannot be taken away by any third party, even though one may not yet possess the asset. When the right, interest, or title to the present or future possession of a Estate (law), legal estate can be transferred to any other party, it is termed a vested interest. The concept can arise in any number of contexts, but the most common are inheritance law and retirement plan law. In real estate, to vest is to create an Entitlement (fair division), entitlement to a privilege or a right. For example, one may cross someone else's property regularly and unrestrictedly for several years, and one's right to an easement becomes vested. The original owner still retains the possession, but can no longer prevent the other party fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remainder (law)
In property law of the United Kingdom and the United States and other common law countries, a remainder is a future interest given to a person (who is referred to as the transferee or remainderman) that is capable of becoming possessory upon the natural end of a prior estate created by the same instrument. Thus, the prior estate must be one that is capable of ending naturally, for example upon the expiration of a term of years or the death of a life tenant. A future interest following a fee simple absolute cannot be a remainder because of the preceding infinite duration. For example: : A person, , conveys (gives) a piece of real property called " Blackacre" "to for life, and then to and her heirs". :* receives a life estate in Blackacre. :* holds a ''remainder'', which can become ''possessory'' when the prior estate naturally terminates ('s death). However, cannot claim the property during 's lifetime. There are two types of remainders in property law: ''vested'' and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Employer Matching Program
In the United States, an employer matching program is an employer's potential payment to their 401(k) plan that depends on participating employees' contribution to the plan. Background An employee's 401(k) plan is a retirement savings plan. The option of an employer matching program varies from company to company. It is not mandatory for a company to offer a contribution to their 401(k) plans. Contributions may benefit the company in various ways: as an employee benefit to attract and retain employees, as a business tax deduction, or as a safe harbor contribution to automatically pass certain annual testing of the plan required by the IRS and Department of Labor or to fulfill the plan's top-heavy provisions. Many companies add to an employee's charity contribution. Through a corporate matching gift program, a company can double or even triple an employee's contribution toward a charity. This should not be confused with an employer matching program. "100% of the first 6%" A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ownership
Ownership is the state or fact of legal possession and control over property, which may be any asset, tangible or intangible. Ownership can involve multiple rights, collectively referred to as '' title'', which may be separated and held by different parties. The process and mechanics of ownership are fairly complex: one can gain, transfer, and lose ownership of property in a number of ways. To acquire property one can purchase it with money, trade it for other property, win it in a bet, receive it as a gift, inherit it, find it, receive it as damages, earn it by doing work or performing services, make it, or homestead it. One can transfer or lose ownership of property by selling it for money, exchanging it for other property, giving it as a gift, misplacing it, or having it stripped from one's ownership through legal means such as eviction, foreclosure, seizure, or taking. Ownership implies that the owner of a property also owns any economic benefits or deficits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Employee Stock Option
Employee stock options (ESO or ESOPs) is a label that refers to compensation contracts between an employer and an employee that carries some characteristics of Options (finance), financial options. Employee stock options are commonly viewed as an internal agreement providing the possibility to participate in the share capital of a company, granted by the company to an employee as part of the employee's remuneration, remuneration package. Regulators and economists have since specified that ESOs are compensation contracts. These nonstandard contracts exist between employee and employer, whereby the employer has the liability of delivering a certain number of shares of the employer stock, when and if the employee stock options are exercised by the employee. The contract length varies, and often carries terms that may change depending on the employer and the current employment status of the employee. In the United States, the terms are detailed within an employer's "Stock Option A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repurchase Agreement
A repurchase agreement, also known as a repo, RP, or sale and repurchase agreement, is a form of secured short-term borrowing, usually, though not always using government securities as collateral. A contracting party sells a security to a lender and, by agreement between the two parties, repurchases the security back shortly afterwards, at a slightly higher contracted price. The difference in the prices and the time interval between sale and repurchase creates an effective interest rate on the loan. The mirror transaction, a "reverse repurchase agreement," is a form of secured contracted lending in which a party buys a security along with a concurrent commitment to sell the security back in the future at a specified time and price. Because this form of funding is often used by dealers, the convention is to reference the dealer's position in a transaction with an end party. Central banks also use repo and reverse repo transactions to manage banking system reserves. When the Feder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Board
An advisory board is a body that provides non-binding strategic advice to the management of a corporation, organization, or foundation. The informal nature of an advisory board gives greater flexibility in structure and management compared to the board of directors. Unlike the board of directors, the advisory board does not have authority to vote on corporate matters or bear legal fiduciary A fiduciary is a person who holds a legal or ethical relationship of trust with one or more other parties (legal person or group of persons). Typically, a fiduciary prudently takes care of money or other assets for another person. One party, ... responsibilities. Many new or small businesses choose to have advisory boards in order to benefit from the knowledge of others, without the expense or formality of the board of directors. Function The function of an advisory board is to offer assistance to enterprises with anything from marketing to managing human resources to influencing the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Directors
A board of directors is a governing body that supervises the activities of a business, a nonprofit organization, or a government agency. The powers, duties, and responsibilities of a board of directors are determined by government regulations (including the jurisdiction's corporate law) and the organization's own constitution and by-laws. These authorities may specify the number of members of the board, how they are to be chosen, and how often they are to meet. In an organization with voting members, the board is accountable to, and may be subordinate to, the organization's full membership, which usually elect the members of the board. In a stock corporation, non-executive directors are elected by the shareholders, and the board has ultimate responsibility for the management of the corporation. In nations with codetermination (such as Germany and Sweden), the workers of a corporation elect a set fraction of the board's members. The board of directors appoints the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent Contractor
Employment is a relationship between two parties regulating the provision of paid labour services. Usually based on a contract, one party, the employer, which might be a corporation, a not-for-profit organization, a co-operative, or any other entity, pays the other, the employee, in return for carrying out assigned work. Employees work in return for wages, which can be paid on the basis of an hourly rate, by piecework or an annual salary, depending on the type of work an employee does, the prevailing conditions of the sector and the bargaining power between the parties. Employees in some sectors may receive gratuities, bonus payments or stock options. In some types of employment, employees may receive benefits in addition to payment. Benefits may include health insurance, housing, and disability insurance. Employment is typically governed by employment laws, organization or legal contracts. Employees and employers An employee contributes labour and expertise to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Stock
Common stock is a form of corporate equity ownership, a type of security. The terms voting share and ordinary share are also used frequently outside of the United States. They are known as equity shares or ordinary shares in the UK and other Commonwealth realms. This type of share gives the stockholder the right to share in the profits of the company, and to vote on matters of corporate policy and the composition of the members of the board of directors. The owners of common stock do not directly own any assets of the company; instead each stockholder owns a fractional interest in the company, which in turn owns the assets. As owners of a company, common stockholders are eligible to receive dividends from its recent or past earnings, proceeds from a sale of the company, and distributions of residual (left-over) money if it is liquidated. In general, common stockholders have lowest priority to receive payouts from the company. They may not receive dividends until the company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
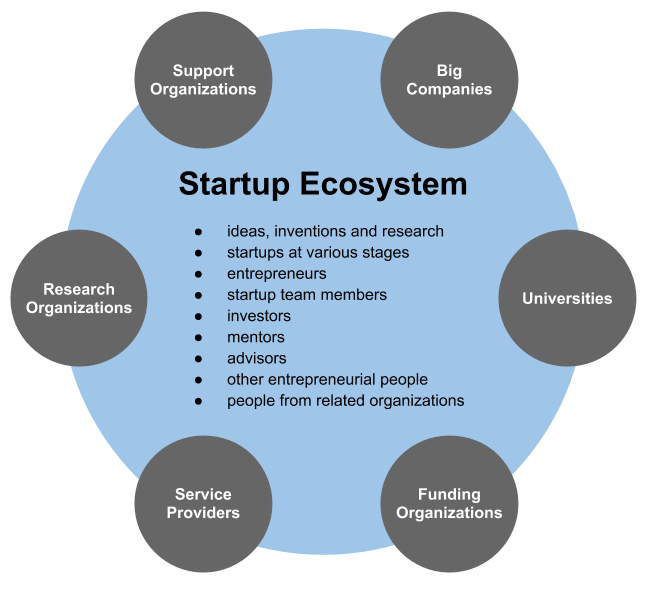
Startup
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship includes all new businesses including self-employment and businesses that do not intend to go public, startups are new businesses that intend to grow large beyond the solo-founder. During the beginning, startups face high uncertainty and have high rates of failure, but a minority of them do go on to become successful and influential, such as unicorns.Erin Griffith (2014)Why startups fail, according to their founders, Fortune.com, 25 September 2014; accessed 27 October 2017 Actions Startups typically begin by a founder (solo-founder) or co-founders who have a way to solve a problem. The founder of a startup will do the market validation by problem interview, solution interview, and building a minimum viable product (MVP), i.e. a prototype, to develop and validate their business models. The startup process can take a long perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Employee Retirement Income Security Act
The Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA) (, codified in part at ) is a U.S. federal tax and labor law that establishes minimum standards for pension plans in private industry. It contains rules on the federal income tax effects of transactions associated with employee benefit plans. ERISA was enacted to protect the interests of employee benefit plan participants and their beneficiaries by: * Requiring the disclosure of financial and other information concerning the plan to beneficiaries; * Establishing standards of conduct for plan fiduciaries; * Providing for appropriate remedies and access to the federal courts. ERISA is sometimes used to refer to the full body of laws that regulate employee benefit plans, which are mainly in the Internal Revenue Code and ERISA itself. Responsibility for interpretation and enforcement of ERISA is divided among the Department of Labor, the Department of the Treasury (particularly the Internal Revenue Service), and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retirement Plans In The United States
A retirement plan is a financial arrangement designed to replace employment income upon retirement. These plans may be set up by employers, insurance companies, trade unions, the government, or other institutions. United States Congress, Congress has expressed a desire to encourage responsible retirement planning by granting favorable tax treatment to a wide variety of plans. Federal tax aspects of retirement plans in the United States are based on provisions of the Internal Revenue Code and the plans are regulated by the United States Department of Labor, Department of Labor under the provisions of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA). Types of retirement plans Retirement plans are classified as either Defined benefit pension plan, defined benefit plans or Defined contribution plan, defined contribution plans, depending on how benefits are determined. In a defined benefit (or pension) plan, benefits are calculated using a fixed formula that typically factors in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |