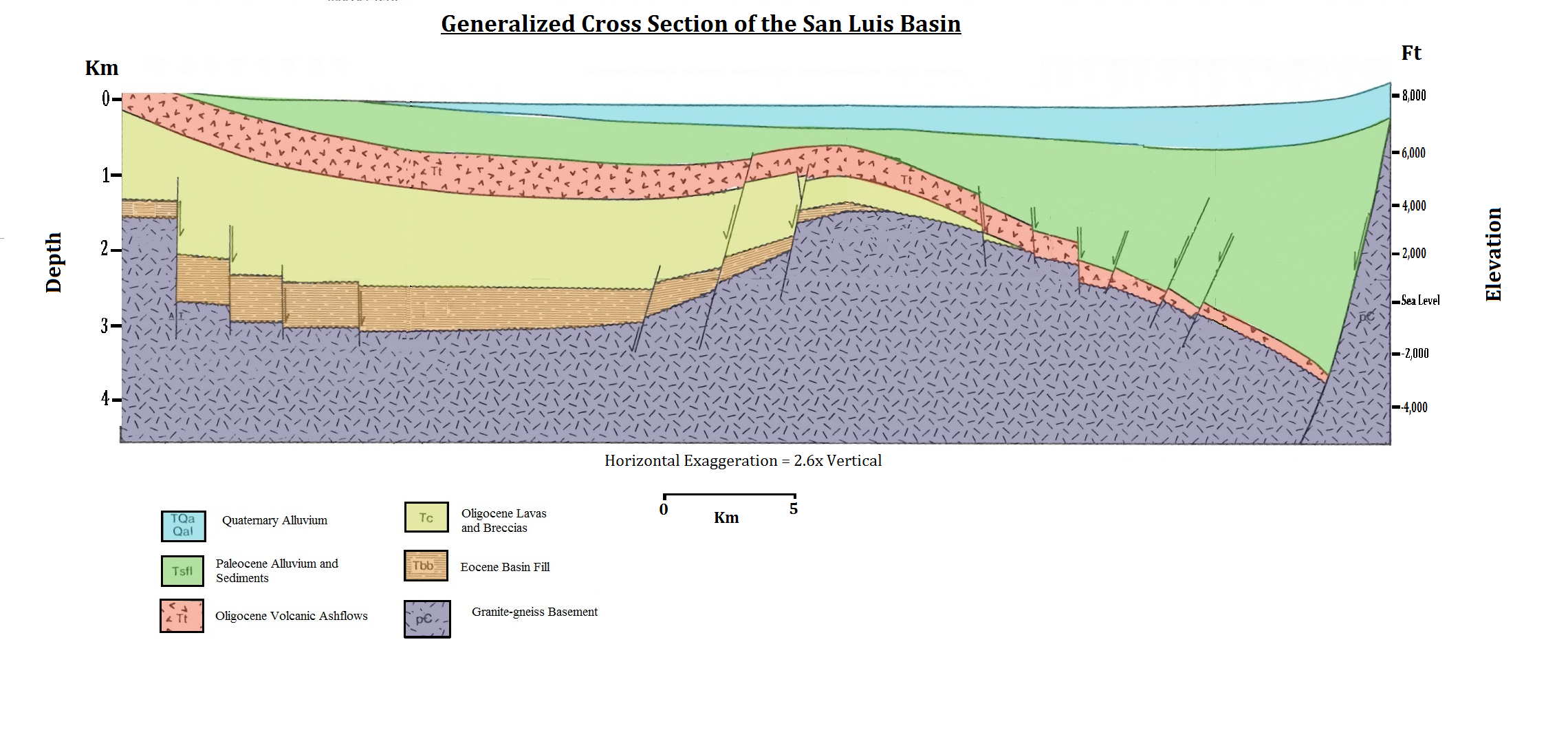
|
Velká Javořina
Velká Javořina () is a mountain massif on the border of the Czech Republic and Slovakia. At above sea level, it is the highest peak of the White Carpathians mountain range. Name The name Javořina/Javorina is derived from the Slavic word ''javor'' ('maple'). In Slovakia, there is another peak with the name Veľká Javorina, located in the Čergov mountains in eastern Slovakia, hence sometimes the distinguishing name ''Veľká Javorina Bielokarpatská'' is used. Geological structure and soils The massif of Velká Javořina is located in the southwest part of the White Carpathians and is built of Carpathian Flysch Belt, flysch rocks with significant thickness, in which layers of sandstone (dating from the Upper Cretaceous to the Lower Paleocene) and fine-grained marine Sedimentary rock, sediments (shales and marls) rhythmically repeat. The massif has the character of a mountainous erosional-denudational landscape. Its main feature is a significant surface area with large dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Carpathians
The White Carpathians (; ; ) are a mountain range on the border of the Czech Republic and Slovakia, part of the Carpathians. They are part of the macroregion of Slovak-Moravian Carpathians, stretching from the Váh river and the Little Carpathians in the south along the border between the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the Morava and the Javorníky range in the north. The mean elevation is 473 m (1,552 ft) and the highest peaks are: * Velká Javořina/Veľká Javorina, * Chmeľová, * Jelenec, * Velký Lopeník/Veľký Lopeník, * Kobylinec, The landscape is protected on both sides of the mountains: Biele Karpaty Protected Landscape Area in Slovakia, founded in 1979, and Bílé Karpaty Protected Landscape Area in the Czech Republic, founded in 1980, a Man and Biosphere Reserve since 1996. The areas contain a wide variety of fauna and flora. Some species found there are endemic, especially some types of orchids which grow only in the meadows of the Whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ridge
A ridge is a long, narrow, elevated geomorphologic landform, structural feature, or a combination of both separated from the surrounding terrain by steep sides. The sides of a ridge slope away from a narrow top, the crest or ridgecrest, with the terrain dropping down on either side. The crest, if narrow, is also called a ridgeline. Limitations on the dimensions of a ridge are lacking. Its height above the surrounding terrain can vary from less than a meter to hundreds of meters. A ridge can be either depositional, erosional, tectonic, or a combination of these in origin and can consist of either bedrock, loose sediment, lava, or ice depending on its origin. A ridge can occur as either an isolated, independent feature or part of a larger geomorphological and/or structural feature. Frequently, a ridge can be further subdivided into smaller geomorphic or structural elements. Classification As in the case of landforms in general, there is a lack of any commonly agreed clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tributary
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream (''main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they flow, drain the surrounding drainage basin of its surface water and groundwater, leading the water out into an ocean, another river, or into an endorheic basin. The Irtysh is a chief tributary of the Ob (river), Ob river and is also the longest tributary river in the world with a length of . The Madeira River is the largest tributary river by volume in the world with an average discharge of . A confluence, where two or more bodies of water meet, usually refers to the joining of tributaries. The opposite to a tributary is a distributary, a river or stream that branches off from and flows away from the main stream. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring (hydrology)
A spring is a natural exit point at which groundwater emerges from an aquifer and flows across the ground surface as surface water. It is a component of the hydrosphere, as well as a part of the water cycle. Springs have long been important for humans as a source of fresh water, especially in arid regions which have relatively little annual rainfall. Springs are driven out onto the surface by various natural forces, such as gravity and hydrostatic pressure. A spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater is known as a hot spring. The yield of spring water varies widely from a volumetric flow rate of nearly zero to more than for the biggest springs. Formation Springs are formed when groundwater flows onto the surface. This typically happens when the water table reaches above the surface level, or if the terrain depresses sharply. Springs may also be formed as a result of karst topography, aquifers or volcanic activity. Springs have also been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luhačovice
Luhačovice (; ) is a spa town in Zlín District in the Zlín Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 5,000 inhabitants. It is known for the largest spa in Moravia and for architecturally valuable buildings designed by the architect Dušan Jurkovič. The historic town centre with the spa infrastructure is well preserved and is protected as an Cultural monument (Czech Republic)#Monument zones, urban monument zone. Administrative division Luhačovice consists of four municipal parts (in brackets population according to the 2021 census): *Luhačovice (4,160) *Kladná Žilín (192) *Polichno (257) *Řetechov (233) Polichno and Řetechov form two Enclave and exclave, exclaves of the municipal territory. Etymology The name was probably derived from the personal name Luhač. The name could also be derived from ''luhy'', which means "meadows on wetter soil". Geography Luhačovice is located about south of Zlín. It lies in the hilly landscape in the Vizovice Highlands. The highest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Spring
Mineral springs are naturally occurring springs that produce hard water, water that contains dissolved minerals. Salts, sulfur compounds, and gases are among the substances that can be dissolved in the spring water during its passage underground. In this they are unlike sweet springs, which produce soft water with no noticeable dissolved gasses. The dissolved minerals may alter the water's taste. Mineral water obtained from mineral springs, and the precipitated salts such as Epsom salt have long been important commercial products. Some mineral springs may contain significant amounts of harmful dissolved minerals, such as arsenic, and should not be drunk. Sulfur springs smell of rotten eggs due to hydrogen sulfide (H2S), which is hazardous and sometimes deadly. It is a gas, and it usually enters the body when it is breathed in. The quantities ingested in drinking water are much lower and are not considered likely to cause harm, but few studies on long-term, low-level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggradation
Aggradation (or alluviation) is the term used in geology for the increase in land elevation, typically in a river system, due to the deposition of sediment. Aggradation occurs in areas in which the supply of sediment is greater than the amount of material that the system is able to transport. The mass balance between sediment being transported and sediment in the bed is described by the Exner equation. Typical aggradational environments include lowland alluvial rivers, river deltas, and alluvial fans. Aggradational environments are often undergoing slow subsidence which balances the increase in land surface elevation due to aggradation. After millions of years, an aggradational environment will become a sedimentary basin, which contains the deposited sediment, including paleochannels and ancient floodplains. Aggradation can be caused by changes in climate, land use, and geologic activity, such as volcanic eruption, earthquake An earthquakealso called a quake, tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion procee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stream
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long, large streams are usually called rivers, while smaller, less voluminous and more intermittent river, intermittent streams are known, amongst others, as brook, creek, rivulet, rill, run, tributary, feeder, freshet, narrow river, and streamlet. The flow of a stream is controlled by three inputs – surface runoff (from precipitation or meltwater), daylighting (streams), daylighted subterranean river, subterranean water, and surfaced groundwater (Spring (hydrology), spring water). The surface and subterranean water are highly variable between periods of rainfall. Groundwater, on the other hand, has a relatively constant input and is controlled more by long-term patterns of pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rendzina
Rendzina (or ''rendsina'') is a soil type recognized in various soil classification systems, including those of Britain and Germany as well as some obsolete systems. They are humus-rich shallow soils that are usually formed from carbonate- or occasionally sulfate-rich parent material. Rendzina soils are often found in karst and mountainous regions. The term ''rendzina'' originated via Russian from the Polish ''rędzina'' (the word "rędzina" comes from the old Polish word "rzędzić" (to speak, to drone). In the World Reference Base for Soil Resources, rendzina soils would be classified as leptosols, chernozems, kastanozems, or phaeozems, depending on their specific characteristics. Development and distribution Rendzina soils typically develop from solid or unconsolidated rocky material that is carbonate- or sulphate-rich. Limestone is by far the most common, but others include dolomite, gypsum, marble, chalk and marlstone. Alongside physical weathering, which breaks down t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambisol
A Cambisol in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB) is a soil in the beginning of soil formation. The horizon differentiation is weak. This is evident from weak, mostly brownish discolouration and/or structure formation in the soil profile. Cambisols are developed in medium and fine-textured materials derived from a wide range of rocks, mostly in alluvial, colluvial and aeolian deposits. Most of these soils make good agricultural land and are intensively used. Cambisols in temperate climates are among the most productive soils on earth. Cambisols cover an estimated 15 million square kilometres worldwide. They are well represented in temperate and boreal regions that were under the influence of glaciation during the Pleistocene, partly because the soil's parent material is still young, but also because soil formation is comparatively slow in the cool, northern regions. Cambisols are less common in the tropics and subtropics, but they are common in areas with active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvium
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not Consolidation (geology), consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present Scientific consensus, consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined ''alluvion'' (the French term for al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |