|
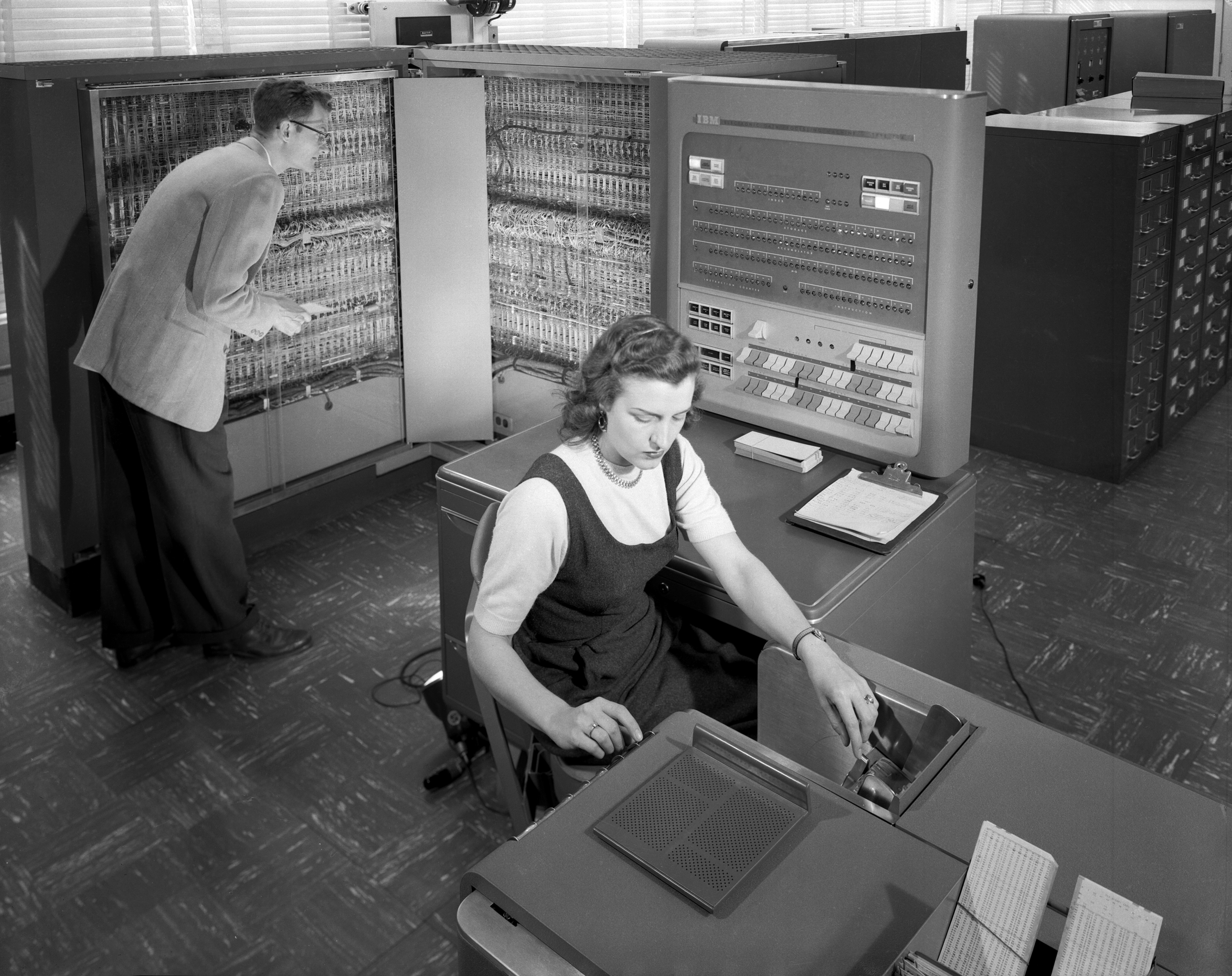
Vacuum Column (tape Drive)
9-track tape is a format for magnetic-tape data storage, introduced with the IBM System/360 in 1964. The wide magnetic tape media and reels have the same size as the earlier IBM 7-track format it replaced, but the new format has eight data tracks and one parity track for a total of nine parallel tracks. Data is stored as 8-bit characters, spanning the full width of the tape (including the parity bit). Various recording methods have been employed during its lifetime as tape speed and data density increased, including PE ( phase encoding), GCR ( group-coded recording), and NRZI (non-return-to-zero, inverted, sometimes pronounced "nur-zee"). Tapes come in various sizes up to in length. The standard size of a byte was effectively set at eight bits with the S/360 and nine-track tape. For over 30 years the format dominated offline storage and data transfer, but by the end of the 20th century it was obsolete, and the last manufacturer of tapes ceased production in early 2002, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM System 360 Tape Drives
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is a publicly traded company and one of the 30 companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average. IBM is the largest industrial research organization in the world, with 19 research facilities across a dozen countries; for 29 consecutive years, from 1993 to 2021, it held the record for most annual U.S. patents generated by a business. IBM was founded in 1911 as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR), a holding company of manufacturers of record-keeping and measuring systems. It was renamed "International Business Machines" in 1924 and soon became the leading manufacturer of Tabulating machine, punch-card tabulating systems. During the 1960s and 1970s, the IBM mainframe, exemplified by the IBM System/360, System/360 and its successors, wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonewheel
A tonewheel or tone wheel is a simple electromechanical apparatus used for generating electric musical notes in electromechanical electronic organ, organ instruments such as the Hammond Organ, Hammond organ and in telephony to generate audible signals such as ringing tone. It was developed by Thaddeus Cahill for the telharmonium c. 1896 and patented in 1897. It was reinvented around 1910 by Rudolph Goldschmidt for use in pre–vacuum tube, vacuum-tube radio receivers as a beat frequency oscillator (BFO) to make continuous wave radiotelegraphy (Morse code) signals audible. Description The tonewheel assembly consists of a synchronous AC motor and an associated Transmission (mechanics), gearbox that drives a series of rotating disks. Each disk has a given number of smooth bumps at the rim; these generate a specific frequency as the disk rotates close to a Pick up (music technology), pickup assembly that consists of a magnet and electromagnetic coil. As each bump in the wheel appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-return-to-zero, Inverted
In telecommunications, a non-return-to-zero (NRZ) line code is a Binary coding, binary code in which ones are represented by one significant condition, usually a positive voltage, while zeros are represented by some other significant condition, usually a negative voltage, with no other neutral or rest condition. For a given data signaling rate, i.e., bit rate, the NRZ code requires only half the Bandwidth (signal processing), baseband bandwidth required by the Manchester code (the passband bandwidth is the same). The pulses in NRZ have more energy than a return-to-zero (RZ) code, which also has an additional rest state beside the conditions for ones and zeros. When used to represent data in an asynchronous communication scheme, the absence of a neutral state requires other mechanisms for bit synchronization when a separate clock signal is not available. Since NRZ is not inherently a self-clocking signal, some additional synchronization technique must be used for avoiding bit s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INCITS
The InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS), (pronounced "insights"), is an ANSI-accredited standards development organization composed of Information technology developers. It was formerly known as the X3 and NCITS. INCITS is the central U.S. forum dedicated to creating technology standards. INCITS is accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and is affiliated with the Information Technology Industry Council, a global policy advocacy organization that represents U.S. and global innovation companies. INCITS coordinates technical standards activity between ANSI in the US and joint ISO/ IEC committees worldwide. This provides a mechanism to create standards that will be implemented in many nations. As such, INCITS' Executive Board also serves as ANSI's Technical Advisory Group for ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1. JTC 1 is responsible for International standardization in the field of information technology. INCITS operates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international standards so that American products can be used worldwide. ANSI accredits standards that are developed by representatives of other standards organizations, government agencies, consumer groups, companies, and others. These standards ensure that the characteristics and performance of products are consistent, that people use the same definitions and terms, and that products are tested the same way. ANSI also accredits organizations that carry out product or personnel certification in accordance with requirements defined in international standards. The organization's headquarters are in Washington, D.C. ANSI's operations office is located in New York City. The ANSI annual operating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Write Protection
Write protection is any physical mechanism that prevents writing, modifying, or erasing data on a device. Most commercial software, audio and video on writeable media is write-protected when distributed. Examples * IBM -inch magnetic tape reels, introduced in the 1950s, had a circular groove on one side of the reel, into which a soft plastic ring had to be placed in order to write on the tape. ("No ring, no write.") * Audio cassettes and VHS videocassettes have tabs on the top/rear edge that can be broken off (uncovered = protected). * 8 and -inch floppies can have, respectively, write-protect and write-enable notches on the right side (8-inch punched = protected; -inch covered/notch not present = protected). A common practice with single-sided floppies was to punch a second notch on the opposite side of the disk to enable use of both sides of the media, creating a flippy disk, so called because one originally had to flip the disk over to use the other side. * -inch floppy di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum Foil
Aluminium foil (or aluminum foil in American English; occasionally called tin foil) is aluminium prepared in thin metal leaves. The foil is pliable and can be readily bent or wrapped around objects. Thin foils are fragile and are sometimes laminated with other materials such as plastics or paper to make them stronger and more useful. Annual production of aluminium foil was approximately in Europe in 2014, and in the U.S. in 2003."Foil & Packaging" . The Aluminum Association (USA). Approximately 75% of aluminium foil is used for of |
EBCDIC
Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC; ) is an eight- bit character encoding used mainly on IBM mainframe and IBM midrange computer operating systems. It descended from the code used with punched cards and the corresponding six-bit binary-coded decimal code used with most of IBM's computer peripherals of the late 1950s and early 1960s. It is supported by various non-IBM platforms, such as Fujitsu-Siemens' BS2000/OSD, OS-IV, MSP, and MSP-EX, the SDS Sigma series, Unisys VS/9, Unisys MCP and ICL VME. History EBCDIC was devised in 1963 and 1964 by IBM and was announced with the release of the IBM System/360 line of mainframe computers. It is an eight-bit character encoding, developed separately from the seven-bit ASCII encoding scheme. It was created to extend the existing Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) Interchange Code, or BCDIC, which itself was devised as an efficient means of encoding the two ''zone'' and ''number'' punches on punched cards into six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM AS/400
The IBM AS/400 (Application System/400) is a family of midrange computers from IBM announced in June 1988 and released in August 1988. It was the successor to the System/36 and System/38 platforms, and ran the OS/400 operating system. Lower-cost but more powerful than its predecessors, an estimated 111,000 installations existed by the end of 1990 and annual revenue reaching $14 billion that year, increasing to 250,000 systems by 1994, and about 500,000 shipped by 1997. A key concept in the AS/400 platform is IBM i#TIMI, Technology Independent Machine Interface (TIMI), a platform-independent instruction set architecture (ISA) that is translated to native machine language instructions. The platform has used this capability to change the underlying processor architecture without breaking application compatibility. Early systems were based on a 48-bit Complex instruction set computer, CISC instruction set architecture known as the ''Internal Microprogrammed Interface'' (IMPI), original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM System/36
The IBM System/36 (often abbreviated as S/36) was a midrange computer marketed by IBM from 1983 to 2000 - a multi-user, multi-tasking successor to the System/34. Like the System/34 and the older System/32, the System/36 was primarily programmed in the RPG II language. One of the machine's optional features was an off-line storage mechanism (on the 5360 model) that utilized "magazines" – boxes of 8-inch floppies that the machine could load and eject in a nonsequential fashion. The System/36 also had many mainframe features such as programmable job queues and scheduling priority levels. While these systems were similar to other manufacturer's minicomputers, IBM themselves described the System/32, System/34 and System/36 as "small systems" and later as midrange computers along with the System/38 and succeeding IBM AS/400 range. The AS/400 series and IBM Power Systems running IBM i can run System/36 code in the System/36 Environment, although the code needs to be recompil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM System/370
The IBM System/370 (S/370) is a range of IBM mainframe computers announced as the successors to the IBM System/360, System/360 family on June 30, 1970. The series mostly maintains backward compatibility with the S/360, allowing an easy migration path for customers; this, plus improved performance, were the dominant themes of the product announcement. Early 370 systems differed from the 360 largely in their internal circuitry, moving from the Solid Logic Technology hybrid integrated circuits containing separate transistors to more modern monolithic integrated circuits containing multiple transistors per integrated circuit, which IBM referred to as Monolithic System Technology, or MST. The higher density packaging allowed several formerly optional features from the 360 line to be included as standard features of the machines, floating-point support for instance. The 370 also added a small number of new instructions. At the time of its introduction, the development of virtual mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 729
The IBM 729 Magnetic Tape Unit was IBM's tape mass storage system from the late 1950s through the mid-1960s. Part of the IBM 7-track family of tape units, it was used on late 700, most 7000 and many 1400 series computers. Like its predecessor, the IBM 727 and many successors, the 729 used magnetic tape up to long wound on reels up to diameter. To allow rapid tape acceleration (and thus reduced seek/access times), long vacuum columns were placed between the tape reels and the read/write heads to absorb sudden increases in tape tension which would otherwise break the tape. Write protection was provided by a removable plastic ring in the back of the tape reel. Data format The tape had seven parallel tracks, six for data and one to maintain parity. Tapes with character data (BCD) were recorded in even parity. Binary tapes used odd parity (709 manual, p. 20). Aluminum strips were glued several feet from the ends of the tape to serve as physical beginning and end of tape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |