|
VSAM
Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM) is an IBM direct-access storage device (DASD) file storage access method, first used in the OS/VS1, OS/VS2 Release 1 (SVS) and Release 2 (MVS) operating systems, later used throughout the Multiple Virtual Storage (MVS) architecture and now in z/OS. Originally a record-oriented filesystem, VSAM comprises four data set ''organizations'': key-sequenced (KSDS), relative record (RRDS), entry-sequenced (ESDS) and linear (LDS). The KSDS, RRDS and ESDS organizations contain records, while the LDS organization (added later to VSAM) contains a sequence of pages with no intrinsic record structure, for use as a memory-mapped file. Overview An IBM ''Redbook'' named "VSAM PRIMER" (especially when used with the "Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM) Options for Advanced Applications" manual) explains the concepts needed to make use of VSAM. IBM uses the term ''data set'' in official documentation as a synonym for ''file'', and ''direct-access storage dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OS/360 And Successors
OS/360, officially known as IBM System/360 Operating System, is a discontinued batch processing operating system developed by IBM for their then-new System/360 mainframe computer, announced in 1964; it was influenced by the earlier IBSYS/IBJOB and Input/Output Control System (IOCS) packages for the IBM 7090/7094 and even more so by the PR155 Operating System for the IBM 1410/ 7010 processors. It was one of the earliestJust a few years after Atlas Supervisor, Burroughs MCP and GECOS operating systems to require the computer hardware to include at least one direct access storage device. Although OS/360 itself was discontinued, successor operating systems, including the virtual storage MVS and the 64-bit z/OS, are still run and maintain application-level compatibility with OS/360. Overview IBM announced three different levels of OS/360, generated from the same tapes and sharing most of their code. IBM eventually renamed these options and made some significant design changes: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CICS
IBM CICS (Customer Information Control System) is a family of mixed-language application servers that provide online business transaction management, transaction management and connectivity for applications on IBM mainframe systems under z/OS and z/VSE. CICS family products are designed as middleware and support rapid, high-volume online transaction processing. A CICS ''transaction'' is a unit of processing initiated by a single request that may affect one or more objects. This processing is usually interactive (screen-oriented), but background transactions are possible. CICS Transaction Server (CICS TS) sits at the head of the CICS family and provides services that extend or replace the functions of the operating system. These services can be more efficient than the generalized operating system services and also simpler for programmers to use, particularly with respect to communication with diverse terminal devices. Applications developed for CICS may be written in a variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Mainframe Utility Programs
This article discusses support programs included in or available for OS/360 and successors. IBM categorizes some of these programs as utilities and others as service aids; the boundaries are not always consistent or obvious. Many, but not all, of these programs match the types in utility software. The following lists describe programs associated with OS/360 and successors. No DOS, TPF or VM utilities are included. Naming convention IBM uses a naming convention for modules where the first three letters identify the "component" to which a module belongs. In OS/VS, IBM renamed most of the IMx messages as AMx for OS/VS2 and HMx for OS/VS1. History/Common JCL Many of these programs were designed by IBM users, through the group SHARE, and then modified or extended by IBM from versions originally written by a user. These programs are usually invoked via Job Control Language (JCL). They tend to use common JCL DD identifiers (in the OS, now z/OS operating systems) for their d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Virtual Storage
Multiple Virtual Storage, more commonly called MVS, is the most commonly used operating system on the System/370, System/390 and IBM Z IBM mainframe computers. IBM developed MVS, along with OS/VS1 and SVS, as a successor to OS/360. It is unrelated to IBM's other mainframe operating system lines, e.g., VSE, VM, TPF. Overview First released in 1974, MVS was extended by program products with new names multiple times, retaining the term MVS in the nomenclature: * first to MVS/SE (MVS/System Extensions),some print media used the singular, MVS/System Extension: Computerworld, 15 Dec 1980 - Page 5; 26 June 1978 - Page 8 * next to MVS/SP (MVS/System Product) Version 1, * next to MVS/XA (MVS/eXtended Architecture), * next to MVS/ESA (MVS/Enterprise Systems Architecture), and then extended * to OS/390 for the System/390 systems, and * finally to z/OS (when 64-bit support was added with the zSeries models). IBM added UNIX support (originally called OpenEdition MVS) in MVS/SP V4. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISAM
Indexed Sequential Access Method (ISAM) is a method for creating, maintaining, and manipulating computer files of data so that records can be retrieved sequentially or randomly by one or more keys. Indexes of key fields are maintained to achieve fast retrieval of required file records in indexed files. IBM originally developed ISAM for mainframe computers, but implementations are available for most computer systems. The term ''ISAM'' is used for several related concepts: *The IBM ISAM product and the algorithm it employs. *A database system where an application developer directly uses an application programming interface to search indexes in order to locate records in data files. In contrast, a relational database uses a query optimizer which automatically selects indexes. *An indexing algorithm that allows both sequential and keyed access to data. Most databases use some variation of the B-tree for this purpose, although the original IBM ISAM and VSAM implementations did not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Set (IBM Mainframe)
In the context of IBM mainframe computers in the S/360 line, a data set (IBM preferred) or dataset is a computer file having a record-oriented file, record organization. Use of this term began with, e.g., DOS/360, OS/360, and is still used by their successors, including the current z/OS. Documentation for these systems historically preferred this term rather than ''computer file, file''. A data set is typically stored on a direct access storage device (DASD) or magnetic tape, however unit record devices, such as punch card readers, card punches, line printers and page printers can provide input/output (I/O) for a data set (file). Data sets are not unstructured streams of bytes, but rather are organized in various logical record and block structures determined by the DSORG (data set organization), RECFM (record format), and other parameters. These parameters are specified at the time of the data set allocation (creation), for example with Job Control Language DD statements. Withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Data Set
A linear data set (LDS) is a type of data set organization used by IBM's VSAM Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM) is an IBM direct-access storage device (DASD) file storage access method, first used in the OS/VS1, OS/VS2 Release 1 (SVS) and Release 2 (MVS) operating systems, later used throughout the Multiple Virtual S ... computer data storage system. The LDS has a control interval size of 4096 bytes to 32768 bytes in increments of 4096. A LDS does not have embedded control information, because it does not contain control information, the LDS cannot be accessed as if it contained individual records. Addressing within an LDS is by Relative Byte Address (RBA), which allows it to be used by systems such as IBM Db2 or the Operating system. The benefit of this is that systems such as the OS can access multiple disk spindles and view it as a single storage implementation. The limitations of this, though, is that this does not make this particularly useful to higher level abstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key-sequenced Data Set
A key-sequenced data set (KSDS) is a type of data set used by IBM's VSAM computer data storage system. Each record in a KSDS data file is embedded with a unique key. A KSDS consists of two parts, the data component and a separate index file known as the index component which allows the system to physically locate the record in the data file by its key value. Together, the data and index components are called a cluster. Records can be accessed randomly or in sequence and can be variable-length. As a VSAM data set, the KSDS data and index components consist of control intervals which are further organized in control areas. As records are added at random to a KSDS, control intervals fill and need to be split into two new control intervals, each new control interval receiving roughly half of the records. Similarly, as the control intervals in a control area are used up, a control area will be split into two new control areas, each new control area receiving roughly half the control i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entry-sequenced Data Set
An entry-sequenced data set (ESDS) is a type of data set used by IBM's VSAM computer data storage system. Records are accessed based on their sequential order, that is, the order in which they were written to the file; which means that accessing a particular record involves searching all the records sequentially until it is located, or by using a relative physical address (''Relative byte address'', RBA), i.e. the number of bytes from the beginning of the file to start reading. Keys may be used to access records in an ESDS by defining an alternate index. See also * Key Sequenced Data Set *Linear Data Set * Relative Record Data Set *Random access Random access (also called direct access) is the ability to access an arbitrary element of a sequence in equal time or any datum from a population of addressable elements roughly as easily and efficiently as any other, no matter how many elemen ... References Computer file systems {{Compu-storage-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Record Data Set
A relative record data set (RRDS) is a type of data set organization used by IBM's VSAM computer data storage system. Records are accessed based on their ordinal position in the file (''relative record number'', RRN). For example, the desired record to be accessed might be the 42nd record in the file out of 999 total. The concept of RRDS is similar to sequential access method, but it can access with data in random access and dynamic access. Structure An RRDS consists of data records in sequence, with the record number indicating the record's logical position in the data set. A program can access records randomly using this positional number or access records sequentially. But unlike a Key Sequenced Data Set, an RRDS has no keys, so the program cannot access records by key value. See also *Key-sequenced data set *Entry-sequenced data set *Linear data set A linear data set (LDS) is a type of data set organization used by IBM's VSAM Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Job Control Language
Job Control Language (JCL) is a scripting language used on IBM mainframe operating systems to instruct the system on how to run a batch processing, batch job or start a subsystem. The purpose of JCL is to say which programs to run, using which files or devices for input or output, and at times to also indicate under what conditions to skip a step. Parameters in the JCL can also provide accounting information for tracking the resources used by a job as well as which machine the job should run on. There are two distinct IBM Job Control Languages: * one for the operating system lineage that begins with DOS/360 and whose latest member is z/VSE; and * the other for the lineage from OS/360 to z/OS, the latter now including Job Entry Subsystem 2/3, JES extensions, #Job Entry Control Language, Job ''Entry'' Control Language (JECL). They share some basic syntax rules and a few basic concepts, but are otherwise very different. The VM (operating system), VM operating system does not have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
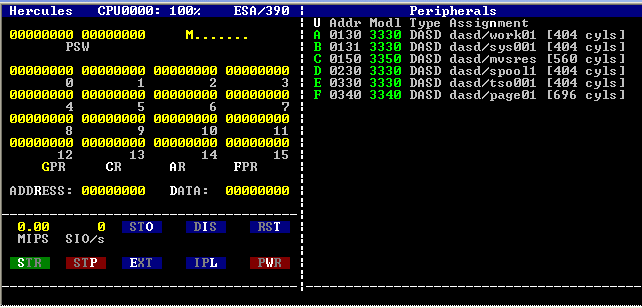
Direct Access Storage Device
A direct-access storage device (DASD) (pronounced ) is a secondary storage device in which "each physical record has a discrete location and a unique address". The term was coined by IBM to describe devices that allowed random access to data, the main examples being drum memory and hard disk drives. Later, optical disc drives and flash memory units are also classified as DASD. The term DASD contrasts with sequential access storage device such as a magnetic tape drive, and unit record equipment such as a punched card device. A record on a DASD can be accessed without having to read through intervening records from the current location, whereas reading anything other than the "next" record on tape or deck of cards requires skipping over intervening records, and requires a proportionally long time to access a distant point in a medium. Access methods for DASD include sequential, partitioned, indexed, and direct. The DASD storage class includes both fixed and removable me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |