|
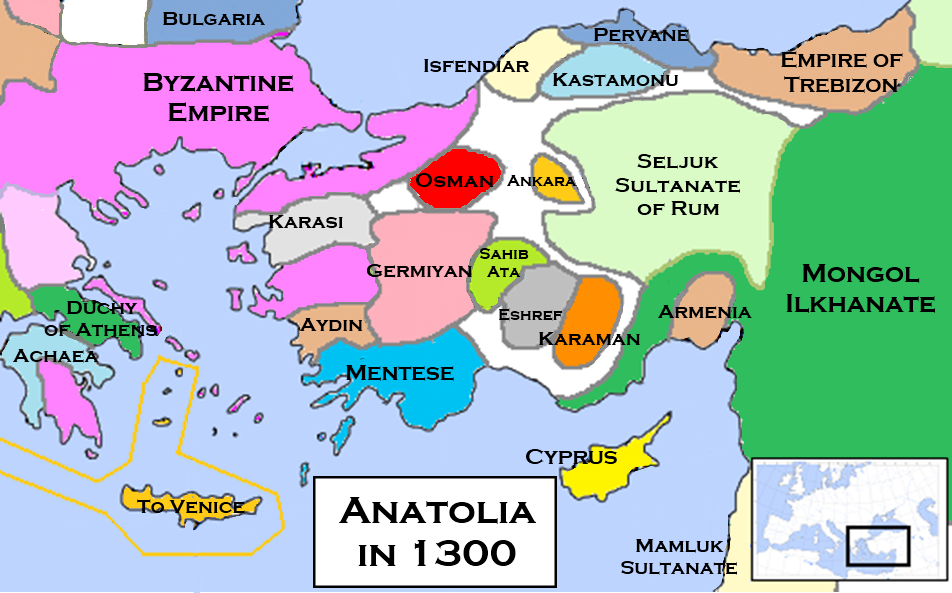
Uç Bey
An ''uç bey'' or ''uch bey'' () was the title given to semi-autonomous warrior chieftains during the Sultanate of Rum and the Rise of the Ottoman Empire. As leaders of ''akinji'' warrior bands, they played a leading role during the conquests of the Byzantine Empire and the other Christian states of the Balkans. The term is analogous to Persian ''marzban'' or Western European margrave. Uch beys were proclaimed ghazis and as a rule were dervishes. After Michael VIII Palaiologos removed the '' akritai'' and the land grants through which they survived, many Byzantine renegades went over to Ottoman service Rumelia's first ''uch bey'' was Lala Şahin Pasha, who conquered Edirne, Boruj, Plovdiv, and was later the ''beylerbey'' of the Rumelia Eyalet. Pasha Yiğit Bey was an ''uch bey'' from Skopje to the Serbian and Greek lands, advancing to Bosnia and the Morea. Ertuğrul, father of the first Ottoman Sultan Osman I, was ''uch bey'' of Söğüt Söğüt (, ) is a town in Bilecik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Rum
The Sultanate of Rum was a culturally Turco-Persian Sunni Muslim state, established over conquered Byzantine territories and peoples (Rum) of Anatolia by the Seljuk Turks following their entry into Anatolia after the Battle of Manzikert in 1071. The name ''Rum'' was a synonym for the medieval Eastern Roman Empire and its peoples, as it remains in modern Turkish. The name is derived from the Aramaic () and Parthian () names for ancient Rome, via the Greek () meaning the Anatolia. The Sultanate of Rum seceded from the Seljuk Empire under Suleiman ibn Qutalmish in 1077. It had its capital first at Nicaea and then at Iconium. It reached the height of its power during the late 12th and early 13th century, when it succeeded in taking key Byzantine ports on the Mediterranean and Black Sea coasts. In the east, the sultanate reached Lake Van. Trade through Anatolia from Iran and Central Asia was developed by a system of caravanserai. Especially strong trade ties with the Genoese forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plovdiv
Plovdiv (, ) is the List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, second-largest city in Bulgaria, 144 km (93 miles) southeast of the capital Sofia. It had a population of 490,983 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is a cultural hub in Bulgaria and was the European Capital of Culture in 1999 and 2019. The city is an important economic, transport, cultural, and educational centre. Plovdiv joined the UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities in 2016. Archeological symbols of Plovdiv Plovdiv is in a fertile region of south-central Bulgaria on the two banks of the Maritsa River. The city has historically developed on seven syenite hills, some of which are high. Because of these hills, Plovdiv is often referred to in Bulgaria as "The City of the Seven Hills". There is evidence of habitation in the area dating back to the 6th millennium BCE, when the first Neolithic settlements were established. The city was subsequently a Thracians, Thracian settlement, later being conq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of The Ottoman Empire
The Military of the Ottoman Empire () was the armed forces of the Ottoman Empire. It was founded in 1299 and dissolved in 1922. Army The Military of the Ottoman Empire can be divided in five main periods. The foundation era covers the years between 1300 (Byzantine expedition) and 1453 ( Conquest of Constantinople), the classical period covers the years between 1451 (second enthronement of Sultan Mehmed II) and 1606 ( Peace of Zsitvatorok), the reformation period covers the years between 1606 and 1826 ( Vaka-i Hayriye), the modernisation period covers the years between 1826 and 1858 and decline period covers the years between 1861 (enthronement of Sultan Abdülaziz) and 1918 ( Armistice of Mudros). The Ottoman army is the forerunner of the Turkish Armed Forces. Foundation period (1300–1453) The earliest form of the Ottoman military was a steppe-nomadic cavalry force.Mesut Uyar, Edward J. Erickson, ''A Military History of the Ottomans: From Osman to Atatürk'', Pleager Secu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Titles
This is a list of titles and appellations used in the Ottoman Empire. In place of surnames, Muslims in the Empire carried titles such as "Sultan", " Paşa", "Ağa", "Hoca", "Bey", " Hanım", " Efendi", etc. These titles either defined their formal profession (such as Pasha, Hoca, etc.) or their informal status within the society (such as Bey, Agha, Hanım, Efendi, etc.). Later, family surnames were made mandatory in Turkey by the 1934 Surname Law. Usage by Ottoman royalty The sovereigns' main titles were Sultan, Padishah (Emperor) and Khan; which were of various origins such as Arabic, Persian and Turkish or Mongolian, respectively. His full style was the result of a long historical accumulation of titles expressing the empire's rights and claims as successor to the various states it annexed or subdued. Beside these imperial titles, Caesar of Rome was among the important titles claimed by Sultan Mehmed II after the conquest of Constantinople. The title sultan (), originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghaza Thesis
The Ghaza or Ghazi thesis (from , ''ġazā'', "holy war", or simply "raid") is a since disputed historical paradigm first formulated by Paul Wittek which has been used to interpret the nature of the Ottoman Empire during the earliest period of its history, the fourteenth century, and its subsequent history. The thesis addresses the question of how the Ottomans were able to expand from a small principality on the frontier of the Byzantine Empire into a centralized, intercontinental empire. According to the Ghaza thesis, the Ottomans accomplished this by attracting recruits to fight for them in the name of Islamic holy war against the non-believers. Such a warrior was known in Ottoman Turkish as a '' ghazi'', and thus this thesis sees the early Ottoman state as a "Ghazi State," defined by an ideology of holy war. The Ghaza thesis dominated early Ottoman historiography throughout much of the twentieth century before coming under increasing criticism beginning in the 1980s. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osman's Dream
''Osman's Dream'' is a mythological story about the life of Osman I, founder of the Ottoman Empire. The story describes a dream experienced by Osman while staying in the home of a religious figure, Sheikh Edebali, in which he sees a metaphorical vision predicting the growth and prosperity of an empire to be ruled by him and his descendants. The story emerged in the fifteenth century, more than a hundred years after Osman's death, and is thought to have been created in order to provide a foundational myth for the empire, as well as to embellish the life of Osman and explain his subsequent success. When Osman tells Sheikh Edebali about the dream, the dervish interprets it as a sign that Osman would achieve great glory and fame in the name of Islam, and allows Osman to marry his daughter Rabia Bala Hatun. Ottoman writers attached great importance to this supposed dream of the founder of their empire. Story Osman, a young prince, was known and praised widely for his religious p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Söğüt
Söğüt (, ) is a town in Bilecik Province, Turkey. It is the seat of Söğüt District.İlçe Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 30 January 2023. Its population is 13,566 (2021). The mayor is İsmet Sever ( MHP), elected in 2019. Söğüt is notable as the founding location and first capital of the from 1281 to 1335. Name and etymology The name of the settlement is first attested under the ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osman I
Osman I or Osman Ghazi (; or ''Osman Gazi''; died 1323/4) was the eponymous founder of the Ottoman Empire (first known as a bey, beylik or emirate). While initially a small Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman principality during Osman's lifetime, his beylik transformed into a vast empire in the centuries after his death. It existed until 1922 shortly after the end of World War I, when the sultanate was abolished. Owing to the scarcity of historical sources dating from his lifetime, very little factual information about Osman has survived. Not a single written source survives from Osman's reign, and the Ottomans did not record the history of his life until the fifteenth century, more than a hundred years after his death. Because of this, historians find it very challenging to differentiate between fact and myth in the many stories told about him. One historian has even gone so far as to declare it impossible, describing the period of Osman's life as a "black hole". According to late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ertuğrul
Ertuğrul or Ertuğrul Ghazi (; died ) was a 13th-century uch bey (marcher-lord), who was the father of Osman I. Little is known about Ertuğrul's life. According to Ottoman Empire, Ottoman tradition, he was the son of Suleyman Shah, the leader of the Kayı (tribe), Kayı tribe (a claim which has come under criticism from many historians) of the Oghuz Turks (then known as Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkomans), which fled from western Central Asia to Anatolia to escape the Mongol conquests; but according to contemporary numinastic evidence, he was the son of Gündüz Alp. According to the legend, after the death of his father, Ertuğrul and his followers entered the service of the Sultanate of Rum, for which he was rewarded with dominion over the town of Söğüt on the frontier with the Byzantine Empire. This set off the chain of events that would ultimately lead to the Rise of the Ottoman Empire, founding of the Ottoman Empire. Biography Nothing is known with certainty about Ertuğrul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morea
Morea ( or ) was the name of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The name was used by the Principality of Achaea, the Byzantine province known as the Despotate of the Morea, by the Ottoman Empire for the Morea Eyalet, and later by the Republic of Venice for the short-lived Kingdom of the Morea. Etymology There is some uncertainty over the origin of the medieval name "Morea", which is first recorded in the 10th century in the Byzantine chronicles. Traditionally, scholars thought the name to have originated from the word ''morea'' (μορέα), meaning morus or mulberry, a tree which, though known in the region from the ancient times, gained value after the 6th century, when mulberry-eating silkworms were smuggled from China to Byzantium. The British Byzantinist Steven Runciman suggested that the name comes "from the likeness of its shape to that of a mulberry leaf". History After the conquest of Constantinople by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to the north and southwest, with a coast on the Adriatic Sea in the south. Bosnia (region), Bosnia has a moderate continental climate with hot summers and cold, snowy winters. Its geography is largely mountainous, particularly in the central and eastern regions, which are dominated by the Dinaric Alps. Herzegovina, the smaller, southern region, has a Mediterranean climate and is mostly mountainous. Sarajevo is the capital and the largest city. The area has been inhabited since at least the Upper Paleolithic, with permanent human settlement traced to the Neolithic cultures of Butmir culture, Butmir, Kakanj culture, Kakanj, and Vučedol culture, Vučedol. After the arrival of the first Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-Europeans, the area was populated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skopje
Skopje ( , ; ; , sq-definite, Shkupi) is the capital and largest city of North Macedonia. It lies in the northern part of the country, in the Skopje Basin, Skopje Valley along the Vardar River, and is the political, economic, and cultural center of the country. As of the 2021 North Macedonia census, 2021 census, the city had a population of 526,502. Skopje covers 571.46 km² and includes both urban and rural areas, bordered by several Municipalities of North Macedonia, municipalities and close to the borders of Kosovo and Serbia. The area of Skopje has been continuously inhabited since at least the Chalcolithic period. The city — known as ''Scupi'' at the time — was founded in the late 1st century during the rule of Domitian, and abandoned in 518 after an earthquake destroyed the city. It was rebuilt under Justinian I. It became a significant settlement under the First Bulgarian Empire, the Serbian Empire (when it served briefly as a capital), and later under the Otto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |