|
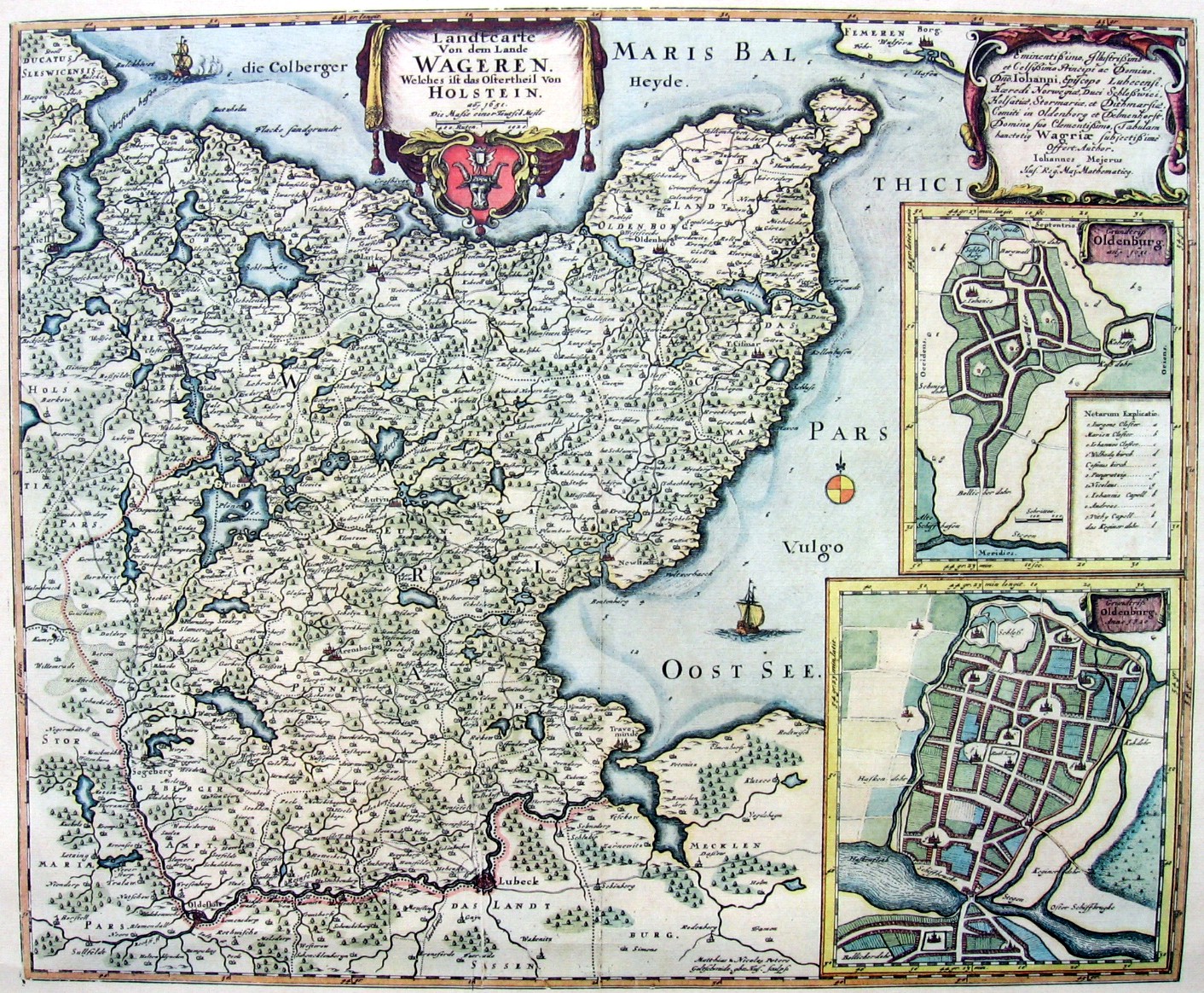
Utin Castle
Utin (in Latin letters VTIN - also "Uthine") was the name of a Wends, Wendish castle that was built in the 9th century on Pheasant Island (Eutin), Pheasant Island in the lake known as the Großer Eutiner See in what is now the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It was the centre of the eponymous Wendish ''Gau (region), Gau''. The castle was linked to the shore via a bridge next to which a settlement, also called Utin, grew up. The castle was destroyed by the Holcetae tribe when they conquered Wagria in 1138/39. The site of the settlement - which was the origin of the present-day town of Eutin - on the shore of the Großer Eutiner See, survived and retained the name "Utin" (also e.g. "Uthine") which over the course of time became "Eutin". The four letters "VTIN" became part of the coat of arms of the town of Eutin. Origin of the name The place name "Utin" is derived from the personal name ''Uta'' (or ''Uto'') - embellished by the suffix ''-in'' - and means "Uta's settleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutin - Fasaneninsel - Utin
Eutin () is the district capital of Ostholstein, Eastern Holstein county located in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein. As of December 2022, the town had some 17,000 inhabitants. History The name Eutin (originally Utin) is of Slavic origin. Its meaning is not quite clear; it is probably derived from the personal name "Uta". The Slavic Obotrites tribe settled eastern Holstein in the 7th/8th centuries A.D. and built a Utin (castle), castle on Pheasant Island (Eutin), Pheasant Island in the lake now called the Großer Eutiner See. The originally Slavonic settlement of ''Utin'' was populated in the twelfth century by Dutch settlers. In 1156 Eutin became a market town. Town rights were granted in the year 1257. It later became the seat of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck, as Lübeck itself was an imperial free city. When the bishopric was secularized in 1803, Eutin became part of the Duchy of Oldenburg. As a result of the Greater Hamburg Act of 1937, Eutin passed from the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wends
Wends is a historical name for Slavs who inhabited present-day northeast Germany. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people, tribes or groups depending on where and when it was used. In the modern day, communities identifying as Wendish exist in Slovenia, Austria, Lusatia, the United States (such as the Wends of Texas, Texas Wends), and in Australia. In German-speaking Europe during the Middle Ages, the term "Wends" was interpreted as synonymous with "Slavs" and sporadically used in literature to refer to West Slavs and South Slavs living within the Holy Roman Empire. The name has possibly survived in Finnic languages ( ; ; ), denoting modern Russia. Term According to one theory, Germanic peoples first applied this name to the Vistula Veneti, ancient Veneti. For the North Germanic peoples, medieval Scandinavians, the term Wends (''Vender'') meant Slavs living near the southern shore of the Baltic Sea (''Vendland''), and the term was therefore used to refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheasant Island (Eutin)
Pheasant Island () is one of the two islands in the south of the lake of Großer Eutiner See, which itself lies in the borough of in the district of in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. The island is about across. From the 9th century, Pheasant Island was the site of a Wends, Wendish castle which was given the name Utin (castle), Utin and was the centre of the eponymous . The castle was linked to the shore over a bridge. The castle was destroyed in 1138/39 by the Holsteiners during the conquest of Wagria. The subsequent settlement was built on the shore and developed into the present-day town of . Pheasant Island is one of the landmarks of the visual axes of the former Baroque garden of Eutin Castle. The name "Pheasant Island" is derived from the old pheasantry that used to exist on the island. Today, the island is privately owned and inhabited. References Bibliography * Otto Rönnpag: ''Die Fasaneninsel, der Ursprung Eutins''. In: ''Jahrbuch für Heimatkunde'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Großer Eutiner See
The Großer Eutiner See is a lake in Holstein Switzerland, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It lies northeast of the town of Eutin. It has an area of , is up to 17 metres deep and lies at a height of about . It northern side borders directly on the woods of the Seeschaarwald. In the western part of the lake, separated by the Bebensund Bridge, the Fissauer Bucht, its main inflow, the River Schwentine enters, and then leaves again a little further west. For boating enthusiasts the Schwentine is only navigable upstream as far as the Großer Eutiner See. There are two islands in the Großer Eutiner See: Pheasant Island (Eutin), Pheasant Island (''Fasaneninsel'') on which the origins of the settlement in that area are located, and which used to be a visual axis point for the former Baroque garden at Eutin Castle and which has been re-occupied today and is in private hands, and the so-called ''Liebesinsel'' ("Love Island"). Musicals take place during the summer in the castle garden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; ; ; ; ; occasionally in English ''Sleswick-Holsatia'') is the Northern Germany, northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg. It covers an area of , making it the 5th smallest German federal state by area (including the city-states). Historically, the name can also refer to a larger region, containing both present-day Schleswig-Holstein and the former South Jutland County (Northern Schleswig; now part of the Region of Southern Denmark) in Denmark. Schleswig, named South Jutland at the time, was under Danish control during the Viking Age, but in the 12th century it became a duchy within Denmark due to infighting in the Danish Royal House. It bordered Holstein, which was a part of the Holy Roman Empire. Beginning in 1460, the King of Denmark ruled both Schleswig and Holstein as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gau (region)
''Gau'' (German: ; ; or ) is a Germanic term for a region within a country, often a former or current province. It was used in the Middle Ages, when it can be seen as roughly corresponding to an English shire. The administrative use of the term was revived as a subdivision during the period of Nazi Germany in 1933–1945. It still appears today in regional names, such as the Rheingau or Allgäu. Middle Ages Etymology The Germanic word is reflected in Gothic ''gawi'' (neuter; genitive ''gaujis'') and early Old High German ''gewi, gowi'' (neuter) and in some compound names ''-gawi'' as in Gothic (e.g. ''Durgawi'' "Canton of Thurgau", ''Alpagawi'' "Allgäu"), later ''gâi, gôi'', and after loss of the stem suffix ''gaw, gao'', and with motion to the feminine as ''gawa'' besides ''gowo'' (from ''gowio''). Old Saxon shows further truncation to ''gâ, gô''. As an equivalent of Latin ''pagus'', a ''gau'' is analogous with a ''pays'' of the Kingdom of France, or of Lotharin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holcetae
Holstein (; ; ; ; ) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of Germany. Holstein once existed as the German County of Holstein (; 811–1474), the later Duchy of Holstein (; 1474–1866), and was the northernmost territory of the Holy Roman Empire. The history of Holstein is closely intertwined with the history of the Danish Duchy of Schleswig (). The capital of Holstein is Kiel. Holstein's name comes from the Holcetae, a Saxon tribe mentioned by Adam of Bremen as living on the north bank of the Elbe, to the west of Hamburg. The name means "dwellers in the wood" or "hill-sitters" (Northern Low Saxon: ; ). History Origins After the Migration Period of the Early Middle Ages, Holstein was adjacent to the Obotrites on the coast of the Baltic Sea and the land of the Danes in Jutland. With the conquest of Old Saxony by Charlemagne ''circa'' 800, he granted the land north of the Eider River (Schleswig) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wagria
WagriaArnold, Benjamin (1991). ''Princes and territories in medieval Germany'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York, p. 156. . (, ''Waierland'' or ''Wagerland'') is the northeastern part of Holstein in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein, corresponding roughly to the districts of Plön and Ostholstein. The word "Wagria" is derived from the Slavic Lechites tribe of Wagri. Geography In the Middle Ages, and as still shown on early modern maps, Wagria was bordered on the north and east by the Baltic Sea from the Kiel Fjord to Lübeck Bay, and inland by the rivers Schwentine and Trave. Today, Wagria generally refers just to the Oldenburg Peninsula (''Oldenburgische Halbinsel'') in Ostholstein. The highest elevation in the peninsula is the Bungsberg at 168 metres. History The Lechitic (Slavic) root of the name, ''Wagria'', meant not only the so-called, present-day Wagrian peninsula, but the entire region between the Kiel Fjord, the middle reaches of the Trav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutin
Eutin () is the district capital of Ostholstein, Eastern Holstein county located in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein. As of December 2022, the town had some 17,000 inhabitants. History The name Eutin (originally Utin) is of Slavic origin. Its meaning is not quite clear; it is probably derived from the personal name "Uta". The Slavic Obotrites tribe settled eastern Holstein in the 7th/8th centuries A.D. and built a Utin (castle), castle on Pheasant Island (Eutin), Pheasant Island in the lake now called the Großer Eutiner See. The originally Slavonic settlement of ''Utin'' was populated in the twelfth century by Dutch settlers. In 1156 Eutin became a market town. Town rights were granted in the year 1257. It later became the seat of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck, as Lübeck itself was an imperial free city. When the bishopric was secularized in 1803, Eutin became part of the Duchy of Oldenburg. As a result of the Greater Hamburg Act of 1937, Eutin passed from the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full achievement (heraldry), heraldic achievement, which in its whole consists of a shield, supporters, a crest (heraldry), crest, and a motto. A coat of arms is traditionally unique to the armiger (e.g. an individual person, family, state, organization, school or corporation). The term "coat of arms" itself, describing in modern times just the heraldic design, originates from the description of the entire medieval chainmail "surcoat" garment used in combat or preparation for the latter. Roll of arms, Rolls of arms are collections of many coats of arms, and since the early Modern Age centuries, they have been a source of information for public showing and tracing the membership of a nobility, noble family, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEU Eutin COA , a state university located in Izmir, Turkey
{{disambiguation ...
DEU may refer to: *Deutsche Eislauf-Union, the figure skating governing body in Germany *''Diccionario del español del Uruguay'', the Dictionary of Uruguayan Spanish *Distinctive environmental uniform, the current uniform of the Canadian Forces, adopted in the late 1980s *Doom Editing Utility, a software utility for the computer game Doom * The ISO 3166-1 alpha-3 country code for Germany (German ''Deutschland'') * The ISO 639-2 (T) and ISO 639-3 code for Standard German * Drug Enforcement Unit, a specialised police unit *Dokuz Eylül University Dokuz Eylül University () (DEÜ) is a Public university, public research university in İzmir, Turkey. Founded in 1982, it is organized into 18 faculties. It holds the distinction of being the first university in Turkey to implement the probl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Germany
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |