|
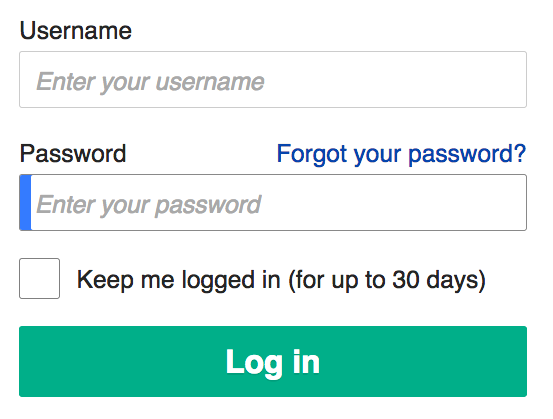
Username
A user is a person who uses a computer or Computer network, network Service (systems architecture), service. A user often has a user account and is identified to the system by a username (or user name). Some software products provide services to other systems and have no direct end users. End user End users are the ultimate human users (also referred to as Operator (profession), operators) of a software product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product such as sysops, database administrators and computer technicians. The term is used to abstract and distinguish those who only use the software from the developers of the system, who enhance the software for end users. In user-centered design, it also distinguishes the software operator from the client who pays for its development and other Stakeholder (corporate), stakeholders who may not directly use the software, but help establish its Software requirements, requirements. This abstracti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Changing Username
A user is a person who uses a computer or network service. A user often has a user account and is identified to the system by a username (or user name). Some software products provide services to other systems and have no direct end users. End user End users are the ultimate human users (also referred to as operators) of a software product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product such as sysops, database administrators and computer technicians. The term is used to abstract and distinguish those who only use the software from the developers of the system, who enhance the software for end users. In user-centered design, it also distinguishes the software operator from the client who pays for its development and other stakeholders who may not directly use the software, but help establish its requirements. This abstraction is primarily useful in designing the user interface, and refers to a relevant subset of characteristics that most exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Icon 2 , a user of a commercial product or service
{{disambiguation ...
Ancient Egyptian roles * User (ancient Egyptian official), an ancient Egyptian nomarch (governor) of the Eighth Dynasty * Useramen, an ancient Egyptian vizier also called "User" Other uses * User (computing), a person (or software) using an information system * User (telecommunications), an entity using a telecommunications system See also * Drug user (other), a person who uses drugs * End user In product development, an end user (sometimes end-user) is a person who ultimately uses or is intended to ultimately use a product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product, such as sysops, system administrato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Password
A password, sometimes called a passcode, is secret data, typically a string of characters, usually used to confirm a user's identity. Traditionally, passwords were expected to be memorized, but the large number of password-protected services that a typical individual accesses can make memorization of unique passwords for each service impractical. Using the terminology of the NIST Digital Identity Guidelines, the secret is held by a party called the ''claimant'' while the party verifying the identity of the claimant is called the ''verifier''. When the claimant successfully demonstrates knowledge of the password to the verifier through an established authentication protocol, the verifier is able to infer the claimant's identity. In general, a password is an arbitrary String (computer science), string of character (computing), characters including letters, digits, or other symbols. If the permissible characters are constrained to be numeric, the corresponding secret is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Management
In organizational studies, resource management is the efficient and effective development of an organization's resources when they are needed. Such resources may include the financial resources, inventory, human skills, production resources, or information technology (IT) and natural resources. In the realm of project management, processes, techniques and philosophies as to the best approach for allocating resources have been developed. These include discussions on functional vs. cross-functional resource allocation as well as processes espoused by organizations like the Project Management Institute (PMI) through their Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) methodology of project management. Resource management is a key element to activity resource estimating and project human resource management. Both are essential components of a comprehensive project management plan to execute and monitor a project successfully. As is the case with the larger discipline of project mana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Security
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and computer network, networks from Threat (security), threats that can lead to unauthorized information disclosure, theft or damage to computer hardware, hardware, software, or Data (computing), data, as well as from the disruption or misdirection of the Service (economics), services they provide. The significance of the field stems from the expanded reliance on computer systems, the Internet, and wireless network standards. Its importance is further amplified by the growth of smart devices, including smartphones, televisions, and the various devices that constitute the Internet of things (IoT). Cybersecurity has emerged as one of the most significant new challenges facing the contemporary world, due to both the complexity of information systems and the societi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accounting
Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the process of recording and processing information about economic entity, economic entities, such as businesses and corporations. Accounting measures the results of an organization's economic activities and conveys this information to a variety of stakeholders, including investors, creditors, management, and Regulatory agency, regulators. Practitioners of accounting are known as accountants. The terms "accounting" and "financial reporting" are often used interchangeably. Accounting can be divided into several fields including financial accounting, management accounting, tax accounting and cost accounting. Financial accounting focuses on the reporting of an organization's financial information, including the preparation of financial statements, to the external users of the information, such as investors, regulators and suppliers. Management accounting focuses on the measurement, analysis and reporting of information for internal use by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Credentials
A credential is a piece of any document that details a qualification, competence, or authority issued to an individual by a third party with a relevant or '' de facto'' authority or assumed competence to do so. Examples of credentials include academic diplomas, academic degrees, certifications, security clearances, identification documents, badges, passwords, user names, keys, powers of attorney, and so on. Sometimes publications, such as scientific papers or books, may be viewed as similar to credentials by some people, especially if the publication was peer reviewed or made in a well-known journal or reputable publisher. Types and documentation of credentials A person holding a credential is usually given documentation or secret knowledge (''e.g.,'' a password or key) as proof of the credential. Sometimes this proof (or a copy of it) is held by a third, trusted party. While in some cases a credential may be as simple as a paper membership card, in other cases, such as di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authenticate
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an assertion, such as the identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicating a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of verifying that identity. Authentication is relevant to multiple fields. In art, antiques, and anthropology, a common problem is verifying that a given artifact was produced by a certain person, or in a certain place (i.e. to assert that it is not counterfeit), or in a given period of history (e.g. by determining the age via carbon dating). In computer science, verifying a user's identity is often required to allow access to confidential data or systems. It might involve validating personal identity documents. In art, antiques and anthropology Authentication can be considered to be of three types: The ''first'' type of authentication is accepting proof of identity given by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Access Control
In physical security and information security, access control (AC) is the action of deciding whether a subject should be granted or denied access to an object (for example, a place or a resource). The act of ''accessing'' may mean consuming, entering, or using. It is often used interchangeably with authorization, although the authorization may be granted well in advance of the access control decision. Access control on digital platforms is also termed admission control. The protection of external databases is essential to preserve digital security. Access control is considered to be a significant aspect of privacy that should be further studied. Access control policy (also access policy) is part of an organization’s security policy. In order to verify the access control policy, organizations use an access control model. General security policies require designing or selecting appropriate security controls to satisfy an organization's risk appetite - access policies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authorization
Authorization or authorisation (see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), spelling differences), in information security, computer security and identity management, IAM (Identity and Access Management), is the function of specifying rights/privileges for accessing resources, in most cases through an access policy, and then deciding whether a particular ''subject'' has privilege to access a particular ''resource''. Examples of ''subjects'' include human users, computer software and other Computer hardware, hardware on the computer. Examples of ''resources'' include individual files or an item's data, computer programs, computer Computer hardware, devices and functionality provided by computer applications. For example, user accounts for human resources staff are typically configured with authorization for accessing employee records. Authorization is closely related to access control, which is what enforces the authorization policy by d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an Logical assertion, assertion, such as the Digital identity, identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicating a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of verifying that identity. Authentication is relevant to multiple fields. In art, antiques, and anthropology, a common problem is verifying that a given artifact was produced by a certain person, or in a certain place (i.e. to assert that it is not counterfeit), or in a given period of history (e.g. by determining the age via carbon dating). In computer science, verifying a user's identity is often required to allow access to confidential data or systems. It might involve validating personal identity documents. In art, antiques and anthropology Authentication can be considered to be of three types: The ''first'' type of authentication is accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |