|
Urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the cellular metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. ''Urea'' is Neo-Latin, , , itself from Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂worsom''. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor base (chemistry), alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably metabolic waste#Nitrogen wastes, nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbamide Peroxide
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the cellular metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. ''Urea'' is Neo-Latin, , , itself from Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂worsom''. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important raw material for the chemical industry. In 1828, Friedr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea Cycle
The urea cycle (also known as the ornithine cycle) is a cycle of biochemical reactions that produces urea (NH2)2CO from ammonia (NH3). Animals that use this cycle, mainly amphibians and mammals, are called ureotelic. The urea cycle converts highly toxic ammonia to urea for excretion. This cycle was the first metabolic cycle to be discovered by Hans Krebs and Kurt Henseleit in 1932, five years before the discovery of the TCA cycle. The urea cycle was described in more detail later on by Ratner and Cohen. The urea cycle takes place primarily in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the kidneys. Function Amino acid catabolism results in waste ammonia. All animals need a way to excrete this product. Most aquatic organisms, or ammonotelic organisms, excrete ammonia without converting it. Organisms that cannot easily and safely remove nitrogen as ammonia convert it to a less toxic substance, such as urea, via the urea cycle, which occurs mainly in the liver. Urea produced by the li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea Phosphate
Urea phosphate is a 1:1 combination of urea and phosphoric acid that is used as a fertilizer. It has an NPK formula of 17-44-0, and is soluble in water, producing a strongly acidic solution. Urea phosphate is available in fertilizer vendor bags that carry a ''UP'' signet on the packaging. It is sometimes added to blends which contain calcium nitrate, magnesium nitrate and potassium nitrate to produce water-soluble formulas such as 15-5-15 and 13-2-20. The acidity of urea phosphate allows Ca, Mg and P to co-exist in solution. Under less acidic conditions, there would be precipitation of Ca–Mg phosphates. Urea phosphate is often used in drip irrigation to clean pipe systems. The phosphoric acid and urea molecules in the urea phosphate crystal structure form a complex hydrogen-bonding network, with the hydrogen atoms bonding more strongly to urea molecules. It freely dissociates when dissolved in water. Urea phosphate is produced as a non-ionic adduct In chemistry, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) with occasional addition of supplements like rock flour for micronutrients. Farmers apply these fertilizers in a variety of ways: through dry or pelletized or liquid application processes, using large agricultural equipment, or hand-tool methods. Historically, fertilization came from natural or organic sources: compost, animal manure, human manure, harvested minerals, crop rotations, and byproducts of human-nature industries (e.g. fish processing waste, or bloodmeal from animal slaughter). However, starting in the 19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Waste
Metabolic wastes or excrements are substances left over from metabolic processes (such as cellular respiration) which cannot be used by the organism (they are surplus or toxic), and must therefore be excreted. This includes nitrogen compounds, water, CO2, phosphates, sulphates, etc. Animals treat these compounds as excretes. Plants have metabolic pathways which transforms some of them (primarily the oxygen compounds) into useful substances. All the metabolic wastes are excreted in a form of water solutes through the excretory organs ( nephridia, Malpighian tubules, kidneys), with the exception of CO2, which is excreted together with the water vapor throughout the lungs. The elimination of these compounds enables the chemical homeostasis of the organism. Nitrogen wastes The nitrogen compounds through which excess nitrogen is eliminated from organisms are called nitrogenous wastes () or nitrogen wastes. They are ammonia, urea, uric acid, and creatinine. All of these subst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
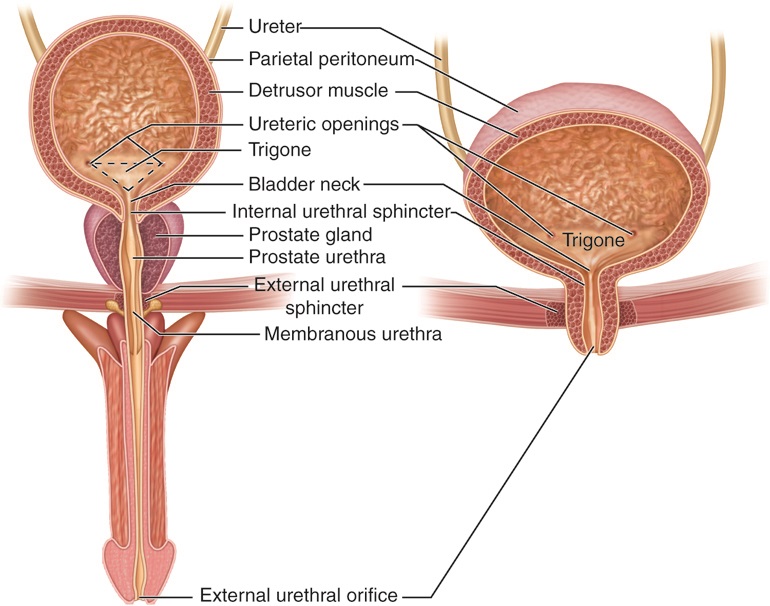
Urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (males) or urethral meatus of the vulva (females) during urination. In other vertebrates, urine is excreted through the cloaca. Urine contains water-soluble by-products of Cell (biology), cellular metabolism that are rich in nitrogen and must be clearance (medicine), cleared from the Circulatory system, bloodstream, such as urea, uric acid and creatinine. A urinalysis can detect nitrogenous wastes of the mammalian body. Urine plays an important role in the earth's nitrogen cycle. In balanced ecosystems, urine fertilizes the soil and thus helps plants to grow. Therefore, Reuse of excreta, urine can be used as a fertilizer. Some animals use it to territory (animal)#Scent marking, mark their territories. Historically, aged or fermented urine (kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbamic Acid
Carbamic acid, which might also be called aminoformic acid or aminocarboxylic acid, is the chemical compound with the formula . It can be obtained by the reaction of ammonia and carbon dioxide at very low temperatures, which also yields ammonium carbamate . The compound is stable only up to about 250 K (−23 °C); at higher temperatures it decomposes into those two gases. The solid apparently consists of dimer (chemistry), dimers, with the two molecules connected by hydrogen bonds between the two carboxyl groups –COOH.J. B. Bossa, P. Theulé, F. Duvernay, F. Borget and T. Chiavassa (2008): "Carbamic acid and carbamate formation in NH3:CO2 ices – UV irradiation versus thermal processes". ''Astronomy and Astrophysics'', volume 492, issue 3, pages 719-724. Carbamic acid could be seen as both an amine and carboxylic acid, and therefore an amino acid;R. K. Khanna and M. H. Moore (1999): "Carbamic acid: molecular structure and IR spectra". ''Spectrochimica Acta Part A: M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxycarbamide
Hydroxycarbamide, also known as hydroxyurea, is an antimetabolite medication used in sickle-cell disease, essential thrombocythemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, polycythemia vera, and cervical cancer. In sickle-cell disease it increases fetal hemoglobin and decreases the number of attacks. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, fevers, loss of appetite, psychiatric problems, shortness of breath, and headaches. There is also concern that it increases the risk of later cancers. Use during pregnancy is typically harmful to the fetus. Hydroxycarbamide is in the antineoplastic family of medications. It is believed to work by blocking the making of DNA. Hydroxycarbamide was approved for medical use in the United States in 1967. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Hydroxycarbamide is available as a generic medication. Medical uses Hydroxycarbamide is used for the following indications: * Myeloprolifera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl Fluoride
Carbonyl fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a carbon oxohalide. This gas, like its analog phosgene, is colourless and highly toxic. The molecule is planar with ''C''2v symmetry, bond lengths of 1.174 Å (C=O) and 1.312 Å (C–F), and an F–C–F bond angle of 108.0°. Preparation and properties Carbonyl fluoride is usually produced as a decomposition product of fluorinated hydrocarbons in the thermal decomposition thereof, for example from trifluoromethanol or tetrafluoromethane in the presence of water: : Carbonyl fluoride can also be prepared by reaction of phosgene with hydrogen fluoride and the fluorination of carbon monoxide, although the latter tends to result in over-fluorination to carbon tetrafluoride. The fluorination of carbon monoxide with silver difluoride is convenient: : Carbonyl fluoride is unstable in the presence of water, hydrolyzing to carbon dioxide and hydrogen fluoride Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an Inorganic chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone) is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly Volatile organic compound, volatile, and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odor. Acetone is miscibility, miscible with properties of water, water and serves as an important organic solvent in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and for production of methyl methacrylate and bisphenol A, which are precursors to widely used plastics.Acetone World Petrochemicals report, January 2010Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. It is a common building block in organic chemistry. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |