|
Upper Motor Neuron Syndrome
Upper motor neuron syndrome (UMNS) is the motor control changes that can occur in skeletal muscle after an upper motor neuron lesion. Following upper motor neuron lesions, affected muscles potentially have many features of altered performance including: *weakness (decreased ability for the muscle to generate force) *decreased motor control including decreased speed, accuracy and dexterity *altered muscle tone (hypotonia or hypertonia) – a decrease or increase in the baseline level of muscle activity *decreased endurance *exaggerated deep tendon reflexes including spasticity, and clonus (a series of involuntary rapid muscle contractions) Such signs are collectively termed the "upper motor neuron syndrome". Affected muscles typically show multiple signs, with severity depending on the degree of damage and other factors that influence motor control. In neuroanatomical circles, it is often joked, for example, that hemisection of the cervical spinal cord leads to an "upper lower mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Control
Motor control is the regulation of movements in organisms that possess a nervous system. Motor control includes conscious voluntary movements, subconscious muscle memory and involuntary reflexes, as well as instinctual taxes. To control movement, the nervous system must integrate multimodal sensory information (both from the external world as well as proprioception) and elicit the necessary signals to recruit muscles to carry out a goal. This pathway spans many disciplines, including multisensory integration, signal processing, coordination, biomechanics, and cognition, and the computational challenges are often discussed under the term sensorimotor control. Successful motor control is crucial to interacting with the world to carry out goals as well as for posture, balance, and stability. Some researchers (mostly neuroscientists studying movement, such as Daniel Wolpert and Randy Flanagan) argue that motor control is the reason brains exist at all. Neural control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of stroke may include an hemiplegia, inability to move or feel on one side of the body, receptive aphasia, problems understanding or expressive aphasia, speaking, dizziness, or homonymous hemianopsia, loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than 24 hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. subarachnoid hemorrhage, Hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a thunderclap headache, severe headache. The symptoms of stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and Urinary incontinence, loss of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baclofen
Baclofen, sold under the brand name Lioresal among others, is a medication used to treat muscle spasticity, such as from a spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis. It may also be used for hiccups and muscle spasms near the end of life, and off-label to treat alcohol use disorder or opioid withdrawal symptoms. It is taken orally or by intrathecal pump (delivered into the spinal canal via an implantable pump device). It is sometimes used transdermally (applied topically to the skin) in combination with gabapentin and clonidine prepared at a compounding pharmacy. It is believed to work by decreasing levels of certain neurotransmitters. Baclofen should be avoided in the setting of chronic kidney disease and end stage renal disease as even small doses can cause excessive toxicity. Common side effects include sleepiness, weakness, and dizziness. Serious side effects, such as seizures and rhabdomyolysis, may occur if use of baclofen is stopped abruptly. Use during pregn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Stimulation
Functional electrical stimulation (FES) is a technique that uses low-energy electrical pulses to artificially generate body movements in individuals who have been paralyzed due to injury to the central nervous system. More specifically, FES can be used to generate muscle contraction in otherwise paralyzed limbs to produce functions such as grasping, walking, bladder voiding and standing. This technology was originally used to develop neuroprostheses that were implemented to permanently substitute impaired functions in individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI), head injury, stroke and other neurological disorders. In other words, a person would use the device each time he or she wanted to generate a desired function.M.R. Popovic, K. Masani and S. Micera, "Chapter 9 – Functional Electrical Stimulation Therapy: Recovery of function following spinal cord injury and stroke," In press, Neurorehabilitation Technology – Second Edition, Z. Rymer, T. Nef and V. Dietz, Ed. Springer Sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
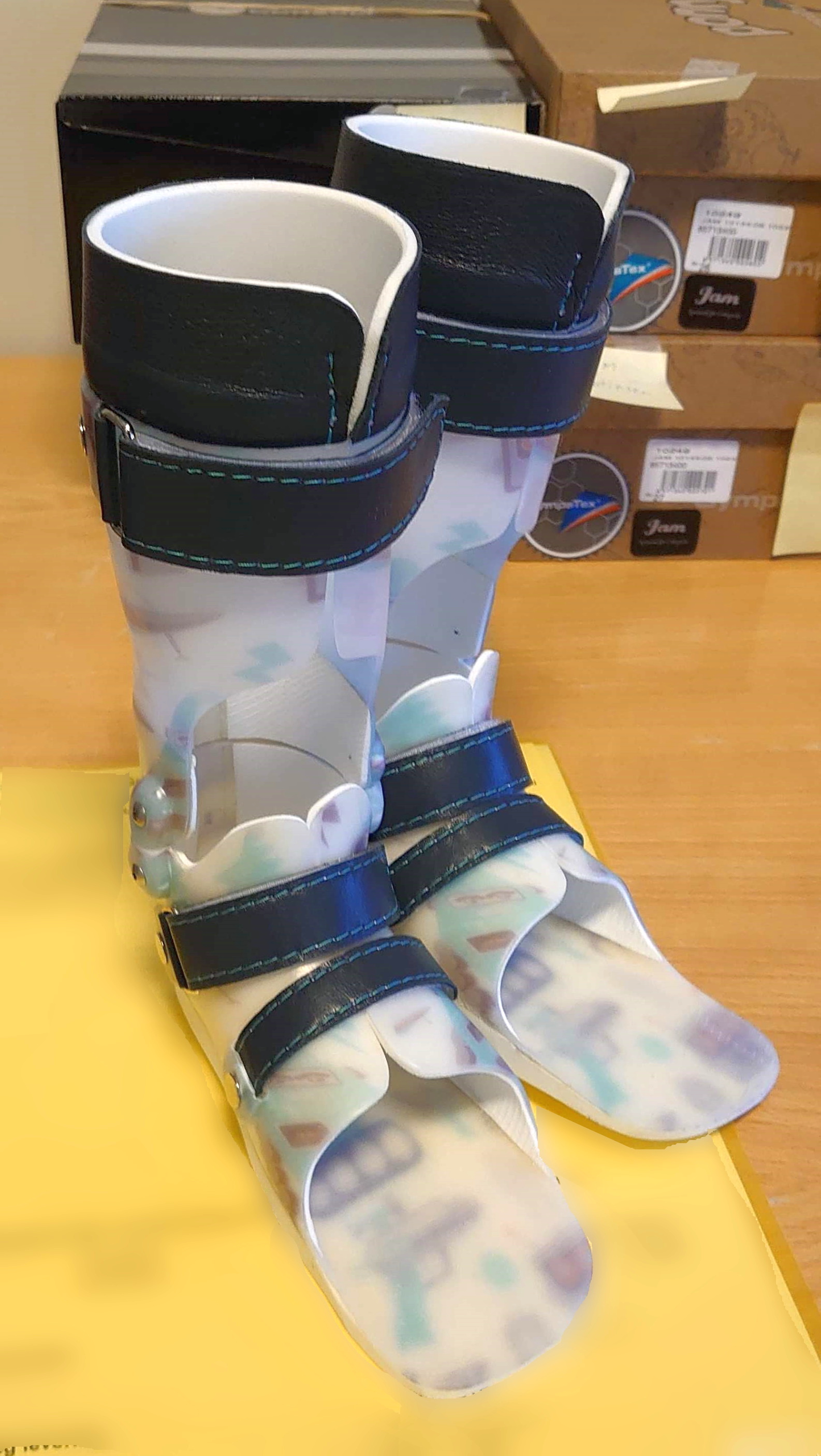
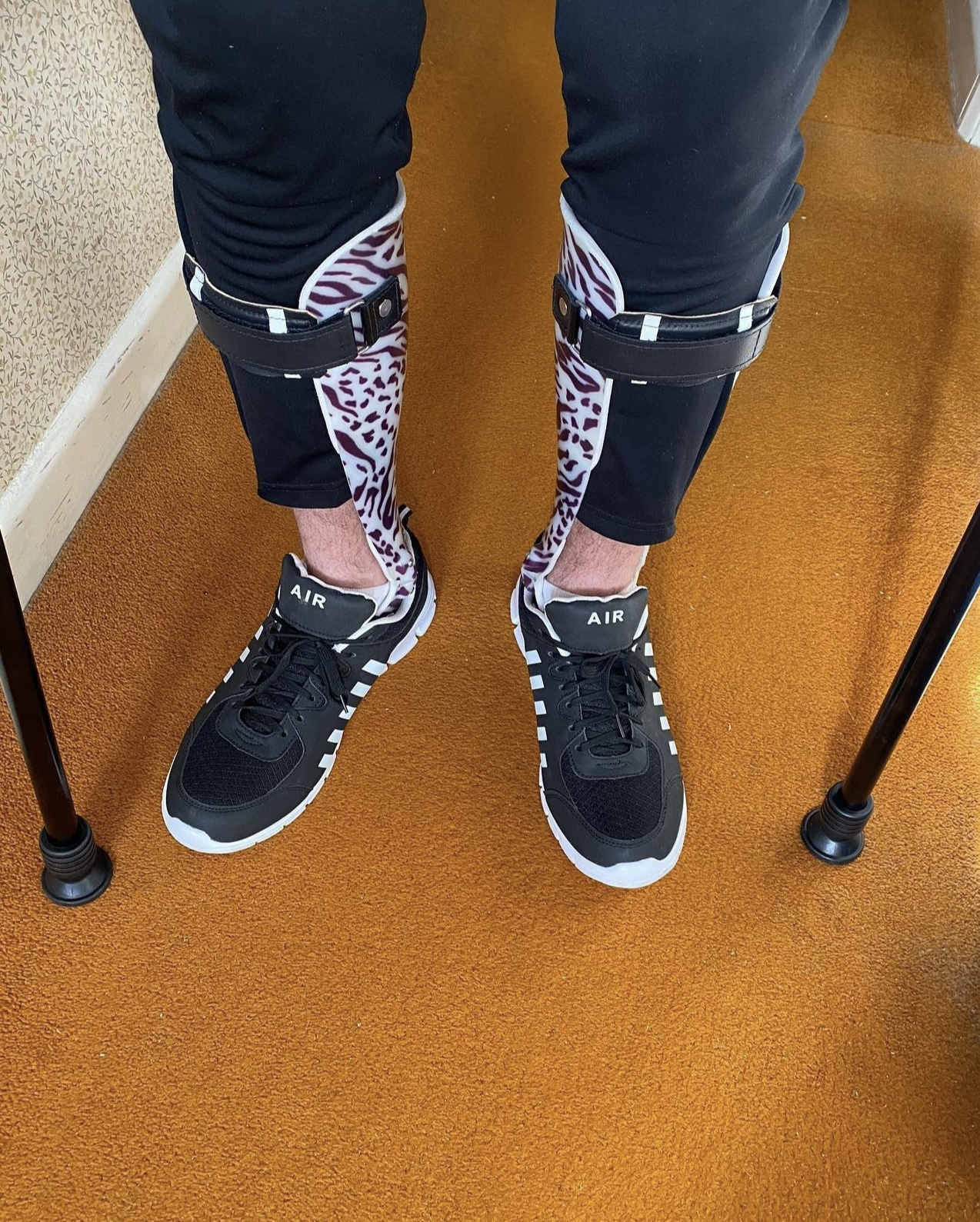
Orthotics
Orthotics () is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, sometimes known as braces, calipers, or splints. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functional characteristics of the neuromuscular and skeletal systems." Orthotists are medical professionals who specialize in designing orthotic devices such as braces or foot orthoses. Classification Orthotic devices are classified into four areas of the body according to the international classification system (ICS): orthotics of the lower extremities, orthotics of the upper extremities, orthotics for the trunk, and orthotics for the head. Orthoses are also classified by function: paralysis orthoses and relief orthoses. Under the International Standard terminology, orthoses are classified by an acronym describing the anatomical joints they support. Some examples include KAFO, or knee-ankle-foot orthoses, which span the knee, ankle, and foot; TLSO, or thor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Therapist
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease prevention, and health promotion. Physical therapist is the term used for such professionals in the United States, and physiotherapist is the term used in many other countries. The career has many specialties including musculoskeletal, orthopedics, cardiopulmonary, neurology, endocrinology, sports medicine, geriatrics, pediatrics, women's health, wound care and electromyography. PTs practice in many settings, both public and private. In addition to clinical practice, other aspects of physical therapy practice include research, education, consultation, and health administration. Physical therapy is provided as a primary care treatment or alongside, or in conjunction with, other medical services. In some jurisdictions, such as the United Kingdom, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contracture
In pathology, a contracture is a shortening of muscles, tendons, skin, and nearby soft tissues that causes the joints to shorten and become very stiff, preventing normal movement. A contracture is usually permanent, but less commonly can be temporary (such as in McArdle disease), or resolve over time but reoccur later in life (such as in Bethlem myopathy 1). It is usually in response to prolonged hypertonic spasticity in a concentrated muscle area, such as is seen in the tightest muscles of people with conditions like spastic cerebral palsy, but can also be due to the congenital abnormal development of muscles and connective tissue in the womb. Contractures develop usually when normally elastic tissues such as muscles or tendons are replaced by inelastic tissues ( fibrosis). This results in the shortening and hardening of these tissues, ultimately causing rigidity, joint deformities and a total loss of movement around the joint. Most of the physical therapy, occupational th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Fibres
A muscle cell, also known as a myocyte, is a mature contractile cell in the muscle of an animal. In humans and other vertebrates there are three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac (cardiomyocytes). A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a ''muscle fiber''. Muscle cells develop from embryonic precursor cells called myoblasts. Skeletal muscle cells form by fusion of myoblasts to produce multinucleated cells (syncytia) in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells both contain myofibrils and sarcomeres and form a striated muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle cells form the cardiac muscle in the walls of the heart chambers, and have a single central nucleus. Cardiac muscle cells are joined to neighboring cells by intercalated discs, and when joined in a visible unit they are described as a ''cardiac muscle fiber''. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stiffness
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force. The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is. Calculations The stiffness, k, of a body is a measure of the resistance offered by an elastic body to deformation. For an elastic body with a single degree of freedom (DOF) (for example, stretching or compression of a rod), the stiffness is defined as k = \frac where, * F is the force on the body * \delta is the displacement produced by the force along the same degree of freedom (for instance, the change in length of a stretched spring) Stiffness is usually defined under quasi-static conditions, but sometimes under dynamic loading. In the International System of Units, stiffness is typically measured in newtons per meter (N/m). In Imperial units, stiffness is typically measured in pounds (lbs) per inch. Generally speaking, deflections (or motions) of an infinitesima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupational Therapists
Occupational therapists (OTs) are health care professionals specializing in occupational therapy and occupational science. OTs and occupational therapy assistants (OTAs) use scientific bases and a holistic perspective to promote a person's ability to fulfill their daily routines and roles. OTs have training in the physical, psychological, and social aspects of human functioning deriving from an education grounded in anatomical and physiological concepts, and psychological perspectives. They enable individuals across the lifespan by optimizing their abilities to perform activities that are meaningful to them ("occupations"). Human occupations include activities of daily living, work/vocation, play, education, leisure, rest and sleep, and social participation. OTs work in a variety of fields, including pediatrics, orthopedics, neurology, low vision therapy, physical rehabilitation, mental health, assistive technology, oncological rehabilitation, and geriatrics. OTs are employed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthotists
An orthotist is a healthcare professional who specializes in the provision of Orthotics, orthoses. An orthotist has an overall responsibly of orthotics treatment, who can supervise and mentor the practice of other personnel. They are clinicians trained to assess the needs of the user, prescribe treatment, determine the precise technical specifications of orthotic devices, take measurements and image of body segments, prepare model of the evaluation, fit devices and evaluate treatment outcome. In the United States, orthotists work by prescription from a licensed healthcare provider. Physical therapists are not legally authorized to prescribe orthoses in the U.S. In the U.K., orthotists will often accept open referrals for orthotic assessment without a specific prescription from doctors or other healthcare professionals. Scope The scope of an orthotist includes the design and application of Orthotics, orthoses (braces or Orthotics, orthotic devices). The definition of an orthosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |