|
Untouchability
Untouchability is a form of social institution that legitimises and enforces practices that are discriminatory, humiliating, exclusionary and exploitative against people belonging to certain social groups. Although comparable forms of discrimination are found all over the world, untouchability involving the Caste system in India, caste system is largely unique to South Asia. The term is most commonly associated with treatment of the Dalit communities in the Indian subcontinent who were considered "polluting". The term has also been used to refer to other groups, including the ''Burakumin'' of Japan, the Baekjeong of Korea, and the Social class in Tibet#Ragyabpa, Ragyabpa of Tibet, as well as the Romani people and Cagot in Europe, and the Al-Akhdam in Yemen. Traditionally, the groups characterized as untouchable were those whose occupations and habits of life involved ritually "polluting" activities, such as pursuing a career based on killing (e.g. fishermen) or engaging in commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalit
Dalit ( from meaning "broken/scattered") is a term used for untouchables and outcasts, who represented the lowest stratum of the castes in the Indian subcontinent. They are also called Harijans. Dalits were excluded from the fourfold varna of the caste hierarchy and were seen as forming a fifth varna, also known by the name of ''Panchama''. Several scholars have drawn parallels between Dalits and the '' Burakumin'' of Japan, the '' Baekjeong'' of Korea and the peasant class of the medieval European feudal system. Dalits predominantly follow Hinduism with significant populations following Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, and Islam. The constitution of India includes Dalits as one of the Scheduled Castes; this gives Dalits the right to protection, positive discrimination (known as reservation in India), and official development resources. Terminology The term ''Dalit'' is for those called the "untouchables" and others that were outside of the traditional Hindu caste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
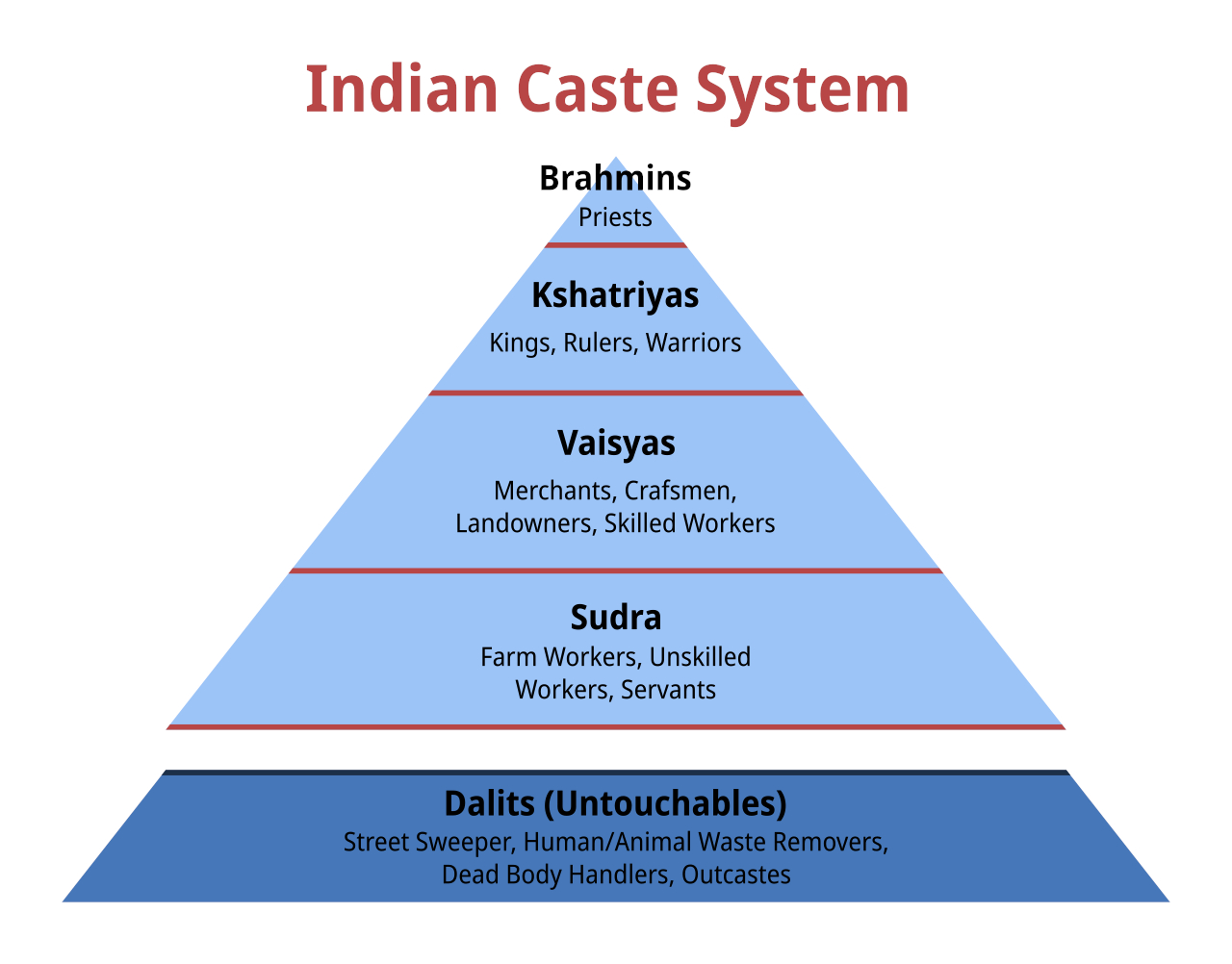
Caste System In India
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic instance of social classification based on castes. It has its origins in ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval, early-modern, and modern India, especially in the aftermath of the collapse of the Mughal Empire and the establishment of the British Raj. Beginning in ancient India, the caste system was originally centered around '' varna'', with ''Brahmins'' (priests) and, to a lesser extent, ''Kshatriyas'' (rulers and warriors) serving as the elite classes, followed by '' Vaishyas'' (traders, merchants, and farmers) and finally '' Shudras'' (labourers). Outside of this system are the oppressed, marginalised, and persecuted '' Dalits'' (also known as " Untouchables") and '' Adivasis'' (tribals). Over time, the system became increasingly rigid, and the emergence of '' jati'' led to further entrenchment, introducing thousands of new castes and sub-castes. With the arrival of Islamic rule, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
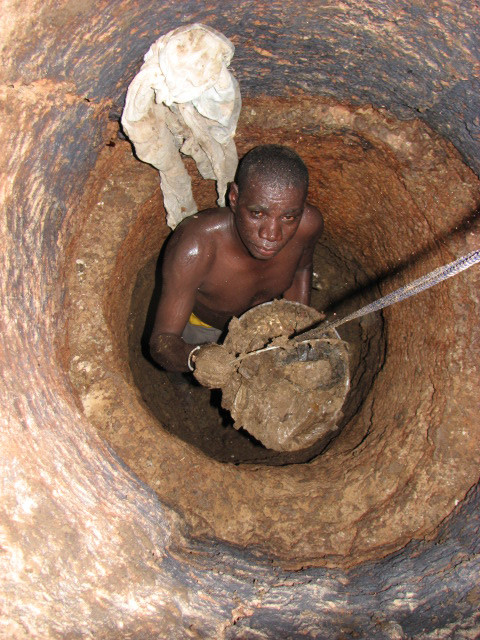
Manual Scavenging
Manual scavenging is a term used mainly in India for "manually cleaning, carrying, disposing of, or otherwise handling, human excreta in an insanitary latrine or in an open drain or sewer or in a septic tank or a pit". Manual scavengers usually use hand tools such as buckets, brooms and shovels. The workers have to move the excreta, using brooms and tin plates, into baskets, which they carry to disposal locations sometimes several kilometers away. The practice of employing human labour for cleaning of sewers and septic tanks is also prevalent in Bangladesh and Pakistan. These sanitation workers, called "manual scavengers", rarely have any personal protective equipment. The work is regarded as a dehumanizing practice. The occupation of sanitation work is intrinsically linked with caste in India. All kinds of cleaning are considered lowly and are assigned to people from the lowest rung of the social hierarchy. In the caste-based society, it is mainly the Dalits who work as sanitati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caste System In Nepal
The Nepalese caste system is the traditional system of social stratification of Nepal. The Nepalese caste system broadly borrows the classical Hindu ''Chaturvarnashram'' model, consisting of four broad social classes or varna: Brahmin, Kshatriya, Vaishya, Sudra. The caste system defines social classes by a number of hierarchical endogamous groups often termed ''jaat''. This custom was traditionally only prevalent in the three Indo Aryan societies of the Khas, Madhesi, and Newars. However, since the unification of Nepal in the 18th century, Nepal's various non-Hindu ethnic nationalities and tribes, previously called "Matwalis" (alcohol-drinkers) and now termed as "Adivasi/Janajati" (indigenous/nationalities), have been incorporated within the caste hierarchy to varying degrees of success. Despite the forceful integration by the state into the pan-Hindu social structure, the traditionally non-Hindu groups and tribes do not necessarily adhere to the customs and practices of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varna (Hinduism)
Varna (, ), in the context of Hinduism, refers to a social class within a hierarchical traditional Hindu society. The ideology of varna is epitomized in texts like '' Manusmriti'', which describes and ranks four varnas, and prescribes their occupations, requirements and duties, or '' Dharma''. *Brahmins: Vedic scholars, priests or teachers. * Kshatriyas: Rulers, administrators or warriors. * Vaishyas: Agriculturalists, farmers or merchants. * Shudras: Artisans, labourers or servants. This quadruple division is a form of social stratification, quite different from the more nuanced system of '' Jātis'', which correspond to the term "caste". The varna system is discussed in Hindu texts, and understood as idealised human callings. The concept is generally traced back to the '' Purusha Sukta'' verse of the Rigveda. In the post- Vedic period, the varna division is described in the '' Mahabharata,'' ''Puranas'' and in the '' Dharmashastra literatures''. The commentary on the Varna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China China–Nepal border, to the north, and India India–Nepal border, to the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a Geography of Nepal, diverse geography, including Terai, fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten List of highest mountains#List, tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and List of cities in Nepal, its largest city. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious, and multi-cultural state, with Nepali language, Nepali as the official language. The name "Nepal" is first record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burakumin
The are a social grouping of Japanese people descended from members of the feudal class associated with , mainly those with occupations related to death such as executioners, gravediggers, slaughterhouse workers, butchers, and tanners. Burakumin are physically indistinguishable from other Japanese but have historically been regarded as a socially distinct group. When identified, they are often subject to discrimination and prejudice. , there were an estimated 3 million ''burakumin'' living in the country, mostly in western Japan. During Japan's feudal era, these occupations acquired a hereditary status of oppression, and later became a formal class within the class system of the Edo period (1603–1868). The stratum immediately below merchants comprised the '' hinin'' (literally "non-persons"), and below them the ''eta'' ("great filth"), who were together known as the ''senmin'' ("base people"). They were subject to various legal restrictions, such as being forced to live i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaishya
Vaishya (Sanskrit: वैश्य, ''vaiśya'') is one of the four varnas of the Vedic Hindu social order in India. Vaishyas are classed third in the order of Varna hierarchy. The occupation of Vaishyas consists mainly of agriculture, taking care of cattle, trade and other business pursuits as mentioned in the Bhagavad Gita. Traditional duties Hindu religious texts assigned Vaishyas to traditional roles in agriculture and cattle-rearing, but over time they came to be landowners, traders and money-lenders. They ranked third in the varna system below Brahmins and Kshatriyas and traditionally had the responsibility to provide sustenance or patronage for the higher varnas. The Vaishyas, along with members of the Brahmin and Kshatriya varnas, claim ''dvija'' status ("twice born", a second or spiritual birth) after sacrament of initiation as in Hindu theology. Indian traders were widely credited for the spread of Indian culture to regions as far as southeast Asia. Historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adivasi
The Adivasi (also transliterated as Adibasi) are heterogeneous tribal groups across the Indian subcontinent. The term is a recent invention from the 20th century and is now widely used as a self-designation by groups classified as Scheduled Tribes by the Indian government. They are officially recognized as " Scheduled Tribes" in India and as " Ethnic Minorities" in Bangladesh. They comprise 8.6% of India's population and 1.1% of Bangladesh's; or 104.2 million in India, according to the 2011 census, and 2 million in Bangladesh according to the 2010 estimate. Claiming to be among the original inhabitants of the Indian subcontinent, many present-day Adivasi communities formed during the flourishing period of the Indus Valley Civilization or after the decline of the IVC, harboring various degrees of ancestry from ancient Dravidians, Indus Valley Civilization, Indo-Aryan, Austroasiatic and Tibeto-Burman language speakers. Adivasi studies is a new scholarly field, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outcast (person)
An outcast is someone who is rejected or cast out, as from home or from society or in some way excluded, looked down upon, or ignored. In common English speech, an outcast may be anyone who does not fit in with normal society, which can contribute to a sense of isolation. Compare the concept of sending to Coventry. History In Ancient Greece, the Athenians had a procedure known as ostracism in which all citizens could write a person's name on a shard of broken pottery (called ostraka) and place it in a large container in a public place. If an individual's name was written a sufficient number of times, he was ostracized—banished from the city for ten years. In early modern German society, executioners and their families were considered " dishonourable people" (''unehrliche Leute''). In France, executioners and their families were ostracized and lived in social isolation. India Outcasts, in the caste system in India, are individuals or a group that for some reason wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |