|
Università Degli Studi Di Foggia
The University of Foggia, located in Foggia, Italy, was founded in 1991 and was fully recognized in 1999. Although it has taken some time for the university to receive its entitlement and acknowledgement, through that timestamp it has branched off from five faculties to six: the Faculty of Economics, the Faculty of Law, the Faculty of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, the Faculty of Medical and Surgical Sciences, the Faculty of Agricultural Sciences, Food and Environment, and the Faculty of the Humanities: Literature, Cultural Heritage, and Educational Sciences. It has also been named as the best university of southern Italy by the newspaper ''Il Sole 24 Ore'', which has full ownership of the Italian employers' federation. Departments The University of Foggia is divided into these seven departments: * Department of Law * Department of Economics * Department of Economics, Management and Territory (DEMeT) * Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine * Department of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for Nutrient, nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or Fungus, fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, protein (nutrient), proteins, vitamins, or Mineral (nutrient), minerals. The substance is Ingestion, ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's Cell (biology), cells to provide energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth. Different species of animals have different List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that satisfy the needs of their metabolisms and have evolved to fill a specific ecological niche within specific geographical contexts. Omnivore, Omnivorous humans are highly adaptable and have adapted to obtaining food in many different ecosystems. Humans generally use cooking to prepare food for consumption. The majority of the food energy required is supplied by the industrial food industry, which produces food through Intensive farming, intensive agricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giuliano Volpe
Giuliano Volpe (born 1958 in Terlizzi) is an Italian academic and politician. Life Volpe was the rector of the University of Foggia from 1 November 2008 to 31 October 2013. He is currently the president of the Superior Council for Cultural and Scenic Goods of the Ministry of Cultural Heritage and Activities and Tourism The Ministry of Culture () is the ministry of the Government of Italy in charge of national museums and maintenance of historical monuments. MiC's headquarters are located in the historic Collegio Romano Palace (via del Collegio Romano 27, in ... (MiBACT). ReferencesFebbraio e la democrazia feudale - Sudcritica 22 December 2013 External links Official site 1958 births Living people People from Terlizzi Left Ecology Freedom politicians 21st-century Italian politicians {{Italy-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Easter
Easter, also called Pascha ( Aramaic: פַּסְחָא , ''paskha''; Greek: πάσχα, ''páskha'') or Resurrection Sunday, is a Christian festival and cultural holiday commemorating the resurrection of Jesus from the dead, described in the New Testament as having occurred on the third day of his burial following his crucifixion by the Romans at Calvary . It is the culmination of the Passion of Jesus, preceded by Lent (or Great Lent), a 40-day period of fasting, prayer, and penance. Easter-observing Christians commonly refer to the last week of Lent, before Easter, as Holy Week, which in Western Christianity begins on Palm Sunday (marking the entrance of Jesus in Jerusalem), includes Spy Wednesday (on which the betrayal of Jesus is mourned), and contains the days of the Easter Triduum including Maundy Thursday, commemorating the Maundy and Last Supper, as well as Good Friday, commemorating the crucifixion and death of Jesus. In Eastern Christianity, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating Nativity of Jesus, the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a Religion, religious and Culture, cultural celebration among billions of people Observance of Christmas by country, around the world. A liturgical year, liturgical feast central to Christianity, Christmas preparation begins on the Advent Sunday, First Sunday of Advent and it is followed by Christmastide, which historically in the West lasts Twelve Days of Christmas, twelve days and culminates on Twelfth Night (holiday), Twelfth Night. Christmas Day is a public holiday in List of holidays by country, many countries, is observed religiously by a majority of Christians, as well as celebrated culturally by many non-Christians, and forms an integral part of the annual Christmas and holiday season, holiday season. The traditional Christmas narrative recounted in the New Testament, known as the Nativity of Jesus, says that Jesus was born in Bethlehem, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TEMPUS
The TEMPUS (Trans-European Mobility Programme for University Studies) is a program that encouraged higher education institutions in the EU Member States and partner countries to engage in structured cooperation through the establishment of "consortia". The "consortia" implemented Joint European Projects (JEPs) with a clear set of objectives to promote exchanges and mobility of teaching staff and trainers. Such projects could receive financial aid for two or three years. Tempus also provided Individual Mobility Grants (IMGs) to individuals working in the higher education sector to help them work on certain specified activities in other countries.Syrquin, Ari (16 July 2008)"What's New in the EU: Tempus office opens in Jerusalem" ''Jerusalem Post''. Retrieved 3 June 2013. TEMPUS was adopted on 7 May 1990 by The Council of the European Communities. As of 1 January 2014, Tempus-like activities, namely capacity building activities, became part of a new cooperation programme called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonardo Da Vinci Programme
The Leonardo da Vinci programme is a European Commission funding programme focused on the teaching and training needs of those involved in professional education. The programme is part of the European Commission's Lifelong Learning Programme 2007–2013 and aims to help the European labour market by helping European citizens acquire qualifications and have them recognised across borders. History The Leonardo da Vinci programme was started in 1995. In 1998, the whistleblowing of Paul van Buitenen criticised misdirection of funds in the EU, particularly in Leonardo da Vinci professional training programmes. A second, broader phase (Leonardo II 2000–2006) more focused on skills and employability of young people was evaluated for the Directorate General for Education and Culture of the European Commission in 2008. Of the 21,000 projects financed in this phase, 19,000 out of the 367,000 individuals had to do with mobility. The budget was €1.45 billion. In 2007, a new progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
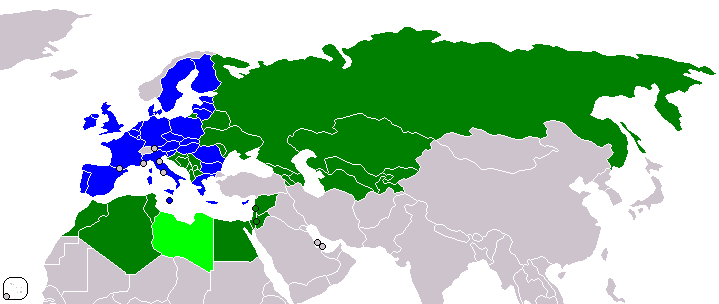
Socrates Programme
The SOCRATES programme was an educational initiative of the European Commission; 31 countries took part. The initial Socrates programme ran from 1994 until 31 December 1999 when it was replaced by the Socrates II programme on 24 January 2000, which ran until 2006. This, in turn, was replaced by the Lifelong Learning Programme 2007–2013. The countries participating in the programme were the then 25 countries, the then candidate countries and |
Culture Heritage
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). ''Primitive Culture''. Vol 1. New York: J. P. Putnam's Son Culture often originates from or is attributed to a specific region or location. Humans acquire culture through the learning processes of enculturation and socialization, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies. A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group. Accepting only a monoculturalism, monoculture in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |