|
Union Pacific GTELs
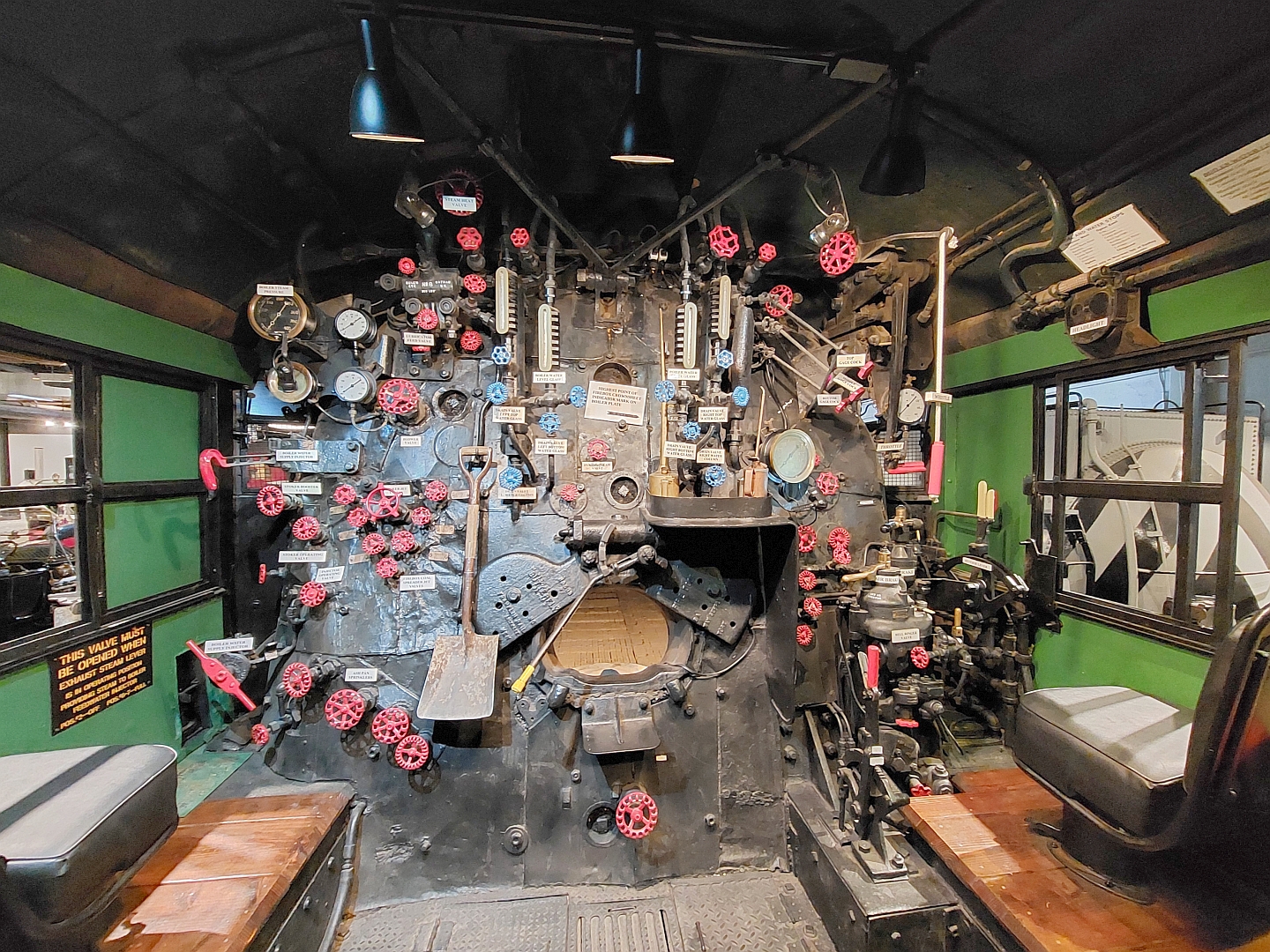
The Union Pacific GTELs were a series of gas turbine–electric locomotives built by Alco-GE and General Electric from 1952 to 1961 and operated by Union Pacific from 1952 to 1970. Background Union Pacific operated the largest fleet of gas turbine–electric locomotives (GTELs) of any railroad in the world. The prototype, UP 50, was the first in a series built by General Electric for Union Pacific's long-haul cargo services and marketed by the Alco-GE partnership until 1953. The prototype was introduced in 1948 and was followed by three series of production locomotives. At one point, Union Pacific said the GTELs hauled more than 10% of the railroad's freight. Fuel economy was poor, for the turbine consumed roughly twice as much fuel as an equally powerful diesel engine. This was initially not a problem, because Union Pacific's turbines burned Bunker C heavy fuel oil that was less expensive than diesel. But this highly viscous fuel is difficult to handle, with a room-temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Turbine–electric Locomotive
A gas turbine locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a gas turbine. Several types of gas turbine locomotive have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving wheels (drivers). A gas turbine train typically consists of two power cars (one at each end of the train), and one or more intermediate passenger cars. A gas turbine offers some advantages over a piston engine. There are few moving parts, decreasing the need for lubrication and potentially reducing maintenance costs, and the power-to-weight ratio is much higher. A turbine of a given power output is also physically smaller than an equally powerful piston engine, so that a locomotive can be extremely powerful without needing to be inordinately large. However, a gas turbine's power output and efficiency both drop dramatically with rotational speed, unlike a piston engine, which has a comparatively flat power curve. This makes gas turbine–e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Pacific
The Union Pacific Railroad is a Class I freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Pacific is the second largest railroad in the United States after BNSF, with which it shares a duopoly on transcontinental freight rail lines in the Western, Midwestern and West South Central United States. Founded in 1862, the original Union Pacific Rail Road was part of the first transcontinental railroad project, later known as the Overland Route. Over the next century, UP absorbed the Missouri Pacific Railroad, the Western Pacific Railroad, the Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railroad and the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad. In 1995, the Union Pacific merged with Chicago and North Western Transportation Company, completing its reach into the Upper Midwest. In 1996, the company merged with Southern Pacific Transportation Company, itself a giant system that was absorbed by the Denver and Rio Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soot
Soot ( ) is a mass of impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons. Soot is considered a hazardous substance with carcinogenic properties. Most broadly, the term includes all the particulate matter produced by this process, including black carbon and residual pyrolysed fuel particles such as coal, cenospheres, charred wood, and petroleum coke classified as cokes or char. It can include polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals like mercury. Soot causes various types of cancer and lung disease. Terminology Definition Among scientists, exact definitions for soot vary, depending partly on their field. For example, atmospheric scientists may use a different definition compared to toxicologists. Soot's definition can also vary across time, and from paper to paper even among scientists in the same field. A common feature of the definitions is that soot is composed largely of carbon based particles resulting from the incomplete burni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Pacific Big Boy
The Union Pacific Big Boy is a type of simple articulated locomotive, articulated 4-8-8-4 steam locomotive manufactured by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) between 1941 and 1944 and operated by the Union Pacific Railroad in revenue service until 1962. The 25 Big Boy locomotives were built to haul Rail freight transport, freight over the Wasatch Range between Ogden, Utah, and Green River, Wyoming. In the late 1940s, they were reassigned to Cheyenne, Wyoming, where they hauled freight over Sherman Hill Summit, Sherman Hill to Laramie, Wyoming. They were the only locomotives to use a 4-8-8-4 wheel arrangement: four-wheel leading truck for stability entering curves, two sets of eight driving wheels and a four-wheel trailing truck to support the large Firebox (steam engine), firebox. Today, eight Big Boys survive, with most on static display at museums across the United States. One of them, Union Pacific 4014, No. 4014, was re-acquired by Union Pacific, and between 2014 and 2019 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Generator (railroad)
A steam generator is a type of boiler (steam generator), boiler used to produce steam for climate control and potable water heating in railroad Passenger car (rail), passenger cars. The output of a railroad steam generator is low-pressure, saturated steam that is passed through a system of water pipe, pipes and Water pipe, conduits throughout the length of the train. Steam generators were developed when diesel locomotives started to replace steam locomotives on passenger trains. In most cases, each passenger locomotive was fitted with a steam generator and a feedwater supply tank. The steam generator used some of the locomotive's diesel fuel supply for combustion. When a steam-generator–equipped locomotive was not available for a run, a so-called "heating car" fitted with one or two steam generators was inserted between the last locomotive in the consist and the rest of the train. Steam generators would also be fitted to individual cars to enable them to be heated independently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Span Bolster
A span bolster, in rail terminology, is a beam or frame used to link two trucks ( US) or bogies ( UK) so that they can be articulated together and be joined to the locomotive or railroad car at one rotating mounting point. In effect, they make one "super-truck" out of the two, while permitting each truck to move relative to the other. Use Locomotives The most common use on locomotives is to give a more flexible alternative to a four-axle truck; two two-axle trucks linked by a span bolster allows the wheels to follow a curve better, without excessive side forces or the need for lateral motion of the axles in the truck. The use of a span bolster is normally signified in the AAR wheel arrangement notation by a + sign; thus a locomotive with two span bolsters, each with two two-axle trucks (the most common arrangement) is a B+B-B+B. Freight cars Span bolsters have been used for some high-capacity freight cars. The most common use is for large flatcars to haul very heavy loads. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country. Within a given country, different notations may also be employed for different kinds of locomotives, such as steam, electric, and diesel powered. Especially in steam days, wheel arrangement was an important attribute of a locomotive because there were many different types of layout adopted, each wheel being optimised for a different use (often with only some being actually "driven"). Modern diesel and electric locomotives are much more uniform, usually with all axles driven. Major notation schemes The main notations are the Whyte notation (based on counting the wheels), the AAR wheel arrangement notation (based on counting either the axles or the bogies), and the UIC classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AAR Wheel Arrangement
The AAR wheel arrangement system is a method of classifying locomotive A locomotive is a rail transport, rail vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push–pull train, push–pull operation has become common, and in the pursuit for ... (or unit) wheel arrangements that was developed by the Association of American Railroads. Essentially a simplification of the European UIC classification, it is widely used in North America to describe Diesel locomotive, diesel and electric locomotives (including third-rail electric locomotives). It is not used for steam locomotives, which use the Whyte notation instead (except geared steam locomotives, which are instead classified by their model and their number of trucks). The AAR system (like UIC) counts axles, unlike Whyte, which counts wheels. Letters refer to powered axles, and numbers to unpowered (or idler) axles. "A" refers to one powered axle, "B" to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbody Unit
In North American railroad terminology, a cab unit is a railroad locomotive with its own cab and controls. "Carbody unit" is a related term, which may be either a cabless booster unit controlled from a linked cab unit, or a cab unit that contains its own controls. Characteristics With both body styles, a bridge-truss design framework is used to make the body a structural element of the locomotive. The body extends the full width and length of the locomotive. The service walkways are inside the body. Carbody units, gaining rigidity from the body trusswork, require less structural weight to achieve rigidity than do locomotives with non-structural bodies. For that reason, carbody construction was favored to increase the power-to-weight ratio for early diesel locomotives, before the power available with diesel technology was increased. Recent years have seen carbody construction revived in the quest for greater fuel efficiency with passenger locomotives. The full-width body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louver
A louver (American English) or louvre (Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, see spelling differences) is a window blind or window shutter, shutter with horizontal wikt:slat, slats that are angled to admit light and air, but to keep out rain and direct sunshine. The angle of the slats may be adjustable, usually in blinds and windows, or fixed, such as in shutters. History Louvers originated in the Middle Ages as lantern-like constructions in wood that were fitted on top of roof holes in large kitchens to allow ventilation while keeping out rain and snow. They were originally rather crude constructions consisting merely of a barrel. Later, they evolved into more elaborate designs made of pottery, taking the shape of faces where the smoke and steam from cooking would pour out through the eyes and mouth, or into constructions that were more like modern louvers, with slats that could be opened or closed by pulling on a string. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALCO FA
The ALCO FA is a family of B-B diesel locomotives designed to haul freight trains. The locomotives were built by a partnership of ALCO and General Electric in Schenectady, New York, between January 1946 and May 1959. Designed by General Electric's Ray Patten (along with their ALCO PA cousins), they were of a cab unit design; both cab-equipped lead (A unit) FA and cabless booster (B unit) FB models were built. A dual-service passenger-freight version, the FPA/FPB, was also offered. That model was equipped with a steam generator for heating passenger cars. ALCO's designation of F marks these locomotives as being geared primarily for freight use, whereas the P designation of the PA sets indicates that they were geared for higher speeds and passenger use. However, beyond this their design was largely similar - aside from the PA/PB's both being larger A1A-A1A types with an even more striking nose - and many railroads used FA and PA locomotives for both freight and passenger service. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Combustion
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons (piston engine), turbine blades (gas turbine), a rotor (Wankel engine), or a nozzle (jet engine). This force moves the component over a distance. This process transforms chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. The first commercially successful internal combustion engines were invented in the mid-19th century. The first modern internal combustion engine, the Otto engine, was designed in 1876 by the German engineer Nicolaus Otto. The term ''internal combustion engine'' usually r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |