|
Underclass
The underclass is the segment of the population that occupies the lowest possible position in a social class, class hierarchy, below the core body of the working class. This group is usually considered cut off from the rest of the society. The general idea that a class system includes a population ''under'' the working class has a long tradition in the social sciences (for example, lumpenproletariat). However, the specific term, ''underclass'', was popularized during the last half of the 20th century, first by social scientists of American poverty, and then by American journalists. The underclass concept has been a point of controversy among social scientists. Definitions and explanations of the underclass, as well as proposed solutions for managing or fixing the ''underclass problem'' have been highly debated. History Gunnar Myrdal is generally credited as the first proponent of the term ''underclass.'' Writing in the early 1960s on economic inequality in the U.S., Myrdal's un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumpenproletariat
In Marxist philosophy, Marxist theory, the ''Lumpenproletariat'' (; ) is the underclass devoid of class consciousness. Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels coined the word in the 1840s and used it to refer to the unthinking lower strata of society exploited by reactionary and counter-revolutionary forces, particularly in the context of the revolutions of 1848. They dismissed the revolutionary potential of the ''Lumpenproletariat'' and contrasted it with the proletariat. Among other groups, criminals, Vagrancy (people), vagabonds, and prostitution, prostitutes are usually included in this category. The Social Democratic Party of Germany made wide use of the term by the turn of the 20th century. Vladimir Lenin and Leon Trotsky followed Marx's arguments and dismissed the revolutionary potential of the group, while Mao Zedong argued that proper leadership could utilize it. The word ''Lumpenproletariat'', popularized in the West by Frantz Fanon's ''The Wretched of the Earth'' in the 1960s, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghetto
A ghetto is a part of a city in which members of a minority group are concentrated, especially as a result of political, social, legal, religious, environmental or economic pressure. Ghettos are often known for being more impoverished than other areas of the city. Versions of such restricted areas have been found across the world, each with their own names, classifications, and groupings of people. The term was originally used for the Venetian Ghetto in Venice, Italy, as early as 1516, to describe the part of the city where Jewish people were restricted to live and thus segregated from other people. However, other early societies may have formed their own versions of the same structure; words resembling ''ghetto'' in meaning appear in Hebrew, Yiddish, Italian, Germanic, Polish, Corsican, Old French, and -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ..., and Latin. During the Holocaust">Latin"> ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Auletta
Kenneth B. Auletta (born April 23, 1942) is an American author, a political columnist for the New York Daily News, and media critic for ''The New Yorker''. Early life and education The son of an Italian American father and a Jewish American mother, Auletta grew up in the Coney Island section of Brooklyn, New York. His father Pat was a sporting goods store owner and founder of the Coney Island Sports League who was responsible for discovering Sandy Koufax, a young baseball pitcher playing in the league who went on to have a Hall of Fame career with the Brooklyn/Los Angeles Dodgers after Pat urged the team to take a "look at this kid Koufax." Auletta attended Abraham Lincoln High School in Coney Island. He graduated from the State University of New York at Oswego and received his M.A. in political science from the Maxwell School of Citizenship and Public Affairs at Syracuse University. Writing career While in graduate school, Auletta taught and trained Peace Corps volunte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Julius Wilson
William Julius Wilson (born December 20, 1935) is an American sociologist, a professor at Harvard University, and an author of works on urban sociology, race, and class issues. Laureate of the National Medal of Science, he served as the 80th President of the American Sociological Association, was a member of numerous national boards and commissions. He identified the importance of neighborhood effects and demonstrated how limited employment opportunities and weakened institutional resources exacerbated poverty within American inner-city neighborhoods. Career Wilson is Lewis P. and Linda L. Geyser University Professor at Harvard University. He is one of 25 University Professors, the highest professional distinction for a Harvard faculty member. After receiving a PhD from Washington State University in 1966, Wilson taught sociology at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, before joining the University of Chicago faculty in 1972. In 1990 he was appointed the Lucy Flower Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Class
A social class or social stratum is a grouping of people into a set of Dominance hierarchy, hierarchical social categories, the most common being the working class and the Bourgeoisie, capitalist class. Membership of a social class can for example be dependent on education, wealth, occupation, income, and belonging to a particular subculture or social network. Class is a subject of analysis for sociologists, political scientists, anthropologists and Social history, social historians. The term has a wide range of sometimes conflicting meanings, and there is no broad consensus on a definition of class. Some people argue that due to social mobility, class boundaries do not exist. In common parlance, the term social class is usually synonymous with Socioeconomic status, socioeconomic class, defined as "people having the same social, economic, cultural, political or educational status", e.g. the working class, "an emerging professional class" etc. However, academics distinguish socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentrated Poverty
Concentrated poverty concerns the spatial distribution of Poverty, socio-economic deprivation, specifically focusing on the density of poor populations. Within the United States, common usage of the term concentrated poverty is observed in the fields of policy and scholarship referencing areas of "Extreme poverty, extreme" or "high-poverty." These are defined by the US census as areas where "40 percent of the tract population [lives] below the federal Poverty thresholds (United States Census Bureau), poverty threshold." A large body of literature argues that areas of concentrated poverty place additional burdens on poor families residing within them, burdens beyond what these families' individual circumstances would dictate. Research also indicates that areas of concentrated poverty can have effects beyond the neighborhood in question, affecting surrounding neighborhoods not classified as "high-poverty" and subsequently limiting their overall economic potential and Group cohesiveness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbert Model
The Gilbert model was developed by Dennis Gilbert as a means of a more effective way of classifying people in a given society into social classes. It posits the existence of six distinct classes: a capitalist class, an upper middle class, a lower middle class, a working class, a working-poor class, and an underclass. Influences Karl Marx believed that social class is determined by ownership (or non-ownership) of the "means of economic production"ownership of raw materials, farmland, coal mines, factories, etc. His theory contains the idea of a struggle between two social classesthe Bourgeoisie (the capital owners) and the Proletariat (the non-owner workers). Like Marx, Max Weber agreed that social class is determined mostly based on the unequal distribution of economic power and hence the unequal distribution of opportunity. However, he also saw that honour, status and social prestige were key factors in determining what social class people belong to. According to Weber, " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Gans
Herbert Julius Gans (May 7, 1927 – April 21, 2025) was a German-born American sociologist who taught at Columbia University from 1971 to 2007. One of the most prolific and influential sociologists of his generation, Gans came to America in 1940 as a refugee from Nazi Germany and sometimes described his scholarly work as an immigrant's attempt to understand America. He trained in sociology at the University of Chicago, where he studied with David Riesman and Everett Hughes, among others, and in social planning at the University of Pennsylvania, where his dissertation was supervised by Martin Meyerson. Herbert J. Gans served as the 79th President of the American Sociological Association. Biography Herbert Julius Gans was born in Cologne, Germany on May 7, 1927. Gans arrived in the United States in 1940, becoming a citizen in 1945. Gans studied at the University of Chicago, receiving a M.A. in 1950. He went on to receive a PhD in Sociology and Planning from the University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Massey
Douglas Steven Massey (born October 5, 1952) is an American sociologist. Massey is currently a professor of sociology at the Princeton School of Public and International Affairs at Princeton University and is an adjunct professor of sociology at the University of Pennsylvania. Massey specializes in the sociology of immigration, and has written on the effect of residential segregation on the black underclass in the United States. He has been president of the Population Association of America, the American Sociological Association and the American Academy of Political and Social Science. He is a co-editor of the '' Annual Review of Sociology''. Academia Massey received his Bachelor of Arts in Sociology, Psychology, and Spanish, from Western Washington University in 1974. In 1977 he received a Master of Arts in Sociology from Princeton University, and a PhD in 1978. He was a Guggenheim fellow in 1990–1991. Douglas S. Massey is the founder and co-director of the Latin Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance Abuse
Substance misuse, also known as drug misuse or, in older vernacular, substance abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods that are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder, differing definitions of drug misuse are used in public health, medical, and criminal justice contexts. In some cases, criminal or anti-social behavior occurs when some persons are under the influence of a drug, and may result in long-term personality changes in individuals which may also occur. In addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, the use of some drugs may also lead to criminal penalties, although these vary widely depending on the local jurisdiction.. Drugs most often associated with this term include alcohol, amphetamines, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, cannabis, cocaine, hallucinogens, methaqualone, and opioids. The exact cause of substance abuse is sometimes clear, but there are two predominant theories: either a gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gentrifying
Gentrification is the process whereby the character of a neighborhood changes through the influx of more affluent residents (the "gentry") and investment. There is no agreed-upon definition of gentrification. In public discourse, it has been used to describe a wide array of phenomena, sometimes in a pejorative connotation. Gentrification is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and planning. Gentrification often increases the economic value of a neighborhood, but can be controversial due to changing demographic composition and potential displacement of incumbent residents. Gentrification is more likely when there is an undersupply of housing and rising home values in a metropolitan area. The gentrification process is typically the result of increasing attraction to an area by people with higher incomes spilling over from neighboring cities, towns, or neighborhoods. Further steps are increased investments in a community and the related infrastructure by real estate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
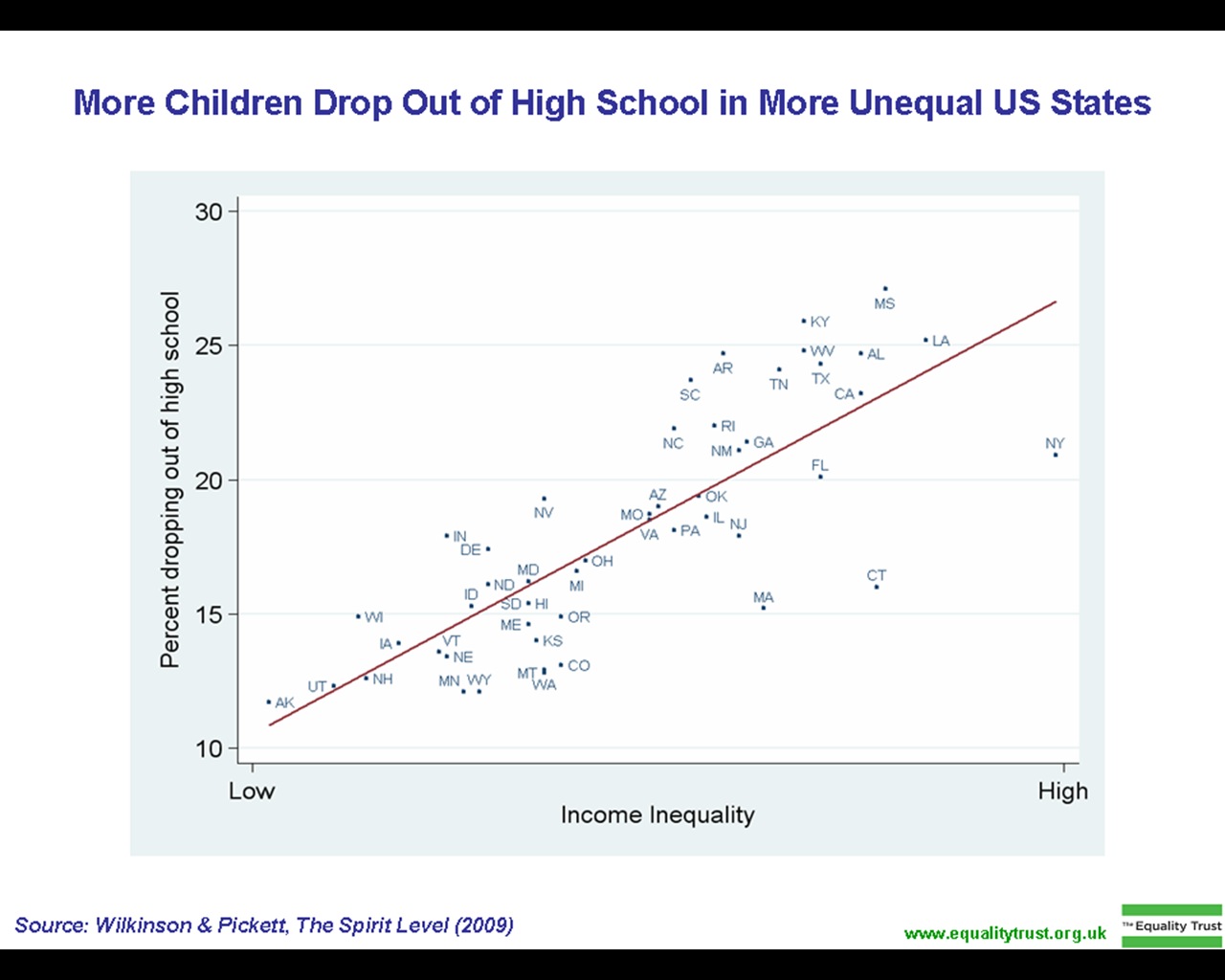
Dropping Out
Dropping out refers to leaving high school, college, university or another group for practical reasons, necessities, inability, apathy, or disillusionment with the system from which the individual in question leaves. Canada In Canada, most individuals graduate from grade 12 by the age of 18, according to Jason Gilmore who collects data on employment and education using the Labour Force Survey (LFS), the official survey used to collect unemployment data in Canada (2010). Using this tool, assessing educational attainment and school attendance can calculate a dropout rate (Gilmore, 2010). It was found by the LFS that by 2009, one in twelve 20- to 24-year-old adults did not have a high school diploma (Gilmore, 2010). The study also found that men still have higher dropout rates than women, and that students outside of major cities and in the northern territories also have a higher risk of dropping out. Although since 1990 dropout rates have gone down from 20% to a low of 9% in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |