|
Ukrainisation
Ukrainization or Ukrainisation ( ) is a policy or practice of increasing the usage and facilitating the development of the Ukrainian language and promoting other elements of Ukrainian culture in various spheres of public life such as education, publishing, government, and religion. The term is also used to describe a process by which non-Ukrainians or Russian-speaking Ukrainians are assimilated to Ukrainian culture and language, either by individual choices or as a result of social processes or policies. In Western historiography, the term ''Ukrainization'' refers also to a policy and resulting process of forcing ethnic minorities living on Ukrainian territories to abandon their ethnic identity by means of the enforced assimilation of Ukrainian culture and identity. During the aftermath of World War II, in the Ukrainian SSR this process had been preceded by the expulsion of some ethnic minoritiesNorman Davies, '' God's Playground, a History of Poland'', Columbia University Press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Language
Ukrainian (, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language, spoken primarily in Ukraine. It is the first language, first (native) language of a large majority of Ukrainians. Written Ukrainian uses the Ukrainian alphabet, a variant of the Cyrillic script. The standard language is studied by the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine and Potebnia Institute of Linguistics. Comparisons are often made between Ukrainian and Russian language, Russian, another East Slavic language, yet there is more mutual intelligibility with Belarusian language, Belarusian,Alexander M. Schenker. 1993. "Proto-Slavonic", ''The Slavonic Languages''. (Routledge). pp. 60–121. p. 60: "[The] distinction between dialect and language being blurred, there can be no unanimity on this issue in all instances..."C.F. Voegelin and F.M. Voegelin. 1977. ''Classification and Index of the World's Languages'' (Elsevier). p. 311, "In terms of immediate mutual intelligibility, the East Slavic zone is a sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theocentrism
Theocentrism is the belief that God is the central aspect to existence, as opposed to anthropocentrism, existentialism and sentientism. In this view, meaning and value of actions done to people or the environment are attributed to God. The tenets of theocentrism, such as humility, respect, moderations, selflessness, and mindfulness, can lend themselves towards a form of environmentalism. In modern theology, theocentrism is often linked with stewardship and environmental ethics or Creation care. It is the belief that human beings should look after the world as guardians and therefore in the way God wants them to. Humans should be considerate to all, from animals to plants to humans themselves. It maintains that human beings are merely here for a short time and should be looking after the world for future generations. In Christian theology, theocentrism has sometimes been used to describe theologies that focus on God the Father, as opposed to those that focus on Christ ( Christoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russia
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor/empress, or imperialism. Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to: Places United States * Imperial, California * Imperial, Missouri * Imperial, Nebraska * Imperial, Pennsylvania * Imperial, Texas * Imperial, West Virginia * Imperial, Virginia * Imperial County, California * Imperial Valley, California * Imperial Beach, California Elsewhere * Imperial (Madrid), an administrative neighborhood in Spain * Imperial, Saskatchewan, a town in Canada Buildings * Imperial Apartments, a building in Brooklyn, New York * Imperial City, Huế, a palace in Huế, Vietnam * Imperial Palace (other) * Imperial Towers, a group of lighthouses on Lake Huron, Canada * The Imperial (Mumbai), a skyscraper apartment complex in India * Imperial War Museum, a British military museum and organisation based in London, UK * * Imperial War Museum Duxford, an aviation museum in Cambridgeshire, UK * * Imperial War Museum Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Revolution Of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution, social change in Russian Empire, Russia, starting in 1917. This period saw Russia Dissolution of the Russian Empire, abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government following two successive revolutions and Russian Civil War, a civil war. It can be seen as the precursor for Revolutions of 1917–1923, other revolutions that occurred in the aftermath of World War I, such as the German Revolution of 1918–1919. The Russian Revolution was a key events of the 20th century, key event of the 20th century. The Russian Revolution was inaugurated with the February Revolution in 1917, in the midst of World War I. With the German Empire inflicting defeats on the front, and increasing logistical problems causing shortages of bread and grain, the Russian Army was losing morale, with large scale mutiny looming. Officials were convinced that if Tsar Nicholas II abdicated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Sciences Of Ukraine
The National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (NASU; , ; ''NAN Ukrainy'') is a self-governing state-funded organization in Ukraine that is the main center of development of Science and technology in Ukraine, science and technology by coordinating a system of research institutes in the country. It is the main research oriented organization along with the five other academies in Ukraine specialized in various scientific disciplines. NAS Ukraine consists of numerous departments, sections, research institutes, scientific centers and various other supporting scientific organizations. The Academy reports on the annual basis to the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine. The presidium of the academy is located at vulytsia Volodymyrska, 54, across the street from the Ukrainian Club Building, Building of Pedagogical Museum, which was used to host the Central Rada, Central Council during the independence period of 1917-18. In 1919–1991 it was a republican branch of the Academy of Sciences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
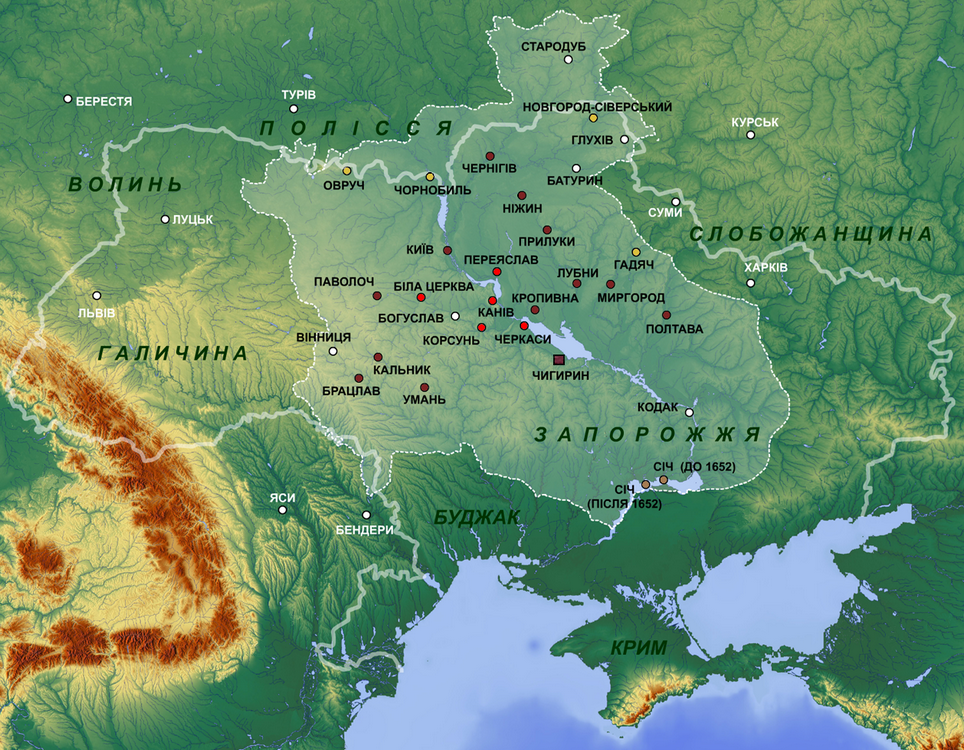
Ukrainian People's Republic
The Ukrainian People's Republic (UPR) was a short-lived state in Eastern Europe. Prior to its proclamation, the Central Council of Ukraine was elected in March 1917 Ukraine after the Russian Revolution, as a result of the February Revolution, and in June, it First Universal of the Ukrainian Central Council, declared Ukrainian autonomy within Russia. Its autonomy was later recognized by the Russian Provisional Government. Following the October Revolution, the Central Council of Ukraine denounced the Bolsheviks, Bolshevik seizure of power and Third Universal of the Ukrainian Central Council, proclaimed the Ukrainian People's Republic with a territory including the area of approximately eight Russian imperial governorates (Kiev Governorate, Kiev, Volhynia Governorate, Volhynia, Kharkov Governorate, Kharkov, Kherson Governorate, Kherson, Yekaterinoslav Governorate, Yekaterinoslav, Poltava Governorate, Poltava, Chernigov Governorate, Chernigov and Podolia Governorate, Podolia). It F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russification Of Ukraine
The Russification of Ukraine (; ) was a system of measures, actions and legislations undertaken by the Imperial Russian, later Soviet, and present-day authorities of the Russian Federation to strengthen Russian national, political and linguistic positions in Ukraine. Background In 1648, Ruthenian commander Bohdan Khmelnytsky began an armed insurgency against the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, known as the Khmelnytsky Uprising. This uprising was successful at ending Polish rule in the Zaporizhzhia Lands, and the local Cossack population established the Cossack Hetmanate. By 1654, the Cossack Hetmanate controlled land encompassing much of present-day Ukraine. To increase pressure on Polish forces, the Cossacks conducted negotiations with the Tsardom of Russia to gain their support. This culminated in the signing of the Pereiaslav Agreement, where Cossack leader Bohdan Khmelnytsky secured Russian military support in exchange for swearing allegiance to the Tsar of Russi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdivisions Of The Russian Empire By Largest Ethnolinguistic Group (1897)
Subdivision may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Subdivision (metre), in music * ''Subdivision'' (film), 2009 * "Subdivision", an episode of ''Prison Break'' (season 2) * ''Subdivisions'' (EP), by Sinch, 2005 * "Subdivisions" (song), by Rush, 1982 Science, technology and mathematics * Subdivision (rank), a taxonomic rank * Subdivision (botany), or subphylum, a taxonomic rank * Subdivision (graph theory), adding new vertices to some edges of a graph, whereby replacing the edges by paths * Subdivision (simplicial complex) * Subdivision (simplicial set) * Subdivision surface, in computer graphics Other uses * Subdivision, an administrative division, a portion of a country * Subdivision (India), an administrative division in India * Subdivision (land), the act of dividing land into smaller pieces See also * * * Division (other) Division may refer to: Mathematics *Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication *Division algorithm, a method for computing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarusian Language
Belarusian (, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language. It is one of the two Languages of Belarus, official languages in Belarus, the other being Russian language, Russian. It is also spoken in parts of Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, Ukraine, and the United States by the Belarusian diaspora. Before Belarus Dissolution of the Soviet Union, gained independence in 1991, the language was known in English language, English as ''Byelorussian'' or ''Belorussian'', or alternatively as ''White Russian''. Following independence, it became known as ''Belarusian'', or alternatively as ''Belarusan''. As one of the East Slavic languages, Belarusian shares many grammatical and lexical features with other members of the group. To some extent, Russian, Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and Belarusian retain a degree of mutual intelligibility. Belarusian descends from a language generally referred to as Ruthenian language, Ruthenian (13th to 18th centuries), which had, in turn, descend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Language
A standard language (or standard variety, standard dialect, standardized dialect or simply standard) is any language variety that has undergone substantial codification in its grammar, lexicon, writing system, or other features and that stands out among related varieties in a community as the one with the highest status or prestige. Often, it is the prestige language variety of a whole country. In linguistics, the process of a variety becoming organized into a standard, for instance by being widely expounded in grammar books or other reference works, and also the process of making people's language usage conform to that standard, is called standardization. Typically, the varieties that undergo standardization are those associated with centres of commerce and government, used frequently by educated people and in news broadcasting, and taught widely in schools and to non-native learners of the language.Trudgill, Peter (2009). ''Sociolinguistics: An Introduction to Language and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Polish
Middle Polish () is the period in the history of the Polish language between the 16th and 18th centuries. It evolved from Old Polish, and gave rise to Modern Polish. Spelling Many various orthographies were proposed to standardize Polish orthography, including Stanisław Zaborowski's in 1514, Jan Seklucjan's in 1549, Stanisław Murzynowski's in 1551, and Onufry Kopczyński's grammars of 1778 and 1785, all with varying degrees of success. Phonology Middle Polish's phonology differs from both Old Polish's and Modern Polish's, mainly in the vowels, but also somewhat in the consonants. Consonants Middle Polish's consonant system differs little from Old Polish's. The clusters ''ir''/''irz''/''yr''/''yrz'' lowered to ''ér''/''érz'' and ultimately to ''er''/''erz''. : ''czyrwony'' > ''czérwony'' > ''czerwony'' Similarly, the clusters ''il''/''ił''/''yl''/''ył'' sporadically and non-permanently lowered to ''el''/''eł''. : ''był'' > ''beł'' There was also a ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruthenian Language
Ruthenian (see also #Nomenclature, other names) is an exonymic linguonym for a closely related group of East Slavic languages, East Slavic linguistic Variety (linguistics), varieties, particularly those spoken from the 15th to 18th centuries in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in East Slavs, East Slavic regions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Regional Sprachraum, distribution of those varieties, both in their Literary language, literary and Vernacular language, vernacular forms, corresponded approximately to the territories of the modern states of Belarus and Ukraine. By the end of the 18th century, they gradually diverged into regional variants, which subsequently developed into the modern Belarusian language, Belarusian, Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and Rusyn language, Rusyn languages, all of which are mutually intelligible. Several Linguistics, linguistic issues are debated among linguists: various questions related to classification of literary and vernacular vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |