|
Uinta County, Wyoming
Uinta County ( ) is a county in the U.S. state of Wyoming. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 20,450. Its county seat is Evanston. Its south and west boundary lines abut the Utah state line. Uinta County, together with Rich County, Utah, comprises the Evanston, WY-UT Micropolitan Statistical Area. History Uinta County was created on December 1, 1869, by the legislature of the Wyoming Territory, with its temporary seat located at Fort Bridger. Originally, it ran along the entire western border of Wyoming, including Yellowstone National Park. The county was named for Utah's Uinta Mountains, which are noticeable from many places in the county. The county was given its present boundaries in 1911 when Lincoln County was carved out of the northern part of Uinta County. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (0.3%) is water. It is the second-smallest county in Wyoming by area. Geology T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uinta Mountains
The Uinta Mountains ( ) are an east-west trending mountain range in northeastern Utah extending a short distance into northwest Colorado and slightly into southwestern Wyoming in the United States. As a subrange of the Rocky Mountains, they are unusual for being the highest range in the contiguous United States running east to west, and lie approximately east of Salt Lake City. The range has peaks ranging from , with the highest point being Kings Peak, also the highest point in Utah. The Mirror Lake Highway crosses the western half of the Uintas on its way to Wyoming. Utah State Route 44 crosses the east end of the Uintas between Vernal and Manila. Etymology The name "Uinta" derives from the Ute word ''Yoov-we-teuh'', meaning "pine forest" or "pine tree". Geology The Uinta Mountains are Laramide uplifted metasedimentary rocks deposited in an intracratonic basin in southwest Laurentia during the time of the breakup of the supercontinent Rodinia. The marine and fluvial m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks. Thrust geometry and nomenclature Reverse faults A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less. If the angle of the fault plane is lower (often less than 15 degrees from the horizontal) and the displacement of the overlying block is large (often in the kilometer range) the fault is called an ''overthrust'' or ''overthrust fault''. Erosion can remove part of the overlying block, creating a ''fenster'' (or ''window'') – when the underlying block is exposed only in a relatively small area. When erosion removes most of the overlying block, leaving island-like remnants resting on the lower block, the remnants are called ''klippen'' (singular '' klippe''). Blind thrust faults If the fault plane terminates before it reaches the Earth's surface, it is called a ''blind thrust'' fault. Because of the lack of surface evidence, blind thrust fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
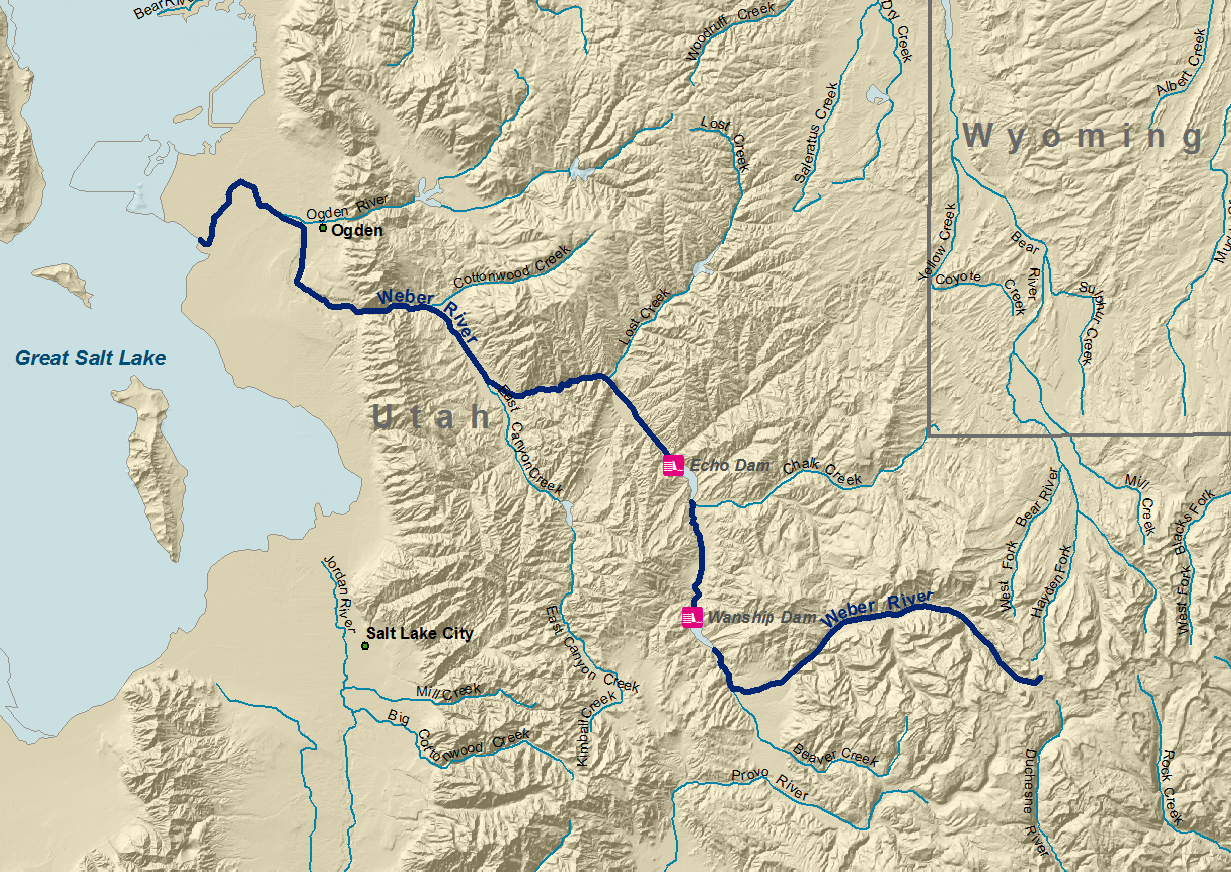
Summit County, Utah
Summit County is a county in the U.S. state of Utah, occupying a rugged and mountainous area. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 42,357. Its county seat is Coalville, and the largest city is Park City. History The county was created by the Utah Territory legislature on January 13, 1854, with its description containing a portion of the future state of Wyoming. It was not organized then but was attached to Great Salt Lake County for administrative and judicial purposes. The county government was completed by March 4, 1861, so its attachment to the other county was terminated. The county boundaries were altered in 1856 and in 1862. In 1868 the Wyoming Territory was created by the US government, effectively de-annexing all Summit County areas falling within the new territory. The boundaries were further altered in 1872 and 1880. Its final alteration occurred on January 7, 1918, when Daggett's creation took a portion of its eastern territory. Its boundary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US 189
U.S. Route 189 is a spur of U.S. Route 89. It currently runs for 322 miles (518 km) from Provo, Utah at Interstate 15 in Utah, Interstate 15 to Jackson, Wyoming. The highway was not part of the original 1926 U.S. Highway system. The highway was created in the 1930s, absorbing former U.S. Route 530 and a portion of U.S. Route 30S (Idaho-Utah-Wyoming), U.S. Route 30S. The portion through Provo Canyon (between Provo and Heber City, Utah) has been designated the Provo Canyon Scenic Byway by the state of Utah. Route description Utah US-189 begins in Provo where it is known as University Avenue, referring to Brigham Young University. The highway then winds up Provo Canyon passing by Deer Creek Reservoir and paralleling the route of the Heber Creeper (now known as the Heber Valley Railroad). The portion in Provo Canyon is designated the Provo Canyon Scenic Byway by the state legislature. The highway exits Provo Canyon near Heber City, Utah. At Heber City US-189 meets U.S. Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstate 80 (Wyoming)
Interstate 80 (I-80) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that runs from San Francisco, California, to Teaneck, New Jersey. In Wyoming, the Interstate Highway runs from the Utah state line near Evanston east to the Nebraska state line in Pine Bluffs. I-80 connects Cheyenne, Wyoming's capital and largest city, with several smaller cities along the southern tier of Wyoming, including Evanston, Green River, Rock Springs, Rawlins, and Laramie. The highway also connects those cities with Salt Lake City to the west and Omaha to the east. In Cheyenne, I-80 intersects I-25 and has Wyoming's only auxiliary Interstate, I-180. The Interstate runs concurrently with US Highway 30 (US 30) for most of their courses in Wyoming. I-80 also has shorter concurrencies with US 189 near Evanston, US 191 near Rock Springs, and US 287 and Wyoming Highway 789 (WYO 789) near Rawlins. The Interstate has business loops through all six cities along its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I-80
Interstate 80 (I-80) is an east–west transcontinental freeway that crosses the United States from San Francisco, California, to Teaneck, New Jersey, in the New York metropolitan area. The highway was designated in 1956 as one of the original routes of the Interstate Highway System; its final segment was opened in 1986. At a length of , it is the second-longest Interstate Highway in the United States, after I-90. It runs through many major cities, including Oakland, Sacramento, Reno, Salt Lake City, Omaha, Des Moines, and Toledo, and passes within of Chicago, Cleveland, and New York City. I-80 is the Interstate Highway that most closely approximates the route of the historic Lincoln Highway, the first road across the United States. The highway roughly traces other historically significant travel routes in the Western United States: the Oregon Trail across Wyoming and Nebraska, the California Trail across most of Nevada and California, the first transcontinental a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bear River State Park
Bear River State Park is a public recreation area straddling the Bear River on the east side of the city of Evanston, Wyoming. The state park was established in 1991 and is managed by Wyoming Division of State Parks and Historic Sites. Activities and amenities The park offers picnicking and a visitors center. Wildlife viewing includes a small herd of captive bison and elk. The park is at the eastern terminus of the Bear River Greenway, a trail system developed by the city that connects the park with downtown Evanston. Other hiking opportunities include of paved trail, an arched footbridge that crosses the river, and of packed gravel trails. Trails are used for cross-country skiing in winter. Park events include the annual Bear River Rendezvous held the weekend before Labor Day Labor Day is a Federal holidays in the United States, federal holiday in the United States celebrated on the first Monday of September to honor and recognize the Labor history of the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Bridger
Fort Bridger was originally a 19th-century fur trading outpost established in 1842, on Blacks Fork of the Green River, in what is now Uinta County, Wyoming, United States and was then part of Mexico. It became a vital resupply point for wagon trains on the Oregon, California, and Mormon Trails. The US Army established a military post here in 1858 during the Utah War, until it was finally closed in 1890. A small town, Fort Bridger, Wyoming, remains near the fort and takes its name from it. Bridger's trading post The post was established by the mountain man Jim Bridger, after whom it is named, and Louis Vasquez. In December 1843, Bridger wrote to Pierre Chouteau Jr., "I have established a small fort, with a blacksmith shop and a supply of iron in the road of emigrants on Black Fork of Green River, which promises fairly." According to Stanley Vestal, "His fort consisted simply of an eight-foot stockade, with a corral adjoining on the north. Within that stockade stood four log ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wasatch National Forest
Wasatch National Forest was established as the Wasatch Forest Reserve by the U.S. Forest Service in Utah on August 16, 1906 with to the east of Salt Lake City and Provo. It became a National Forest on March 4, 1907. On July 1, 1908 Grantsville National Forest and Salt Lake National Forest were added. In 1973 Wasatch was combined administratively with Cache National Forest, creating Wasatch-Cache National Forest. In descending order of acreage, the Wasatch National Forest portion is located in Summit, Tooele, Salt Lake, Davis, Uinta (Wyoming), Duchesne, Wasatch, Morgan, Utah, Weber, and Juab counties in Utah except Uinta, which is in southwestern Wyoming. Its total area was , comprising 56.44% of the combined Wasatch-Cache's as of 2008. There are local ranger district offices in Kamas and Salt Lake City in Utah, and in Evanston and Mountain View in Wyoming. Administrative headquarters reside with the combined Uinta-Wasatch-Cache National Forest in South Jord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanging Wall
In geology, a fault is a Fracture (geology), planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of Rock (geology), rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust (geology), crust result from the action of Plate tectonics, plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction, subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the Plane (geometry), plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geological maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Trap
In petroleum geology, a trap is a geological structure affecting the reservoir rock and caprock of a petroleum system allowing the accumulation of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons in a petroleum reservoir, reservoir. Traps can be of two types: stratigraphic or structural. Structural traps are the most important type of trap as they represent the majority of the world's discovered petroleum resources. Structural traps A structural trap is a type of geological trap that forms as a result of changes in the structure of the subsurface, due to Plate tectonics, tectonic, salt tectonics, diapiric, gravitational, and compactional processes. Anticlinal trap An anticline is an area of the subsurface where the Stratum, strata have been pushed into forming a domed shape. If there is a layer of Permeability (Earth sciences), impermeable rock present in this dome shape, then water-insoluble hydrocarbons can accumulate at the crest until the anticline is filled to the ''spill point'' (the highest p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of Fold (geology), fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest Bed (geology), beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex curve, convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that Strike and dip, dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various Stratum, rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. The progressing age of the rock strata towards the core and uplifted center, are the trademark indications for evidence of anticlines on a geological map. These formations occur because anticlinal ridges typically develop above thrust faults during crustal deformations. The uplifted core of the fold cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |