|
Ueno, Tokyo
is a district in Taitō, Tokyo. The area extending from Ueno to Asakusa is part of the historical Shitamachi (literally "low city") district of Tokyo, which is often associated with working-class traditions and culture as well as their distinct accent. The district's name roughly translates into "Upper Field" in english. The Ueno area, in the strict sense, centres around Ueno Station, which has historically been the terminus for long-distance trains bound for northern Japan, such as the Blue trains and the Shinkansen. To the north, Ueno Park stretches to the area just behind the University of Tokyo's Hongo Campus. Ueno Park houses some of Tokyo's finest cultural sites, including the Tokyo National Museum, the National Museum of Western Art, the National Museum of Nature and Science, and a major public concert hall. Numerous Buddhist temples can also be found in the park, including the Bentendo, dedicated to the goddess Benzaiten, on an island in Shinobazu Pond. The Kan'ei-j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ueno Park
is a spacious public park in the Ueno, Tokyo, Ueno district of Taitō, Tokyo, Japan. The park was established in 1873 on lands formerly belonging to the Buddhist temples in Japan, temple of Kan'ei-ji. Amongst the country's first public parks, it was founded following the Park#History, Western example as part of the borrowing and assimilation of international practices that characterizes the early Meiji period. The home of a number of major museums, Ueno Park is also celebrated in spring for its cherry blossoms and ''hanami''. In recent times the park and its attractions have drawn over ten million visitors a year, making it Japan's most popular city park. History Ueno Park occupies land once belonging to Kan'ei-ji, founded in 1625 in the "Oni (folklore)#Demon Gate, demon gate", the Feng shui, unlucky direction to the northeast of Edo Castle. Most of the temple buildings were destroyed in the Battle of Ueno in 1868 during the Boshin War, when the forces of the Tokugawa shogunate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hongō Campus
The Hongō campus (本郷キャンパス) is the main campus of the University of Tokyo. While some interdisciplinary and advanced research takes place at Komaba or Kashiwa, most faculties and institutes are located at Hongō. Most undergraduates in the senior division and postgraduates study on the campus. The Hongo district campus is divided into three areas: Hongo, Yayoi, and Asano, which are referred to as the Hongo Campus, Yayoi Campus, and Asano Campus, respectively. History Edo Period Most of this area was part of the Tokyo (then Edo) palace of the Maeda Family (Kaga Domain). Other clans based in this regions were: the Toyama and Daishōji (which were cadet branches of the Maeda Family of Kaga) and the Mito and Anjihan (in the Yayoi and Asano campus area). During the Meiji Restoration, most of this land was taken over by the new government and became official land. University of Tokyo Integration In the Meiji era, in 1876, the Tokyo Medical School (the predecess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
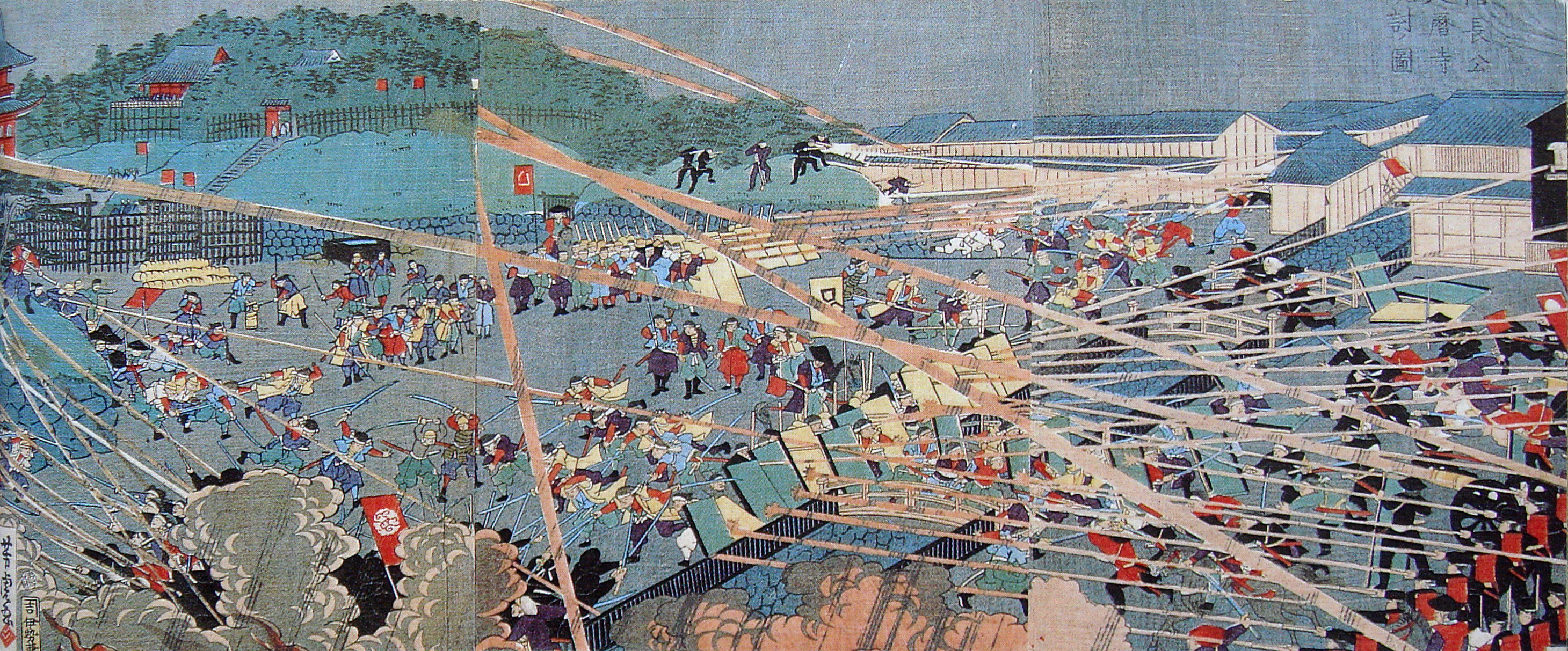
Shōgitai
The Shōgitai (, "Manifest Righteousness Regiment") was an elite samurai shock infantry formation of the Tokugawa shogunate military formed in 1868 by the hatamoto and Hitotsubashi Gosankyō retainer in Zōshigaya, Edo (now Tokyo). The Shōgitai took a large part in the battles of the Boshin War, especially at the Battle of Toba–Fushimi, and, after being assigned the defence of Kan'ei-ji temple, the Battle of Ueno, where they were nearly annihilated. After the Battle of Ueno, some surviving Shōgitai fled north, eventually joining the rebels of the Ezo Republic. Following the defeat of Ezo, most of the few remaining former Shōgitai settled in Hokkaido as tondenhei. Among the survivors was Toyohara Chikanobu , better known to his contemporaries as , was a Japanese painter and printmaker who was widely regarded as a prolific woodblock artist during the Meiji epoch. Names Chikanobu signed his artwork . This was his . The artist's was ; and it ..., who later achieved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boshin War
The , sometimes known as the Japanese Revolution or Japanese Civil War, was a civil war in Japan fought from 1868 to 1869 between forces of the ruling Tokugawa shogunate and a coalition seeking to seize political power in the name of the Imperial Court in Kyoto, Imperial Court. The war stemmed from dissatisfaction among many Kazoku, nobles and young samurai with the shogunate's handling of foreigners following the opening of Japan during the prior decade. Increasing Unequal treaties, Western influence in the economy led to a decline similar to that of other Asian countries at the time. An alliance of western samurai, particularly the domains of Chōshū Domain, Chōshū, Satsuma Domain, Satsuma, and Tosa Domain, Tosa, and court officials secured control of the Imperial Court and influenced the young Emperor Meiji. Tokugawa Yoshinobu, the sitting ''shōgun'', realizing the futility of his situation, abdicated and handed over political power to the emperor. Yoshinobu had hoped t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ueno
The was a battle of the Boshin War, which occurred on July 4, 1868 (''Meiji 1, 15th day of the 5th month''), between the troops of the Shōgitai under Shibusawa Seiichirō and Amano Hachirō, and Imperial "Kangun" troops. Prelude Though the Shōgitai was mainly made up of former Tokugawa retainers and residents of the surrounding provinces, some domains supported the Shōgitai, such as Takada ''han'' (Echigo Province, 150,000 ''koku''), Obama ''han'' (Wakasa Province, 103,000 ''koku''), Takasaki ''han'' (Kōzuke Province, 52,000 ''koku''), and Yūki ''han'' (Shimosa Province, 18,000 ''koku''). Facing them were the combined forces of the Chōshū Domain, Chōshū, Ōmura Domain, Ōmura, Sadowara Domain, Sadowara, Hizen Domain, Hizen, Chikugo Domain, Chikugo, Owari Domain, Owari, Bizen Domain, Bizen, Tsu Domain, Tsu, Inaba Domain, Inaba, and Higo Domain, Higo domains, under the general command of Chōshū's Ōmura Masujirō. Shibusawa and Amano initially posted the 2000-strong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by prolonged peace and stability, urbanization and economic growth, strict social order, Isolationism, isolationist foreign policies, and popular enjoyment of Japanese art, arts and Culture of Japan, culture. In 1600, Tokugawa Ieyasu prevailed at the Battle of Sekigahara and established hegemony over most of Japan, and in 1603 was given the title ''shogun'' by Emperor Go-Yōzei. Ieyasu resigned two years later in favor of his son Tokugawa Hidetada, Hidetada, but maintained power, and defeated the primary rival to his authority, Toyotomi Hideyori, at the Siege of Osaka in 1615 before his death the next year. Peace generally prevailed from this point on, making samurai largely redundant. Tokugawa sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gay Village
A gay village, also known as a gayborhood or gaybourhood, is a geographical area with generally recognized boundaries that is inhabited or frequented by many lesbian, gay, bisexuality, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people. Gay villages often contain a number of gay-oriented establishments, such as gay bars and pubs, gay nightclub, nightclubs, Gay bathhouse, bathhouses, restaurants, boutiques, and bookstores. Such areas may represent an gay friendly, LGBT-friendly oasis in an otherwise hostile city or may simply have a high concentration of gay residents and businesses. Some areas are often associated with being "gay" cities or resorts, due to their image and acceptance of the gay community. Much as other urbanized groups, some LGBT people have managed to utilize their spaces as a way to reflect their cultural values and serve the special needs of individuals in relation to society at large. Today, these neighborhoods can typically be found in the upper-class areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okachimachi Station
is a railway station in Taito, Tokyo, Japan, operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East). Lines Okachimachi Station is served by the circular Yamanote Line and also the Keihin-Tohoku Line. Although not physically connected, on the Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line, on the Tokyo Metro Ginza Line, and on the Toei Oedo Line are within walking distance of Okachimachi and marked as interchanges on route maps. Station layout The station is on a raised viaduct running in a roughly north-south direction. There are two exits, the and . Both exits have ticket vending machines and toilets; however, the north exit has a ''Midori no Madoguchi'' staffed ticket office and escalators to the platforms. Luggage lockers are available at the south exit. Platforms The station has two island platforms with two tracks on either side of each platform. Platforms 1 and 4 (the outermost tracks) serve the Keihin-Tohoku Line, while platforms 2 and 3 (the inner tracks) are used for Yamanote Line trains. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ameya-Yokochō
, often shortened to Ameyoko (アメ横), is an open-air market in the Taito Ward of Tokyo, Japan, located next to Ueno Station. The market is approximately in area, starting just behind the Yodobashi Camera building and following the Yamanote Line south until the Komuro building. There are two theories on the etymology of ''Ameya''. The first is that the name came from , because of all the candy stores that lined the street in the early post-war era when sugar was hard to come by. Even now, there are stores selling candy there. The second theory is that it refers to ; there used to be stores selling surplus American army goods just after World War II World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo .... In either case, it is now commonly referred to simply as ''ameyoko''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Library Of Children's Literature
The is a branch of the National Diet Library in Japan, which provides library services specializing in children's books. It was established in 2000 as Japan's first national library specializing in children's books. It is the center and international hub of children's books-related library services in Japan, including the collection, preservation and provision of children's books and literature related to children's books inside and outside Japan. The facility is located in Ueno Park, Taito-ku, Tokyo, and uses the former Imperial Library building built in 1906. Buildings The original building, known as the "Brick Building", designed by , , and , dates from 1906; it was enlarged in 1929 and again in the Heisei era, with repair and restoration work taking place most recently in 2002 and 2016. It has been placed on the register of by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government, in accordance with the 2006 Tokyo Landscape Regulations. The new "Arch Building", to designs by Tadao Ando and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu (born Matsudaira Takechiyo; 31 January 1543 – 1 June 1616) was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, which ruled from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was the third of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga, Oda Nobunaga and fellow Oda clan, Oda subordinate Toyotomi Hideyoshi. The son of a minor daimyo, Ieyasu once lived as a hostage under daimyo Imagawa Yoshimoto on behalf of his father. He later succeeded as daimyo after his father's death, serving as ally, vassal, and general of the Oda clan, and building up his strength under Oda Nobunaga. After Oda Nobunaga's death, Ieyasu was briefly a rival of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, before declaring his allegiance to Toyotomi and fighting on his behalf. Under Toyotomi, Ieyasu was relocated to the Kantō region, Kanto plains in eastern Japan, away from the Toyotomi power base in Osaka. He built Edo Castle, his castle in the fishing village of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars of the Sengoku period following the collapse of the Ashikaga shogunate. Ieyasu became the ''shōgun,'' and the Tokugawa clan governed Japan from Edo Castle in the eastern city of Edo (Tokyo), Edo (Tokyo) along with the ''daimyō'' lords of the ''samurai'' class. The Tokugawa shogunate organized Japanese society under the strict Edo society, Tokugawa class system and banned most foreigners under the isolationist policies of ''Sakoku'' to promote political stability. The Tokugawa shoguns governed Japan in a feudal system, with each ''daimyō'' administering a ''Han system, han'' (feudal domain), although the country was still nominally organized as provinces of Japan, imperial provinces. Under the Tokugawa shogunate, Japan experienced rapid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |